Remote access configuration
Configuring server for remote access to corporate network via PPTP protocol
PPTP (Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol) is a point-to-point tunneling protocol that allows a computer to establish secure connection with a server by creating a special tunnel in a common unsecured network. PPTP encapsulates PPP frames into IP packets for transmission via global IP network, e.g. the Internet. PPTP may be used for tunnel establishment between two local area networks. РРТР uses an additional TCP connection for tunnel handling.
Configuration algorithm
Step | Description | Command | Keys |
|---|---|---|---|
1 | Create PPTP server profile. | esr(config)# remote-access pptp <NAME> | <NAME> – PPTP server profile name, set by the string of up to 31 characters. |
2 | Specify the description of the configured server (optional). | esr(config-pptp-server)# description <DESCRIPTION> | <DESCRIPTION> – PPTP server description, set by the string of up to 255 characters. |
3 | Specify IP address that should be proceeded by PPTP server. | esr(config-pptp-server)# outside-address | <OBJ-GROUP-NETWORK-NAME> – name of the profile having IP address that should listened by PPTP server, set by the string of up to 31 characters; <ADDR> – range starting IP address, defined as AAA.BBB.CCC.DDD where each part takes values of [0..255]; <IF> – router interface type and identifier; <TUN> – router tunnel type and number. |
4 | IP address of a local gateway. | esr(config-pptp-server)# local-address | <OBJ-GROUP-NETWORK-NAME> – name of the IP addresses profile that includes local gateway IP address, set by the string of up to 31 characters; <ADDR> – range starting IP address, defined as AAA.BBB.CCC.DDD where each part takes values of [0..255]. |
5 | Specify IP addresses list from which dynamic IP addresses are leased to remote users by PPTP. | esr(config-pptp-server)# remote-address | <OBJ-GROUP-NETWORK-NAME> – name of the IP addresses profile that includes remote users IP addresses list, set by the string of up to 31 characters; <FROM-ADDR> – range starting IP address, defined as AAA.BBB.CCC.DDD where each part takes values of [0..255]; <TO-ADDR> – range ending IP address, defined as AAA.BBB.CCC.DDD where each part takes values of [0..255]. |
6 | Select PPTP clients authentication mode. | esr(config-pptp-server)# authentication mode |
|
7 | Allow necessary authentication methods for remote users | esr(config-pptp-server)# authentication method <METHOD> | <METHOD> – authentication method, possible values: [chap, mschap, mschap-v2, eap, pap]. By default only chap is allowed. |
8 | Specify user name (when using local user authentication). | esr(config-pptp-server) username <NAME> | <NAME> – user name, set by the string of up to 12 characters. |
9 | Specify password (when using local user authentication). | esr(config-pptp-user) password ascii-text | <PASSWORD> – user password, set by the string of up to 32 characters. |
10 | Activate user (when using local user authentication). | esr(config-pptp-user) enable | |
11 | Include the PPTP server in a security zone and configure interaction rules between zones or disable firewall (see section Firewall configuration). | esr(config-pptp-server)# security-zone <NAME> | <NAME> – security zone name, set by the string of up to 31 characters. |
12 | Enable server. | esr(config-pptp-server)# enable | |
13 | Specify outgoing packets DSCP priority (optional). | esr(config-pptp-server)# dscp <DSCP> | <DSCP> – outgoing packets dscp priority [0..63]. |
14 | Enable MPPE encryption for PPTP connections (optional). | esr(config-pptp-server)# encryption mppe | |
15 | Specify MTU size (MaximumTransmissionUnit) for the server (optional). | esr(config-pptp-server) mtu <MTU> | <MTU> – MTU value, takes values in the range of [1280..1500]. Default value: 1500. |
16 | Define the list of DNS servers that will be used by remote users (optional). | esr(config-pptp-server)# dns-servers | <OBJ-GROUP-NETWORK-NAME> – name of the IP addresses profile that includes required DNS servers addresses, set by the string of up to 31 characters. |
17 | Define the list of WINS servers that will be used by remote users (optional). | esr(config-pptp-server)# wins-servers object-group | <OBJ-GROUP-NETWORK-NAME> – name of the IP addresses profile that includes required WINS servers addresses, set by the string of up to 31 characters. |
Configuration example
Objective:
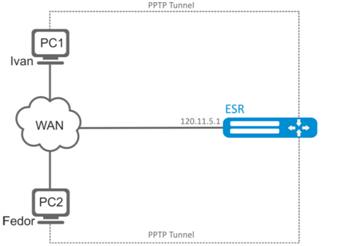
Configure PPTP server on a router.
- PPTP server address: 120.11.5.1;
- Gateway inside the tunnel for connecting clients: 10.10.10.1;
- IP address pool for lease: 10.10.10.5-10.10.10.25;
- DNS servers: 8.8.8.8, 8.8.8.4;
- Accounts for connection: Fedor, Ivan.
Solution:
Create an address profile that contains an address to be listened by the server:
Create address profile that contains local gateway address:
Create address profile that contains client addresses:
Create PPTP server and map profiles listed above:
Select authentication method for PPTP server users:
Specify security zone that user sessions will be related to:
Create PPTP users Ivan and Fedor for PPTP server:
Enable PPTP server:
When a new configuration is applied, the router will listen to 120.11.5.1:1723. To view PPTP server session status, use the following command:
To view PPTP server session counters, use the following command:
To clear PPTP server session counters, use the following command:
To end PPTP server session for user 'fedor', use one of the following commands:
To view PPTP server configuration, use the following command:
In addition to PPTP server creation, open TCP port 1723 designed for connection handling and enable GRE protocol (47) for the tunnel traffic in the firewall.
Configuring server for remote access to corporate network via L2TP protocol
L2TP (Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol) is a sophisticated tunneling protocol used to support virtual private networks. L2TP encapsulates PPP frames into IP packets for transmission via global IP network, e.g. the Internet. L2TP may be used for tunnel establishment between two local area networks. L2TP uses an additional UDP connection for tunnel handling. L2TP protocol does not provide data encryption, therefore it is usually combined with an IPsec protocol group that provides security on a packet level.
Configuration algorithm
Step | Description | Command | Keys |
|---|---|---|---|
1 | Create L2TP server profile. | esr(config)# remote-access l2tp <NAME> | <NAME> – L2TP server profile name, set by the string of up to 31 characters. |
2 | Specify the description of the configured server (optional). | esr(config-l2tp-server)# description <DESCRIPTION> | <DESCRIPTION> – L2TP server description, set by the string of up to 255 characters. |
3 | Specify IP address that should be listened by L2TP server. | esr(config-l2tp-server)# outside-address | <OBJ-GROUP-NETWORK-NAME> – name of the profile having IP address that should be listened by L2TP server, set by the string of up to 31 characters; <ADDR> – range starting IP address, defined as AAA.BBB.CCC.DDD where each part takes values of [0..255]; <IF> – router interface type and identifier; <TUN> – router tunnel type and number. |
4 | Specify the IP address of the local gateway or disable firewall for the PPTP server | esr(config-l2tp-server)# local-address { object-group | <OBJ-GROUP-NETWORK-NAME> – name of the IP addresses profile that includes local gateway IP address, set by the string of up to 31 characters; <ADDR> – range starting IP address, defined as AAA.BBB.CCC.DDD where each part takes values of [0..255]. |
5 | Specify IP addresses list from which dynamic IP addresses are leased to remote users by L2TP. | esr(config-l2tp-server)# remote-address | <OBJ-GROUP-NETWORK-NAME> – name of the IP addresses profile that includes remote users IP addresses list, set by the string of up to 31 characters; <FROM-ADDR> – range starting IP address, defined as AAA.BBB.CCC.DDD where each part takes values of [0..255]; <TO-ADDR> – range ending IP address, defined as AAA.BBB.CCC.DDD where each part takes values of [0..255]. |
6 | Select L2TP clients authentication mode. | esr(config-l2tp-server)# authentication mode |
|
7 | Allow necessary authentication methods for remote users | esr(config-l2tp-server)# authentication method <METHOD> | <METHOD> – authentication method, possible values: [chap, mschap, mschap-v2, eap, pap]. By default only chap is allowed. |
8 | Include the L2TP server in a security zone and configure interaction rules between zones (see section Firewall configuration). | esr(config-l2tp-server)# security-zone <NAME> | <NAME> – security zone name, set by the string of up to 31 characters. |
9 | Specify user name (when using local authentication base). | esr(config-l2tp-server) username < NAME > | <NAME> – user name, set by the string of up to 12 characters. |
10 | Specify user password (when using local authentication base). | esr(config-l2tp-user) password ascii-text | <PASSWORD> – user password, set by the string of up to 32 characters. |
11 | Enable user (when using local authentication base). | esr(config-l2tp-user) enable | |
12 | Select a key authentication method for IKE connection (optional). | esr(config-l2tp-server)# ipsec authentication method pre-shared-key | |
13 | Specify a shared secret authentication key that should be the same for both parties of the tunnel. | esr(config-l2tp-server)# ipsec authentication pre-shared-key | <TEXT> – string [1..64] ASCII characters; <HEX> – number, [1..32] bytes size, set by the string of [2..128] characters in hexadecimal format (0xYYYY ...) or (YYYY ...). <ENCRYPTED-TEXT> – encrypted password, [1..32] bytes size, set by the string of [2..128] characters. <ENCRYPTED-TEXT> – encrypted number, [2..64] bytes size, set by the string of [2..256] characters. |
| 14 | Restrict the authentication and encryption methods used for the IKE protocol (optional). | esr(config-l2tp-server)# ipsec ike proposal <NAME> | <NAME> – name of the previously created IKE profile, set by the string of up to 31 characters. |
| 15 | Restrict the authentication and encryption methods used for the IPsec protocol (optional). | esr(config-l2tp-server)# ipsec proposal <NAME> | <NAME> – name of the previously created IPsec profile, set by the string of up to 31 characters. |
16 | Enable server. | esr(config-l2tp-server)# enable | |
17 | Specify outgoing packets DSCP priority. | esr(config-l2tp-server)# dscp <DSCP> | <DSCP> – outgoing packets dscp priority [0..63]. |
18 | Specify MTU size (MaximumTransmissionUnit) for the server (optional). | esr(config-l2tp-server) mtu <MTU> | <MTU> – MTU value, takes values in the range of [1280..1500]. Default value: 1500. |
19 | Define the list of DNS servers that will be used by remote users (optional). | esr(config-l2tp-server)# dns-servers object-group | <OBJ-GROUP-NETWORK-NAME> – name of the IP addresses profile that includes required DNS servers addresses, set by the string of up to 31 characters. |
20 | Define the list of WINS servers that will be used by remote users (optional). | esr(config-l2tp-server)# wins-servers | <OBJ-GROUP-NETWORK-NAME> – name of the IP addresses profile that includes required WINS servers addresses, set by the string of up to 31 characters. |
Configuration example
Objective:
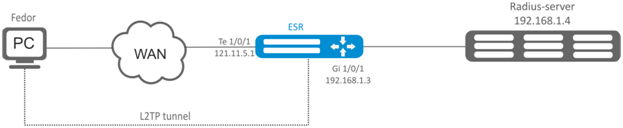
Configure L2TP server on a router for remote user connection to LAN. Authentication is performed on RADIUS server.
- L2TP server address: 120.11.5.1;
- Gateway inside the tunnel: 10.10.10.1;
- Radius server address: 192.168.1.4.
For IPsec, key authentication method is used: key – 'password’.
Solution:
First, do the following:
- Configure RADIUS server connection;
- Configure zones for te1/0/1 and gi1/0/1 interfaces.
- Specify IP addresses for te1/0/1 and te1/0/1 interfaces.
Create address profile that contains local gateway address:
Create address profile that contains DNS servers:
Create L2TP server and map profiles listed above:
Select authentication method for L2TP server users:
Specify security zone that user sessions will be related to:
Specify authentication method for IKE phase 1 and define an authentication key.
Enable L2TP server:
When a new configuration is applied, the router will listen to IP address 120.11.5.1 and port 1701. To view L2TP server session status, use the following command:
To view L2TP server session counters, use the following command:
To clear L2TP server session counters, use the following command:
To end L2TP server session for user 'fedor', use one of the following commands:
To view L2TP server configuration, use the following command:
In addition to creating L2TP server, open UDP port 500, 1701, 4500 designed for connection handling and enable ESP (50) and GRE protocol (47) for the tunnel traffic in the firewall.
Configuring server for remote access to corporate network via OpenVPN protocol
OpenVPN is a sophisticated tool based on SSL that implements Virtual Private Networks (VPN), enables remote access and solves many different tasks related to data transmission security.
Configuration algorithm
Step | Description | Command | Keys |
|---|---|---|---|
1 | Create OpenVPN server profile. | esr(config)# remote-access openvpn <NAME> | <NAME> – OpenVPN server profile name, set by the string of up to 31 characters. |
2 | Specify the description of the configured server (optional). | esr(config-openvpn-server)# description <DESCRIPTION> | <DESCRIPTION> – OpenVPN server description, set by the string of up to 255 characters. |
3 | Define the subnet from which IP addresses are leased to users (only for tunnel ip). | esr(config-openvpn-server)# network <ADDR/LEN> | <ADDR/LEN> – subnet address, set in the following format: AAA.BBB.CCC.DDD/EE – network IP address with prefix mask, where AAA-DDD take values of [0..255] and EE takes values of [16..29]. |
4 | Specify an encapsulated protocol. | esr(config-openvpn-server)# protocol <PROTOCOL> | <PROTOCOL> – encapsulation type, possible values:
|
5 | Define type of connection with a private network via OpenVPN server. | esr(config-openvpn-server)# tunnel <TYPE> | <TYPE> – encapsulation protocol, takes the following values:
|
6 | Specify IP addresses list from which dynamic IP addresses are leased to remote users in L2 mode by OpenVPN server (only for tunnel ethernet). | esr(config-openvpn-server)# address-range <FROM-ADDR>-<TO-ADDR> | <FROM-ADDR> – range starting IP address, defined as AAA.BBB.CCC.DDD where each part takes values of [0..255]; <TO-ADDR> – range ending IP address, defined as AAA.BBB.CCC.DDD where each part takes values of [0..255]. |
7 | Include client connections via OpenVPN in L2 domain (only for tunnel ethernet). | esr(config-openvpn-server)# bridge-group <BRIDGE-ID> | <BRIDGE-ID> – bridge identifying number. |
8 | Specify certificates and keys. | esr(config-openvpn-server)# certificate <CERTIFICATE-TYPE> <NAME> | <CERTIFICATE-TYPE> – certificate or key type, may take the following values:
<NAME> – certificate or key name, set by the string of up to 31 characters. |
9 | Select encryption algorithm used when data transmission. | esr(config-openvpn-server)# encryption algorithm <ALGORITHM> | <ALGORITHM> – encryption protocol identifier, may take values: 3des,blowfish128, aes128. |
10 | Include the OpenVPN server in a security zone and configure interaction rules between zones (see section Firewall configuration). | esr(config-openvpn-server)# security-zone <NAME> | <NAME> – security zone name, set by the string of up to 31 characters. |
11 | Define the additional parameters for a specified OpenVPN server user (when using a local base for user authentication). | esr(config-openvpn-server)# username < NAME > | <NAME> – user name, set by the string of up to 31 characters. |
12 | Define a subnet for the specified user of the OpenVPN server. | esr(config-openvpn-user)# subnet <ADDR/LEN> | <ADDR/LEN> – subnet address, set in the following format: |
13 | Define a static ip address for the specified OpenVPN server user. | esr(config-openvpn-user)# ip address <ADDR> | <ADDR> – address set in the following format: |
14 | Enable OpenVPN server profile. | esr(config-openvpn-server)# enable | |
15 | Enable data transmission blocking between clients (optional). | esr(config-openvpn-server)# client-isolation | |
16 | Set the maximum amount of simultaneous user sessions (optional). | esr(config-openvpn-server)# client-max <VALUE> | <VALUE> – maximum amount of users, takes values of [1..65535]. |
17 | The mechanism of transmitted data compression between clients and the OpenVPN server is enabled (optional). | esr(config-openvpn-server)# compression | |
18 | Define the list of DNS servers that will be used by remote users (optional). | esr(config-openvpn-server)# dns-server <ADDR> | <ADDR> – DNS server IP address, defined as AAA.BBB.CCC.DDD where each part takes values of [0..255]. |
19 | Specify TCP/UDP port that will be listened by OpenVPN server (optional). | esr(config-openvpn-server)# port <PORT> | <PORT> – TCP/UDP port, takes values of [1..65535]. Default value: 1194. |
20 | Enable the default route advertising for OpenVPN connections, which leads to the replacement of the default route on the client side (optional). | esr(config-openvpn-server)# redirect-gateway | |
21 | Enable the advertising of specified subnets, the gateway is OpenVPN server IP address (optional). | esr(config-openvpn-server)# route <ADDR/LEN> | <ADDR/LEN> – subnet address, set in the following format: AAA.BBB.CCC.DDD/EE – network IP address with prefix mask, where AAA-DDD take values of [0..255] and EE takes values of [1..32]. |
22 | Set time interval after which the opposing party is considered to be unavailable (optional). | esr(config-openvpn-server)# timers holdtime <TIME> | <TIME> – time in seconds, takes values of [1..65535]. Default value: 120. |
23 | Set the time interval after which the connection with the opposing party is checked (optional). | esr(config-openvpn-server)# timers keepalive <TIME> | <TIME> – time in seconds, takes values of [1..65535]. Default value: 10. |
24 | Allow multiple users with the same certificate to connect to the OpenVPN server. | esr(config-openvpn-server)# duplicate-cn | |
25 | Define the list of WINS servers that will be used by remote users (optional). | esr(config-openvpn-server)# wins-server <ADDR> | <ADDR> – WINS server IP address, defined as AAA.BBB.CCC.DDD where each part takes values of [0..255]. |
26 | Change the authentication algorithm for OpenVPN clients (optional). | esr(config-openvpn-server)# authentication algorithm <ALGORITHM> | <ALGORITHM> – authentication algorithm:
Default value: sha. |
Configuration example
Objective:
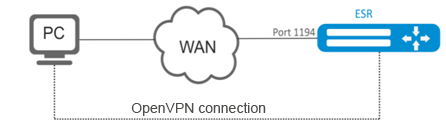
Configure Open VPN server in L3 mode on a router for remote user connection to LAN.
- OpenVPN server subnet: 10.10.100.0/24;
- Mode: L3;
- Authentication based on certificates.
Solution:
First, do the following:
- Prepare certificates and keys:
- CA certificate;
- OpenVPN server key and certificate;
- Diffie-Hellman and HMAC key for TLS.
- Configure zone for te1/0/1 interface;
- Specify IP address for te1/0/1 interface.
Import certificates and keys via TFTP:
Create OpenVPN server and a subnet for its operation:
Specify L3 connection type and encapsulation protocol:
Advert LAN subnets that will be available via OpenVPN connection and define DNS server:
Specify previously imported certificates and keys that will be used with OpenVPN server:
Specify security zone that user sessions will be related to:
Select aes128 encryption algorithm:
Enable OpenVPN server:
When a new configuration is applied, the router will listen to port 1194 (used by default).
To view OpenVPN server session status, use the following command:
To view OpenVPN server session counters, use the following command:
To clear OpenVPN server session counters, use the following command:
To end OpenVPN server session for user 'fedor', use one of the following commands:
To view OpenVPN server configuration, use the following command:
In addition to creating OpenVPN server, open TCP port 1194 in the firewall.
Configuring remote access client via PPPoE
PPPoE is a tunneling protocol that allows encapsulating IP PPP over Ethernet connections and has PPP connection software capabilities, which allows using it to establish virtual connections to a neighboring Ethernet device or a point-to-point connection that is used to transmit IP packets, and also works with PPP features. This allows applying conventional PPP-oriented software to configure the connection that uses not serial communication link but packet-oriented network (for example, Ethernet) to organize a classical connection with login and password for Internet connections. In addition, IP address on the opposite side of connection is assigned only when PPPoE connection is open, allowing the dynamic reuse of IP addresses.
Configuration algorithm
Step | Description | Command | Keys |
|---|---|---|---|
1 | Create a PPPoE tunnel and switch to its configuration mode. | esr(config)# tunnel pppoe <PPPoE> | <PPPoE> – tunnel sequence number from 1 to 10. |
2 | Specify the description of the configured client (optional). | esr(config-pppoe)# description <DESCRIPTION> | <DESCRIPTION> – PPPoE server description, set by the string of up to 255 characters. |
3 | Specify the name of the VRF instance that will use the PPPoE client (optional). | esr(config-pppoe)# ip vrf forwarding <VRF> | <VRF> – VRF name, set by the string of up to 31 characters. |
4 | Specify the interface through which the PPPoE connection will be established. | esr(config-pppoe)# interface <IF> | <IF> – interface or interface group. |
5 | Specify user name and password for connection to PPPoE server. | esr(config-pppoe)# username <NAME> password ascii-text | <NAME> – user name, set by the string of up to 31 characters; <CLEAR-TEXT> – password, set by the string of 8 to 16 characters; <ENCRYPTED-TEXT> – encrypted password, set by the string of [16..128] characters. |
6 | Include the PPPoE tunnel in a security zone and configure interaction rules between zones (see section Firewall configuration). | esr(config-pppoe)# security-zone <NAME> | <NAME> – security zone name, set by the string of up to 31 characters. |
7 | Enable a configured profile. | esr(config-pppoe)# enable | |
8 | Specify authentication method (optional). | esr(config-pppoe)# authentication method <METHOD> | <METHOD> – authentication method, possible values: chap, mschap, mschap-v2, eap, pap Default value: chap. |
9 | Enable the opt-out of receiving the default route from PPPoE server (optional). | esr(config-pppoe)# ignore-default-route | |
10 | Specify the time interval during which the statistics on the load is averaged (optional). | esr(config-pppoe)# load-average <TIME> | <TIME> – time interval in seconds from 5 to 150 (5 seconds by default). |
11 | Specify MTU size (MaximumTransmissionUnit) for PPPoE tunnel. | esr(config-pppoe)# mtu <MTU> | <MTU> – MTU value, takes values in the range of:
Default value: 1500. |
12 | Change the number of failed data-link tests before breaking the session (optional). | esr(config-pppoe)# ppp failure-count <NUM> | <NUM> – the number of failed data-link tests, specified in the range [1..100]. Default value: 10. |
13 | Change the time interval in seconds after which the router sends a keepalive message (optional). | esr(config-pppoe)# ppp timeout keepalive <TIME > | <TIME> – time in seconds, takes values of [1..32767]. Default value: 10. |
14 | Override the MSS (Maximum segment size) field in incoming TCP packets (optional). | esr(config-pppoe)# ip tcp adjust-mss <MSS> | <MSS> – MSS value, takes values in the range of [500..1460]. Default value: 1460. |
15 | Enable recording of the current tunnel usage statistics (optional). | esr(config-pppoe)# history statistics | |
It is also possible to configure the PPPoE client:
| |||
Configuration example
Objective:
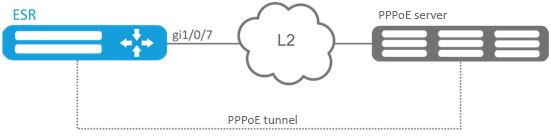
Configure PPPoE client on the router.
- Accounts for connection – tester;
- Account passwords – password;
- The connection should be established from the gigabitethernet 1/0/7 interface.
Solution:
Pre-configure PPPoE server with the accounts.
Enter the PPPoE client configuration mode and disable the firewall:
Specify user name and password for connection to PPPoE server:
Specify the interface through which the PPPoE connection will be established:
To view the tunnel status, use the following command:
To view PPPoE client session counters, use the following command:
Configuring remote access client via PPTP
PPTP ( Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol) is a point-to-point tunneling protocol that allows establishing secure connection with a server by creating a special tunnel in a common unsecured network. PPTP encapsulates PPP frames into IP packets for transmission via global IP network, e.g. the Internet. PPTP may be used for tunnel establishment between two local area networks. РРТР uses an additional TCP connection for tunnel handling.
Configuration algorithm
Step | Description | Command | Keys |
|---|---|---|---|
1 | Create a PPTP tunnel and switch to its configuration mode. | esr(config)# tunnel pptp <INDEX> | <INDEX> – tunnel identifier, set in the range of: [1..10]. |
2 | Specify the description of the configured tunnel (optional). | esr(config-pptp)# description <DESCRIPTION> | <DESCRIPTION> – tunnel description, set by the string of up to 255 characters. |
3 | Specify VRF instance, in which the given PPTP tunnel will operate (optional). | esr(config-pptp)# ip vrf forwarding <VRF> | <VRF> – VRF name, set by the string of up to 31 characters. |
4 | Include the PPTP tunnel in a security zone and configure interaction rules between zones or disable firewall (see section Firewall configuration). | esr(config-pptp)# security-zone <NAME> | <NAME> – security zone name, set by the string of up to 31 characters. |
esr(config-pptp)# ip firewall disable |
| ||
5 | Set remote IP address for tunnel installation. | esr(config-pptp)# remote address <ADDR> | <ADDR> – local gateway IP address, defined as AAA.BBB.CCC.DDD where each part takes values of [0..255]. |
6 | Specify MTU size (MaximumTransmissionUnit) for the tunnel (optional). | esr(config-pptp)# mtu <MTU> | <MTU> – MTU value, takes values in the range of:
Default value: 1500. |
7 | Specify the user and set an encrypted or unencrypted password to authenticate the remote party. | esr(config-pptp)# username <NAME> password ascii-text | <NAME> – user name, set by the string of up to 31 characters. <WORD> – unencrypted password, set by the string of [8..64] characters, may include [0-9a-fA-F] characters. <HEX> – encrypted password, set by the string of [16..128] characters. |
8 | Enable the tunnel. | esr(config-pptp)# enable | |
9 | Override the MSS (Maximum segment size) field in incoming TCP packets (optional). | esr(config-pptp)# ip tcp adjust-mss <MSS> | <MSS> – MSS value, takes values in the range of [500..1460]. Default value: 1460. |
10 | Ignore the default route via the given PPTP tunnel (optional). | esr(config-pptp)# ignore-default-route | |
11 | Specify the time interval during which the statistics on the tunnel load is averaged (optional). | esr(config-pptp)# load-average <TIME> | <TIME> – interval in seconds, takes values of [5..150]. Default value: 5. |
12 | Specify authentication method (optional). | esr(config-pptp)# authentication method <METHOD> | <METHOD> – authentication method, possible values: chap, mschap, mschap-v2, eap, pap Default value: chap. |
13 | Enable recording of the current tunnel usage statistics (optional). | esr(config-pptp)# history statistics | |
14 | Change the time interval in seconds after which the router sends a keepalive message (optional). | esr(config-pptp)# ppp timeout keepalive <TIME > | <TIME> – time in seconds, takes values of [1..32767]. Default value: 10. |
15 | Change the number of failed data-link tests before breaking the session (optional). | esr(config-pptp)# ppp failure-count <NUM> | <NUM> – the number of failed data-link tests, specified in the range [1..100]. Default value: 10. |
Configuration example
Objective:
Configure PPTP tunnel on a router:
- PPTP server address: 20.20.0.1;
- account for connection – login: ivan, password: simplepass.
Solution:
Create PPTP tunnel:
Specify the account (Ivan user) to connect to the server:
Specify the remote gateway:
Specify a security zone:
Enable PPTP tunnel:
To view the tunnel status, use the following command:
To view sent and received packet counters, use the following command:
To view the tunnel configuration, use the following command:
Configuring remote access client via L2TP
L2TP ( Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol) is a sophisticated tunneling protocol used to support virtual private networks. L2TP encapsulates PPP frames into IP packets for transmission via global IP network, e.g. the Internet. L2TP may be used for tunnel establishment between two local area networks. L2TP uses an additional UDP connection for tunnel handling. L2TP protocol does not provide data encryption, therefore it is usually combined with an IPsec protocol group that provides security on a packet level.
Configuration algorithm
Step | Description | Command | Keys |
|---|---|---|---|
1 | Create a L2TP tunnel and switch to its configuration mode. | esr(config)# tunnel l2tp <INDEX> | <INDEX> – tunnel identifier, set in the range of: [1..10]. |
2 | Specify VRF instance, in which the given L2TP tunnel will operate (optional). | esr(config-l2tp)# ip vrf forwarding <VRF> | <VRF> – VRF name, set by the string of up to 31 characters. |
3 | Specify the description of the configured tunnel (optional). | esr(config-l2tp)# description <DESCRIPTION> | <DESCRIPTION> – tunnel description, set by the string of up to 255 characters. |
4 | Include the L2TP tunnel in a security zone and configure interaction rules between zones or disable firewall (see section Firewall configuration). | esr(config-l2tp)# security-zone <NAME> | <NAME> – security zone name, set by the string of up to 31 characters. |
esr(config-l2tp)# ip firewall disable | |||
5 | Set remote IP address for tunnel installation. | esr(config-l2tp)# remote address <ADDR> | <ADDR> – local gateway IP address, defined as AAA.BBB.CCC.DDD where each part takes values of [0..255]. |
6 | Specify the user and set an encrypted or unencrypted password to authenticate the remote party. | esr(config-l2tp)# username <NAME> password ascii-text | <NAME> – user name, set by the string of up to 31 characters. <WORD> – unencrypted password, set by the string of [8..64] characters, may include [0-9a-fA-F] characters. <HEX> – encrypted password, set by the string of [16..128] characters. |
7 | Select a key authentication method for IKE connection. | esr(config-l2tp)# ipsec authentication | |
8 | Specify a shared secret authentication key that should be the same for both parties of the tunnel. | esr(config-l2tp)# ipsec authentication pre-shared-key | <TEXT> – string [1..64] ASCII characters; <HEX> – number, [1..32] bytes size, set by the string of [2..128] characters in hexadecimal format (0xYYYY ...) or (YYYY ...); <ENCRYPTED-TEXT> – encrypted password, [1..32] bytes size, set by the string of [2..128] characters. <ENCRYPTED-TEXT> – encrypted number, [2..64] bytes size, set by the string of [2..256] characters. |
| 9 | Restrict the authentication and encryption methods used for the IKE protocol (optional). | esr(config-l2tp)# ipsec ike proposal <NAME> | <NAME> – name of the previously created IKE profile, set by the string of up to 31 characters. |
| 10 | Restrict the authentication and encryption methods used for the IPsec protocol (optional). | esr(config-l2tp)# ipsec proposal <NAME> | <NAME> – name of the previously created IPsec profile, set by the string of up to 31 characters. |
| 11 | Specify UDP port number on which the connection to the L2TP server is established (optional). | esr(config-l2tp)# port <PORT> | <PORT> – UDP port number, takes values of [1024..65535]. Default value: 1701. |
12 | Enable the tunnel. | esr(config-l2tp)# enable | |
10 | Specify MTU size (MaximumTransmissionUnit) for the tunnel (optional). | esr(config-l2tp)# mtu <MTU> | <MTU> – MTU value, takes values in the range of:
Default value: 1500. |
11 | Ignore the default route via the given L2TP tunnel (optional). | esr(config-l2tp)# ignore-default-route | |
12 | Specify authentication method (optional). | esr(config-l2tp)# authentication method <METHOD> | <METHOD> – authentication method, possible values: chap, mschap, mschap-v2, eap, pap Default value: chap. |
13 | Specify the time interval during which the statistics on the tunnel load is averaged (optional). | esr(config-l2tp)# load-average <TIME> | <TIME> – interval in seconds, takes values of [5..150]. Default value: 5. |
14 | Change the time interval in seconds after which the router sends a keepalive message (optional). | esr(config-l2tp)# ppp timeout keepalive <TIME > | <TIME> – time in seconds, takes values of [1..32767]. Default value: 10. |
15 | Change the number of failed data-link tests before breaking the session (optional). | esr(config-l2tp)# ppp failure-count <NUM> | <NUM> – the number of failed data-link tests, specified in the range [1..100]. Default value: 10. |
It is also possible to configure QoS in basic or advanced mode for the L2TP client (see section QoS management). | |||
Configuration example
Objective:
Configure PPTP tunnel on a router:
- PPTP server address: 20.20.0.1;
- account for connection – login: ivan, password: simplepass.
Solution:
Create L2TP tunnel:
Specify the account (Ivan user) to connect to the server:
Specify the remote gateway:
Specify a security zone:
Specify IPsec authentication method:
Specify IPsec security key:
Enable L2TP tunnel:
To view the tunnel status, use the following command:
To view sent and received packet counters, use the following command:
To view the tunnel configuration, use the following command:
- Configuring server for remote access to corporate network via PPTP protocol
- Configuring server for remote access to corporate network via L2TP protocol
- Configuring server for remote access to corporate network via OpenVPN protocol
- Configuring remote access client via PPPoE
- Configuring remote access client via PPTP
- Configuring remote access client via L2TP