...
| Информация |
|---|
In the current implementation, traffic dropped by the router for any reason will not be included in the statistics. |
Configuration algorithm
Step | Description | Command | Keys |
|---|---|---|---|
1 | Specify Netflow protocol version. | esr(config)# netflow version <VERSION> | <VERSION> – Netflow protocol version: 5, 9 and 10. |
2 | Set the maximum amount of observed sessions. | esr(config)# netflow max-flows <COUNT> | <COUNT> – amount of observed sessions, takes values of [10000..2000000]. Default value: 512000. |
| 3 | Set the interval after which the information on active sessions is exported to the collector. | esr(config)# netflow active-timeout <TIMEOUT> | <TIMEOUT> – delay before sending active sessions information, set in seconds, takes the value of [5..36000]. Default value: 1800 seconds. |
4 | Set the interval after which the information on outdated sessions is exported to the collector. | esr(config)# netflow inactive-timeout <TIMEOUT> | <TIMEOUT> – delay before sending outdated sessions information, set in seconds, takes the value of [0..240]. Default value: 15 seconds. |
5 | Set the rate of the statistics sending to a Netflow collector. | esr(config)# netflow refresh-rate <RATE> | <RATE> – rate of the statistics sending, set in packets/flow, takes the value of [1..10000]. Default value: 10. |
6 | Enable Netflow on the router. | esr(config)# netflow enable | |
7 | Create the Netflow collector and switch to its configuration mode. | esr(config)# netflow collector <ADDR> | <ADDR> – collector IP address, defined as AAA.BBB.CCC.DDD where each part takes values of [0..255]. |
8 | Set the Netflow service port on the statistics collection server. | esr(config-netflow-host)# port <PORT> | <PORT> – UDP port number in the range of [1..65535]. Default value: 2055. |
9 | Enable statistics sending to the Netflow server in the interface/tunnel/network bridge configuration mode. | esr(config-if-gi)# ip netflow export |
| Scroll Pagebreak |
|---|
Configuration example
...
Sflow is a computer network, wireless network and network device monitoring standard designed for traffic accounting and analysis.
Configuration algorithm
Step | Description | Command | Keys |
|---|---|---|---|
1 | Set the rate of sending the unchanged user traffic packets to sFlow collector. | esr(config)# sflow sampling-rate <RATE> | <RATE> – rate of sending the user traffic packets to the collector, takes the value of [1..10000000]. If the rate value is 10, one of ten packets will be sent to the collector. Default value: 1000. |
2 | Set the interval after which the information on the network interface counters is obtained. | esr(config)# sflow poll-interval <TIMEOUT> | <TIMEOUT> – interval after which the information on the network interface counters is obtained, takes values of [1..10000]. Default value: 10 seconds. |
3 | Enable sFlow on the router. | esr(config)# sflow enable | |
4 | Create the sFlow collector and switch to its configuration mode. | esr(config)# sflow collector <ADDR> | <ADDR> – collector IP address, defined as AAA.BBB.CCC.DDD where each part takes values of [0..255]. |
5 | Enable statistics sending to the sFlow server in the interface/tunnel/network bridge configuration mode. | esr(config-if-gi)# ip sflow export |
| Scroll Pagebreak |
|---|
Configuration example
...
SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) is a protocol designed for device management in IP networks featuring TCP/UDP architecture. SNMP provides management data as variables that describe the configuration of a system being managed.
Configuration algorithm
Step | Description | Command | Keys |
|---|---|---|---|
1 | Enable SNMP server. | esr(config)# snmp-server | |
2 | Specify community for the access via SNMPv2c. | esr(config)# snmp-server community <COMMUNITY> [ <TYPE> ] | <COMMUNITY> – community for the access via SNMP; <TYPE> – access level:
<IP-ADDR> – IP address of the client provided with the access, defined as AAA.BBB.CCC.DDD where each part takes values of [0..255]; <IPV6-ADDR> – client IPv6 address, defined as X:X:X:X::X where each part takes values in hexadecimal format [0..FFFF]; <OBJ-GROUP-NETWORK-NAME> – profile name of IP addresses, from which snmp requests are processing, set by the string of up to 31 characters; <VERSION> – the snmp version supported by this community takes the values v1 or v2c; <VIEW-NAME> – SNMP view profile name, set by the string of up to 31 characters; <VRF> – VRF instance name, set by the string of up to 31 characters, for which access will be granted. |
3 | Set the value of SNMP variable that contains contact information. | esr(config)# snmp-server contact <CONTACT> | <CONTACT> – contact information, sets by string with 255 characters length. |
4 | Set the DSCP code value for the use in IP headers of SNMP server egress packets (optional). | esr(config)# snmp-server dscp <DSCP> | <DSCP> – DSCP code value, takes values in the range of [0..63]. Default value: 63. |
5 | Enable router reboot by using snmp messages (optional). | esr(config)# snmp-server system-shutdown | |
6 | Create SNMPv3 user. | esr(config)# snmp-server user <NAME> | <NAME> – user name, set by the string of up to 31 characters. |
7 | Set the value of SNMP value that contains the information on the device location. | esr(config)# snmp-server location <LOCATION> | <LOCATION> – information about equipment location, set by the string up to 255 characters. |
8 | Specify user access level via SNMPv3. | esr(config-snmp-user)# access <TYPE> | <TYPE> – access level:
|
9 | Specify user security mode via SNMPv3. | esr(config-snmp-user)# authentication access <TYPE> | <TYPE> – security mode:
|
10 | Specify SNMPv3 queries authentication algorithm. | esr(config-snmp-user)# authentication algorithm <ALGORITHM> | <ALGORITHM> – encryption algorithm:
|
11 | Set the password for SNMPv3 queries authentication. | esr(config-snmp-user)# authentication key ascii-text | <CLEAR-TEXT> – password, set by the string of 8 to 16 characters;
<ENCRYPTED-TEXT> – encrypted password of 8 to 16 bytes (from 16 to 32 characters) in hexadecimal format (0xYYYY ...) or (YYYY ...). |
12 | Enable filtration and set the profile of IP addresses from which SNMPv3 packets with the given SNMPv3 user name can be received. | esr(config-snmp-user)# client-list <NAME> | <NAME> – name of the previously conscious object-group, specified in a string of up to 31 characters. |
| 13 | Specify vrf for SNMPv3 user (optional). | esr-21(config-snmp-user)# ip vrf forwarding <VRF> | <VRF> – VRF instance name, set by the string of up to 31 characters, which contains SNMP notification collector. |
14 | Enable filtration and set IPv4/IPv6 address which is provided with the access to the router as the given SNMPv3 user. | esr(config-snmp-user)# ip address <ADDR> | <ADDR> – IP address of the client provided with the access, defined as AAA.BBB.CCC.DDD where each part takes values of [0..255]. |
esr(config-snmp-user)# ipv6 address <ADDR> | <IPV6-ADDR> – client IPv6 address, defined as X:X:X:X::X where each part takes values in hexadecimal format [0..FFFF]. | ||
15 | Enable SNMPv3 user. | esr(config-snmp-user)# enable | Default value: process is disabled. |
16 | Specify the transmitted data encryption algorithm. | esr(config-snmp-user)# privacy algorithm <ALGORITHM> | <ALGORITHM> – encryption algorithm:
|
17 | Set password for the transmitted data encryption. | esr(config-snmp-user)# privacy key ascii-text | <CLEAR-TEXT> – password, set by the string of 8 to 16 characters; <ENCRYPTED-TEXT> – encrypted password of 8 to 16 bytes (from 16 to 32 characters) in hexadecimal format (0xYYYY ...) or (YYYY ...). |
18 | Set the snmp view profile permitting or denying the access to one or another OID for user. | esr(config-snmp-user)# view <VIEW-NAME> | <VIEW-NAME> – name of SNMP view profile, on which based access to OID, set by the string up to 31 characters. |
19 | Enable SNMP notifications transmission to the specified IP address and switch to SNMP notifications configuration mode. | esr(config)# snmp-server host | <IP-ADDR> – IP address, defined as AAA.BBB.CCC.DDD where each part takes values of [0..255]. <IPV6-ADDR> – IPv6 address, defined as X:X:X:X::X where each part takes values in hexadecimal format [0..FFFF]; <VRF> – VRF instance name, set by the string of up to 31 characters, which contains SNMP notification collector. |
20 | Define the port of SNMP notifications collector on the remote server (optional). | esr(config-snmp-host)# port <PORT> | <PORT> – UDP port number in the range of [1..65535]. Default value: 162. |
21 | Allow different types of SNMP notifications to be sent. | esr(config)# snmp-server enable traps <TYPE> | <TYPE> – type of filtered messages. May take the following values: config, entry, entry-sensor, environment, envmon, files-operations, flash, flash-operations, interfaces, links, ports, screens, snmp, syslog. Additional parameters depend on the filter type. |
22 | Create the snmp view profile permitting or denying the access to one or another OID for community (SNMPv2) and user (SNMPv3). | esr(config)# snmp-server enable traps <TYPE> | <VIEW-NAME> – SNMP view profile name, set by the string of up to 31 characters. |
Configuration example
Objective:
...
| Блок кода |
|---|
esr(config)# snmp-server user admin |
| Scroll Pagebreak |
|---|
| Блок кода |
|---|
esr(snmp-user)# authentication access priv |
...
A Zabbix proxy is a process capable of collecting monitoring data from one or more monitored devices and sending this information to a Zabbix server.
Configuration algorithm
Step | Description | Command | Keys |
|---|---|---|---|
1 | Switch to the agent/proxy configuration context. | esr(config)# zabbix-agent esr(config)# zabbix-proxy | |
2 | Specify the host name (optional). For active mode, the name must match the host name on the Zabbix server. | esr(config-zabbix)# hostname <WORD> esr(config-zabbix-proxy)# hostname <WORD> | <WORD> – host name, set by the string of up to 255 characters. |
3 | Specify the address of the Zabbix server. | esr(config-zabbix)# server <ADDR> esr(config-zabbix-proxy)# server <ADDR> | <ADDR> – server IP address, defined as AAA.BBB.CCC.DDD where each part takes values of [0..255]. |
4 | Specify the server address for active checks (when using active mode). | esr(config-zabbix)# active-server <ADDR> <PORT> esr(config-zabbix-proxy)# active-server <ADDR> <PORT> | <ADDR> – server IP address, defined as AAA.BBB.CCC.DDD where each part takes values of [0..255]. <PORT> – server port, set in the range of [1..65535]. Default value: 10051. |
5 | Specify the port that will be listened by the agent/proxy (optional). | esr(config-zabbix)# port <PORT> esr(config-zabbix-proxy)# port <PORT> | <PORT> – port that will be listened by zabbix agent/proxy, may take values in the range of [1..65535]. Default value: 10050. |
6 | Allow remote commands execution by Zabbix agent/proxy (when using active mode). | esr(config-zabbix)# remote-commands esr(config-zabbix-proxy)# remote-commands | |
7 | Specify the address from which the server will interact (optional). | esr(config-zabbix)# source-address <ADDR> esr(config-zabbix-proxy)# source-address <ADDR> | <ADDR> – server IP address, defined as AAA.BBB.CCC.DDD where each part takes values of [0..255]. |
8 | Specify the processing time for remote commands (optional). | esr(config-zabbix)# timeout <TIME> esr(config-zabbix-proxy)# timeout <TIME> | <TIME> – timeout, takes value in seconds [1..30]. Default value: 3. It is recommended to set the maximum value since some commands may take longer than the default. If the command is not completed within the specified time, processing of the command will be terminated. |
9 | Enable agent/proxy functionality. | esr(config-zabbix)# enable esr(config-zabbix-proxy)# enable | |
10 | Allow access to the router (to the self zone) on TCP ports 10050, 10051 from the appropriate firewall security zone. See Firewall configuration section. | ||
Zabbix-agent configuration example
...
| Блок кода |
|---|
esr(config-zabbix)# hostname ESR-agent esr(config-zabbix)# active-server 192.168.32.101 esr(config-zabbix)# remote-commands |
...
Set the execution time of the remote commands, and activate the agent’s functionality:
...
Zabbix-server configuration example
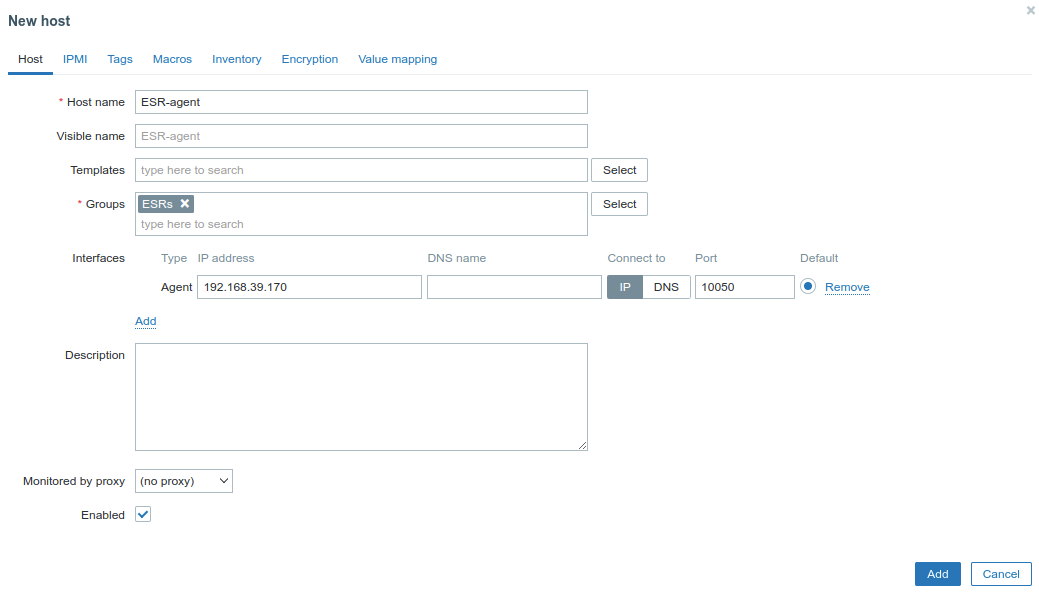
Create the host:
scroll-pagebreak
Create the script (Administration -> Scripts-> Create Script):
...
Syslog (System Log) – standard for sending and registering messages about events occurring in the system is used in networks operating over IP.
Configuration algorithm
Step | Description | Command | Keys |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Enable sending syslog messages as a snmp-trap to snmp server. | esr(config)# syslog snmp | |
| 2 | Enable or disable sending events of individual router processes operation to the snmp server (optional). | esr(config-syslog-snmp)# match [not] process-name <PROCESS-NAME> | <PROCESS-NAME> If allowing criteria are specified (match process-name), only messages of the specified processes are logged. If prohibiting criteria are specified (match not process-name), messages of all not prohibited processes are logged. By default, logging of messages from all processes is allowed. |
3 | Set the severity for messages that will be sent to the SNMP server. | esr(config)# syslog snmp <SEVERITY> | <SEVERITY> – message importance level, takes the following values (in order of decreasing importance):
|
| 4 | Set display of syslog messages during remote connections (Telnet, SSH) (optional). | esr(config)# syslog monitor | |
| 5 | Enable or disable display of the events of individual router processes operation during remote connections (optional). | esr(config-syslog-monitor)# match [not] process-name <PROCESS-NAME> | <PROCESS-NAME> – described in point 2. |
| 6 | Set the severity for messages that will be displayed during remote connections. | esr(config-syslog-monitor)# severity <SEVERITY> | <SEVERITY> – described in point 3. |
| 7 | Enable display of syslog messages on console connection (optional). | esr(config)# syslog console | |
| 8 | Enable or disable display of the events of individual router processes operation during console connections (optional). | esr(config-syslog-console)# match [not] process-name <PROCESS-NAME> | <PROCESS-NAME> – described in point 2. |
| 9 | Set the severity for messages that will be displayed during console connections. | esr(config-syslog-console)# severity <SEVERITY> | <SEVERITY> – described in point 3. |
| 10 | Enable saving of syslog messages of a specified level of importance to the specified log file (when it is necessary to use local syslog file). | esr(config)# syslog file <NAME> | <NAME> – name of the file to which messages of a given level will be recorded, specified by string up to 31 characters. |
| 11 | Enable or disable saving of syslog messages of events of the operation of individual router processes (optional). | esr(config-syslog-file)# match [not] process-name <PROCESS-NAME> | <PROCESS-NAME> – described in point 2. |
| 12 | Set the severity for messages that will be saved to the local syslog file (optional). | esr(config-syslog-file)# severity <SEVERITY> | <SEVERITY> – described in point 3. |
| 13 | Set maximum size of the log file (optional). | esr(config)# syslog file-size <SIZE> | <SIZE> – file size, takes value of [10..10000000] KB. |
| 14 | Set maximum number of files saved during rotation (optional). | esr(config)# syslog max-files <NUM> | <NUM> – maximal number of files, takes values of [1 .. 1000]. |
| 15 | Enable sending of syslog messages to a remote syslog server (when it is necessary to send messages to a remote syslog server). | esr(config)#syslog host <HOSTNAME> <ADDR><TRANSPORT> | <HOSTNAME> – syslog server name, set by the string of up to 31 characters. Used only to identify the server during configuration. The value 'all' is used in the no syslog host command to delete all syslog servers; <ADDR> – IP address, defined as AAA.BBB.CCC.DDD where each part takes values of [0..255]; <TRANSPORT> – data transfer protocol, optional parameter, takes values:
|
| 16 | Specify IPv4/IPv6 address of the remote syslog server. | esr(config-syslog-host)# remote-address { <ADDR> | <IPV6-ADDR> } | <ADDR> – IP address, defined as AAA.BBB.CCC.DDD where each part takes values of [0..255]; <IPV6-ADDR> – IPv6 address, defined as X:X:X:X::X where each part takes values in hexadecimal format [0..FFFF]. |
| 17 | Specify IPv4/IPv6 address of the router from which packets will be sent to the remote syslog server (optional). | esr(config-syslog-host)# source-address { <ADDR> | <IPV6-ADDR> } | <ADDR> – IP address, defined as AAA.BBB.CCC.DDD where each part takes values of [0..255]; <IPV6-ADDR> – IPv6 address, defined as X:X:X:X::X where each part takes values in hexadecimal format [0..FFFF]; Default value: Ipv4/IPv6 interface address from which packets will be sent to the remote syslog server. |
| 18 | Specify transport protocol for packet transmission to the remote syslog server (optional). | esr(config-syslog-host)# transport { tcp | udp } | <VRF> – VRF instance name, set by the string of up to 31 characters, for which access will be granted. Default value: none (global routing table). |
| 19 | Specify name of the VRF instance within which packets will be sent to the remote syslog server (optional). | esr(config-syslog-host)# vrf <VRF> | |
| 20 | Specify number of the TCP/UDP port to which packets with syslog messages will be sent (optional). | esr(config-syslog-host)# port <PORT> | <PORT> – TCP/UDP port number to which packets with syslog messages will be sent. Default value: 514. |
| 21 | Enable or disable sending of the events of individual router processes operation to the remote server (optional). | esr(config-syslog-host)# match [not] process-name <PROCESS-NAME> | <PROCESS-NAME> – described in point 2. |
| 22 | Set the severity for messages that will be saved to local syslog file. | esr(config-syslog-host)# severity <SEVERITY> | <SEVERITY> – described in point 3. |
| 23 | Enable display of debugging messages during device boot (optional). | esr(config)#syslog reload debugging | |
| 24 | Enable logging of the entered user commands to the local syslog server (optional). | esr(config)# syslog cli-commands | |
| 25 | Enable message enumeration (optional). | esr(config)#syslog sequence-numbers | |
| 26 | Enable message date accuracy up to milliseconds (optional). | esr(config)#syslog timestamp msec | |
| 27 | Enable logging of failed authentications (optional). | esr(config)#logging login on-failure | |
| 28 | Enable logging of changes to the audit system settings (optional). | esr(config)#logging syslog configuration | |
| 29 | Enable logging of changes to the user settings (optional). | esr(config)#logging userinfo |
| Якорь | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
...
| Блок кода |
|---|
esr# show syslog ESR |
| Scroll Pagebreak |
|---|
Integrity check
Integrity check involves checking the integrity of stored executable files.
Configuration process
Step | Description | Command | Keys |
|---|---|---|---|
1 | Launch system integrity check. | esr# verify filesystem <detailed> | detailed – detailed information output to the console. |
Configuration example
Objective:
...
ESR routers have the option of local and/or remote configuration file copying by timer or when applying the configuration.
Configuration process
Step | Description | Command | Keys |
|---|---|---|---|
1 | Switch to the configuration file backup mode. | esr(config)# archive | |
2 | Set router configuration backup type (optional). | esr(config-ahchive)# type <TYPE> | <TYPE> – type of the router configuration backup. Takes the following values:
Default value: remote. |
3 | Enable timer configuration backup mode (optional). | esr(config-ahchive)# auto | |
4 | Enable configuration backup after each successful configuration application mode (optional). | esr(config-ahchive)# by-commit | |
5 | Specify a path for remote copying of the router configuration | esr(config-ahchive)# path <PATH> | <PATH> – defines the protocol, server address, location and prefix of the file name on the server |
6 | Set a period of time for automatic configuration backup (optional, relevant only for auto mode). | esr(config-ahchive)# time-period <TIME> | <TIME> – periodicity of automatic redundancy of the configuration, takes the value in minutes [1..35791394]. Default value: 720 minutes. |
7 | Set the maximum number of locally saved configuration backups (optional, relevant for local and both types). | esr(config-ahchive)# count-backup <NUM> | <NUM> – set the maximum number of locally saved configuration backups. Takes values in the range of [1..100]. Default value: 1. |
Configuration example
Objective:
...
After applying this configuration once a day and with each successful change of the router configuration, a configuration file with the 'esr-exampleYYYYMMDD_HHMMSS.cfg' name will be sent to the TFTP server. Also, on the router itself, in the flash:backup/ section, a file with the 'config_YYYYMMDD_HHMMSS' name will be created. When 30 files are accumulated in the flash:backup/ section, the oldest one will be deleted when creating a new one.
Scroll Pagebreak