Optical line terminals LTP-16N, LTP-16NT
User Manual
Firmware version 1.4.0 (27.07.2022)
Terms and definitions
- CBR — Constant bitrate
- DBA — Dynamic Bandwidth Allocation
- DHCP — Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
- ERPS — Ethernet Ring Protection Switching
- FTP — File Transfer Protocol
- FW — Firmware
- GPON — Gigabit PON
- HSI — High Speed Internet
- IGMP — Internet Group Management Protocol
- IP — Internet protocol
- MLD — Multicast Listener Discovery
- OLT — Optical Line Terminal
- ONT — Optical Network Terminal
- ONU — Optical Network Unit
- PCB — Printed Circuit Board
- PPPOE — Point-to-point protocol over Ethernet
- SLA — Service Level Agreement
- SNTP — Simple Network time protocol
- SNMP — Simple Network Management Protocol
- SFP — Small Form-factor Pluggable
- TFTP — Trivial File Transfer Protocol
- URI — Uniform Resource Identifier
- VEIP — Virtual Ethernet Interface Point
Notes and warnings
Notes contain important information, tips or recommendations on device operation and configuration.
Warnings are used to inform the user about harmful situations for the device and the user alike, which could cause malfunction or data loss.
General information
Introduction
GPON is a network of Passive Optical Networks (PON) type. It is one of the most effective state-of-the-art 'last mile' solutions that significantly reduces the required amount of cable and provides data transfer with downstream rate up to 2.5 Gbps and upstream rate up to 1.25 Gbps. Use of GPON-based solutions in access networks allows end users to have access to new services based on IP protocol in addition to more common ones.
The key GPON advantage is the use of one Optical Line Terminal (OLT) for multiple Optical Network Terminals (ONT). OLT converts Gigabit Ethernet and GPON interfaces and is used to connect a PON network with data communication networks of a higher level.
The range of OLT GPON equipment produced by ELTEX presents LTP-16N and LTP-16NT terminals of 16 GPON ports with internal Ethernet switch with RSSI function.
This user manual describes purpose, main technical specifications, installation order, rules of configuration, monitoring, and software update for the devices.
Purpose
The LTP-16N(T) optical line terminal is designed to establish connection with upstream equipment and provide broadband access via passive optical networks. Ethernet connection is established through Gigabit uplink and 10GBASE-X interfaces, and GPON interfaces are used to connect to optical networks. Each PON interface allows connection of up to 128 subscriber optical terminals through one fiber and supports Dynamic Bandwidth Allocation (DBA).
The following services are provided to end users:
- voice communications;
- HDTV;
- VoIP;
- high-speed access to the Internet;
- IPTV;
- video-on-demand (VoD);
- video conferencing;
- online educational and entertainment programs.
The device supports the following functions:
- Dynamic Bandwidth Allocation (DBA);
- security functions;
- remote ONT management;
- power measurement support for signals received from each ONT (RSSI);
- VLAN organisation (VLAN ID range: 1–4094);
- support for IGMP snooping v1/2/3, IGMP proxy;
- support for PPPoE intermediate agent;
- support for DHCP Snooping, DHCP option 82.
Delivery Package
The standard delivery package includes:
- LTP-16N/16NT optical line terminal;
- Mounting set for 19'' rack;
- RJ-45 – DB9(F) console cable;
- CD with User Manual and Quick Configuration Guide (optional);
- Power cable (if equipped with 220 V power supply);
- Technical passport.
Technical specifications
Table 1 – Main specifications of the line terminal
Interfaces | ||
|---|---|---|
Number of Ethernet interfaces | LTP-16N/LTP-16NT | 9 |
Connector | RJ-45 – 1 | SFP – 8 |
Data rate, Mbps | 10/100/1000 duplex/half-duplex | 1000/10000 duplex |
Standards | 1GBASE-X | 10GBASE-X |
Standards | IEEE 802.1D, IEEE 802.1p, IEEE 802.1Q | |
Number of PON interfaces | LTP-16N/LTP-16NT | 16 |
Connector type | SC/UPC (socket) | |
Transmission medium | SMF – 9/125, G.652 fiber optical cable | |
Standards | Digital RSSI (Received Signal Strength Indication) | |
Splitting ratio | 1:4, 1:8, 1:16, 1:32, 1:64, 1:128 | |
Class B+ | Class C++ | |
Range of coverage | 20 km | 40 km |
Transmitter | 1490 nm DFB Laser | 1490 nm DFB Laser |
Data rate | 2488 Mbps | 2488 Mbps |
Average output power | +1.5..+5 dBm | +7..+10 dBm |
Spectral line width with -20dB | 1.0 nm | 1.0 nm |
Receiver | 1310 nm APD/TIA | 1310 nm APD/TIA |
Data rate | 1244 Mbps | 1244 Mbps |
Receiver sensitivity | -28 dBm | -32 dBm |
Receiver optical congestion | -8 dBm | -12 dBm |
Synchronization ports | only for LTP-16NT | |
Processor | ||
Clock frequency | 2.2 GHz | |
Core quantity | 4 | |
RAM | LTP-16N/LTP-16NT | 8 GB |
Non-volatile memory | LTP-16N/LTP-16NT | 8 GB |
Switch | ||
Switch performance | 120 Gbps | |
MAC table | 64K entries | |
VLAN support | up to 4K in accordance with 802.1Q | |
Control | ||
|---|---|---|
Local control | CLI – Command Line Interface | |
Remote management | CLI (SSH, Telnet), SNMP | |
Monitoring | CLI, SNMP | |
Access restriction | by password, by privelege level | |
General parameters | ||
Power supply | AC: 150-250V, 50 Hz | |
Maximum power consumption | LTP-16N/LTP-16NT | 75 W |
Operating temperature range | from -5 to +40 °C | |
Relative humidity | up to 80 % | |
Dimensions (W × H × D) | 19", 1U | |
Dimensions with an installed power module | ||
430 × 42 × 305 mm | ||
Weight | Complete set | |
LTP-16N/LTP-16NT | 3.5 kg | |
Modules | ||
power module | 0.5 kg | |
| Lifetime | at least 15 years | |
Compatible SFP transceivers
Correct and error-free operation of GPON interface requires exact parameters to be chosen and set for each transceiver type. This can be done only under laboratory conditions by the terminal vendor. Table 2 lists SFP transceivers for which seamless terminal operation is guaranteed.
DDMI (Digital Diagnostic Monitoring Interface) provides information on transceiver parameters, such as temperature, power voltage, etc. DDMI also measures the level of ONT signal (RSSI). All compatible transceivers support this function.
Table 2 – List of compatible SFP transceivers
Vendor | SFP transceiver module | Class | DDMI |
|---|---|---|---|
NEOPHOTONICS | PTB38J0-6538E-SC | B+ | + |
NEOPHOTONICS | 38J0-6537E-STH1+ | C+ HP | + |
NEOPHOTONICS | 38J0-6537E-STH2+ | C+ HP | + |
NEOPHOTONICS | 38J0-6537E-STH3+ | C+ HP | + |
Ligent Photonics | LTE3680M-BC | B+ | + |
Ligent Photonics | LTE3680M-BH | B+ | + |
Ligent Photonics | LTE3680P-BC | C+ | + |
| Ligent Photonics | LTE3680P-BC+1 | C+ | + |
Ligent Photonics | LTE3680P-BH | C+ | + |
Ligent Photonics | LTE3680P-BC2 | C+ HP | + |
| Hisense | LTE3680M-BC+ | B+ | + |
| Hisense | LTE3680M-BC+2 | C+ | + |
Design
Front panel
The devices have a metal housing of 1U size available for 19” form-factor rack mount. The front panel layout is shown in figures 1 and 2. Tables 3 and 4 list connectors, LEDs and controls located on the front panel of the terminal.
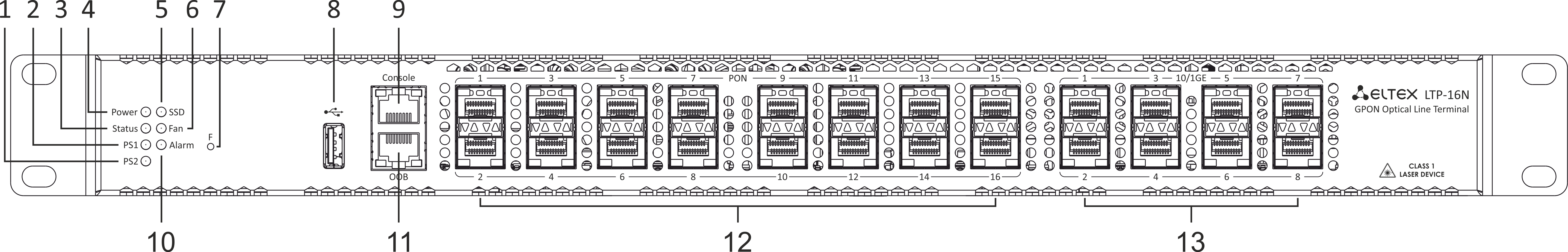
Figure 1 – LTP-16N front panel layout
Table 3 – Description of the connectors, LEDs, and controls located on the front panel of LTP-16N
# | Front panel element | Description |
|---|---|---|
1 | PS2 | Redundant power supply indicator |
2 | PS1 | Primary power supply indicator |
3 | Status | Device operation indicator |
4 | Power | Device power indicator |
5 | SSD | SSD operation indicator |
6 | FAN | Ventilation panels operation indicator |
7 | F | Functional key that reboots the device and resets it to factory default configuration:
|
8 | USB | USB port |
9 | Console | DB9F — RJ45 console port |
10 | Alarm | Alarm indicator |
11 | OOB | Port for connection the board via network |
12 | PON 1..16 | GPON interfaces. 16 chassis for installing xPON 2.5G SFP modules |
13 | 10/1GE | Uplink interfaces. 8 chassis for installing 10G-BASE-X SFP modules |
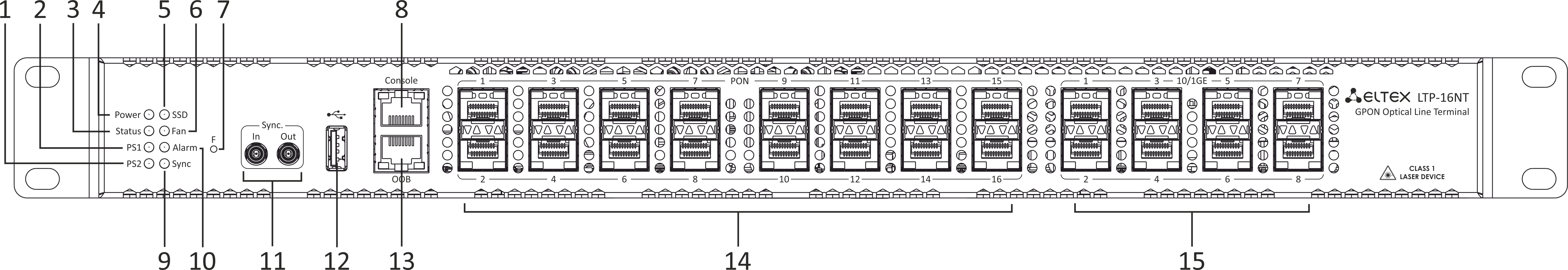
Figure 2 – LTP-16NT front panel layout
Table 4 – Description of the connectors, LEDs, and controls located on the front panel of LTP-16NT
# | Front panel element | Description |
|---|---|---|
1 | PS2 | Redundant power supply indicator |
2 | PS1 | Primary power supply indicator |
3 | Status | Device operation indicator |
4 | Power | Device power indicator |
5 | SSD | SSD operation indicator |
6 | FAN | Ventilation panels operation indicator |
7 | F | Functional key that reboots the device and resets it to factory default configuration:
|
8 | Console | DB9F — RJ45 console port |
9 | Sync | Synchronization operation indicator |
10 | Alarm | Alarm indicator |
11 | Sync ports | Synchronization interfaces |
12 | USB | USB port |
13 | OOB | Port for connection the board via network |
14 | PON 1..16 | GPON interfaces. 16 chassis for installing xPON 2.5G SFP modules |
15 | 10/1GE | Uplink interfaces. 8 chassis for installing 10G-BASE-X SFP modules |
Rear panel
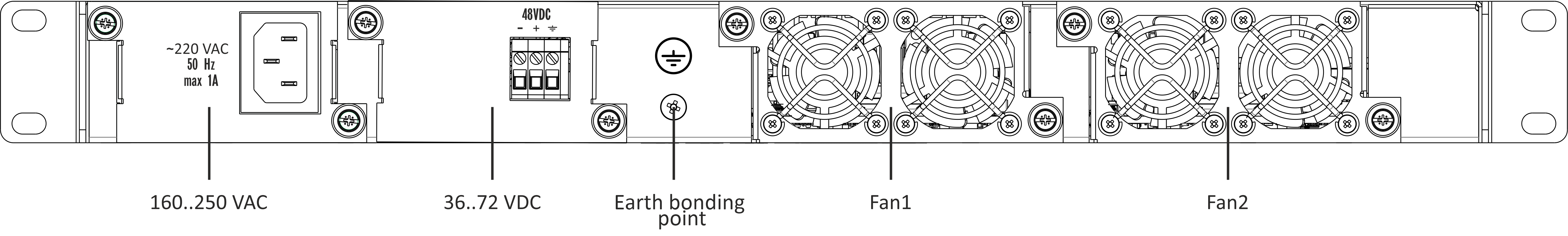
The rear panel of the device is shown in Figure 3.
Table below lists rear panel connectors.
Figure 3 – LTP-16N/16NT optical line terminal rear panel
Table 5 – Rear panel connectors description
Rear panel element | Description |
|---|---|
160-250 VAC, 50Hz, max 1A | Connectors for AC/DC power supply |
Earth bonding point | Earth bonding point |
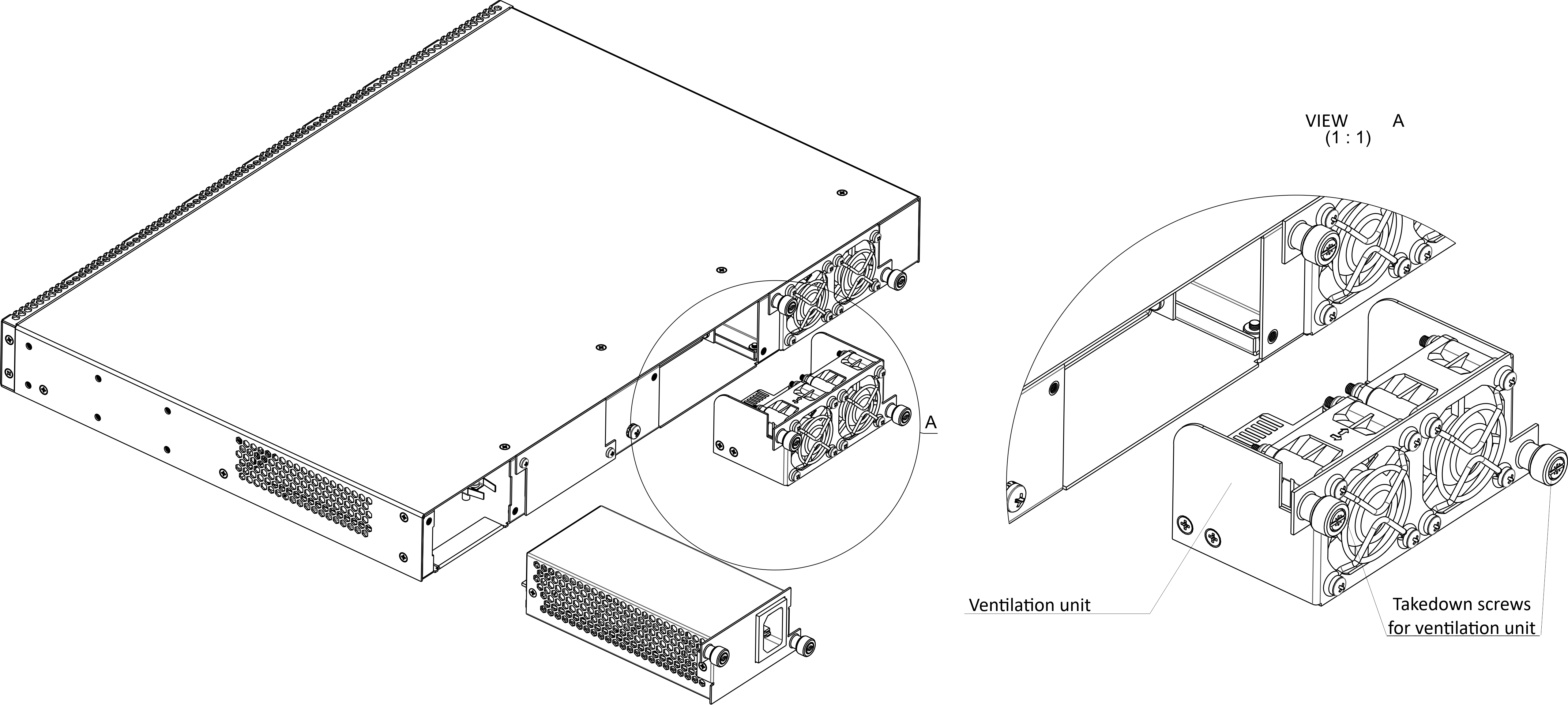
Fan1, Fan2 | Ventilation units |
LED indication
The indicators located on the front panel show the status of the terminal. Table 6 provides possible statuses of the LEDs.
Table 6 – LTP-16N/16NT status light indication
LED name | Indicator State | Device state |
|---|---|---|
Power | Solid green | Power is on, normal device operation |
Off | Power is off | |
Red | Primary power supply failure | |
Status | Solid green | Normal operation |
Solid red | Operation failures | |
Fan | Solid green | All fans are operational |
Flashing red | One or more fans are failed | |
PS1 | Solid green | Primary power supply is connected and operates correctly |
Disabled | Primary power supply is not connected | |
Red | Primary power supply is missing or failed. | |
PS2 | Solid green | Redundant power supply is connected and operates correctly |
Disabled | Redundant power supply is not connected | |
Red | The primary source of the redundant power supply is unavailable or the redundant power supply failed | |
Alarm | Green | Correct device operation |
Flashing red | Alarm | |
SSD | Disabled | Cannot reach the drive |
Flashing green | The drive is being accessed | |
Sync | Solid green | Synchronization is in process |
Disabled | Synchronization is disabled |
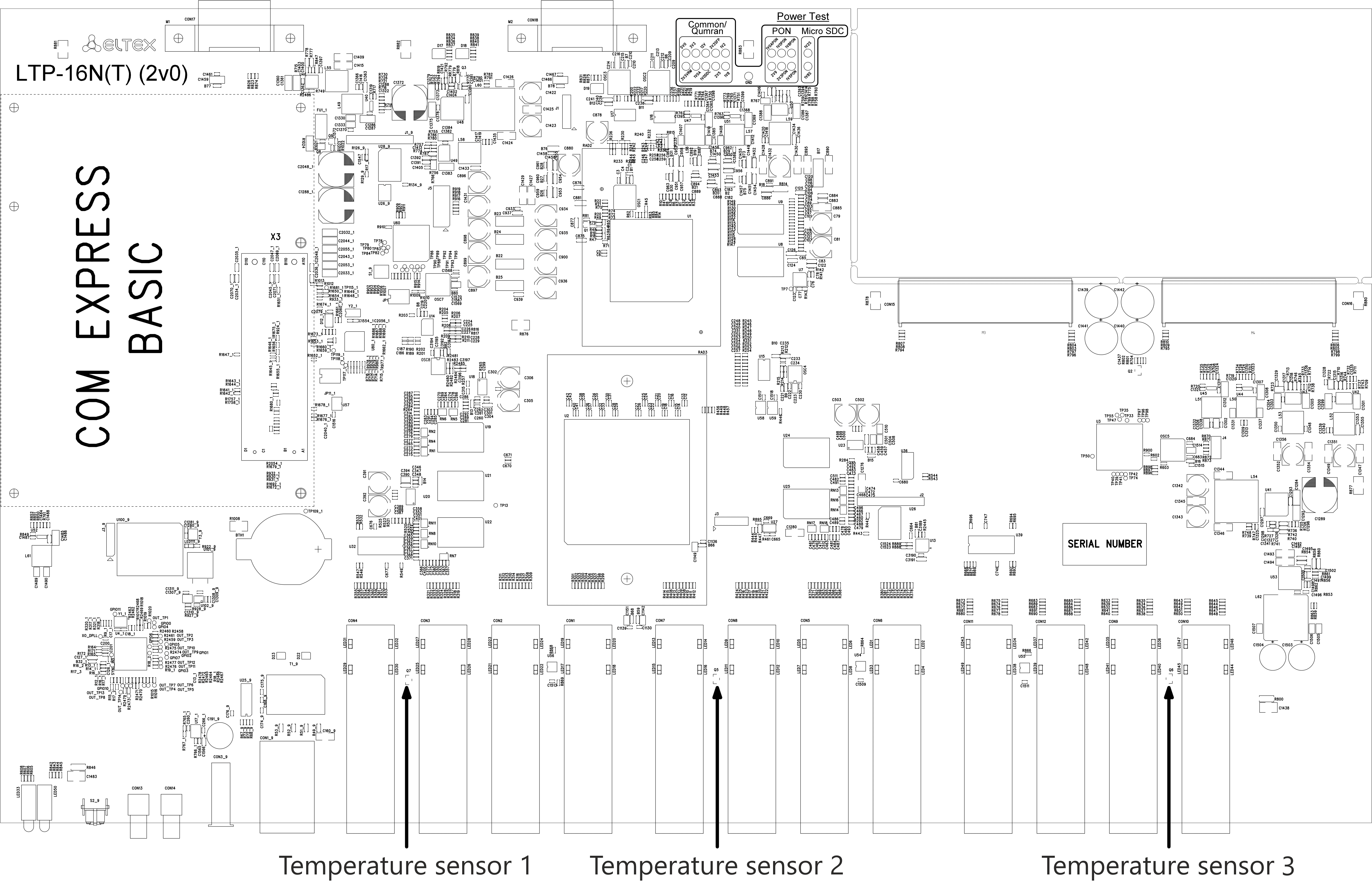
Temperature sensors
4 temperature sensors are used to measure temperature inside the terminal case: 3 external and 1 built into switch.
Figure 4 shows the sensor location on PCB.
Figure 4 – Temperature sensors allocation
Table 7 – Temperature sensors description
Rear panel element | Description |
|---|---|
Temperature sensor 1 | PON-ports SFP 1 |
Temperature sensor 2 | PON-ports SFP 2 |
Temperature sensor 3 | Front-ports SFP |
Temperature sensor 4 | Switch |
Ventilation system
There are ventilation openings on the device rear, front and side panels that serve to remove heat. There are two ventilation units on the rear panel (Figure 3).
Air flows in through the perforated front and side panels, circulates through all internal components, cools them down, and then is removed by fans located on the perforated rear panel.
The device contains two blocks of two fans each. The ventilation units are detachable. The procedure for dismantlement and installation is described in Ventilation units replacement.
Safety rules and installation procedure
This section describes safety measures and installation of the terminal into a rack and connection to a power supply.
Safety requirements
General requirements
Any operation with the equipment should comply with the Rules for the technical operation of consumer electrical installations.
Operations with the terminal should be carried out only by personnel authorized in accordance with the safety requirements.
- Before operating the device, all engineers should undergo special training.
- Connect only serviceable and compatible accessories to the terminal.
To avoid overheating and provide necessary ventilation of the terminal, sufficient space should be provided above and below the terminal. - The device is meant for 24/7 operation if the following requirements are met:
- ambient temperature from -5 to +40°C;
- relative humidity up to 80% at +25°C;
- atmosphere pressure from 6.0x10*4 to 10.7x10*4 Pa (from 450 to 800 mm Hg).
- The terminal should not be exposed to mechanical shock, vibration, smoke, dust, water, and chemicals.
- To avoid components overheating which may result in device malfunction, do not block air vents or place objects on the equipment.
Electrical safety requirements
- Prior to connecting the device to a power source, ensure that the equipment case is grounded with an earth bonding point. The earthing wire should be securely connected to the earth bonding point. The resistance between the earth bonding point and earthing busbar should be less than 0.1 Ω. PC and measurement instruments should be grounded prior to connection to the terminal. The potential difference between the equipment case and the cases of the instruments should be less than 1V.
- Prior to turning the device on, ensure that all cables are undamaged and securely connected.
- Make sure the device is off, when installing or removing the case.
- Follow the instructions given in SFP transceivers replacement to install or remove SFP transceivers. This operation does not require the terminal to be turned off.
Terminal installation
Check the device for visible mechanical damage before installing and turning it on. In case of any damage, stop the installation, fill in a corresponding document and contact your supplier. If the terminal has been at low temperatures for a long time before installation, leave it for 2 hours at ambient temperature prior to operation. If the device has been at high humidity for a long time, leave it for at least 12 hours in normal conditions prior to turning it on.
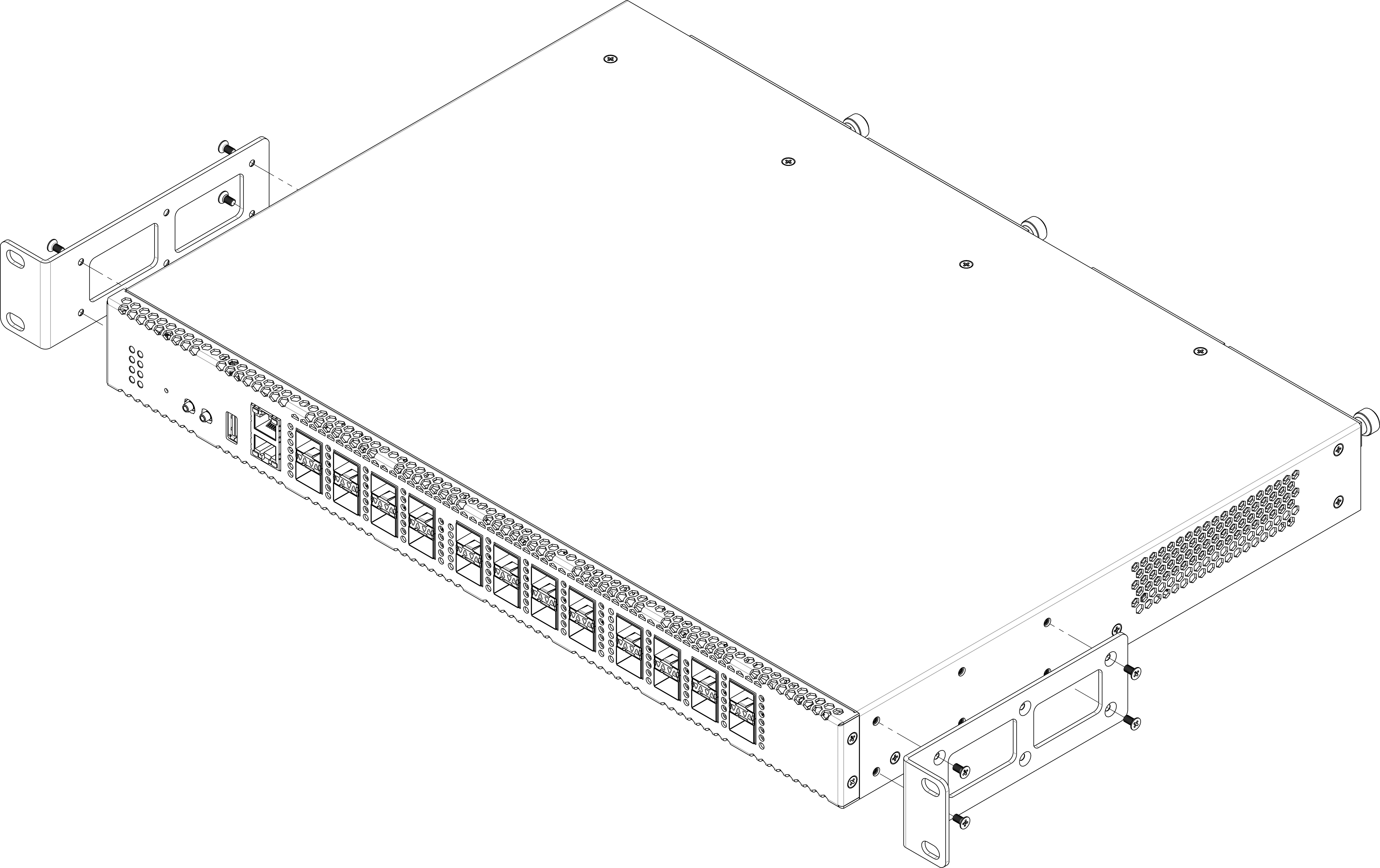
Support brackets mounting
The delivery package includes support brackets for rack installation and mounting screws to fix the terminal case on the brackets. To install the support brackets:
- Step 1. Align six mounting holes in the support bracket with the corresponding holes in the side panel of the device.
- Step 2. Use a screwdriver to screw the support bracket to the case.
- Step 3. Repeat steps 1 and 2 for the second support bracket.
Figure 5 – Support brackets mounting
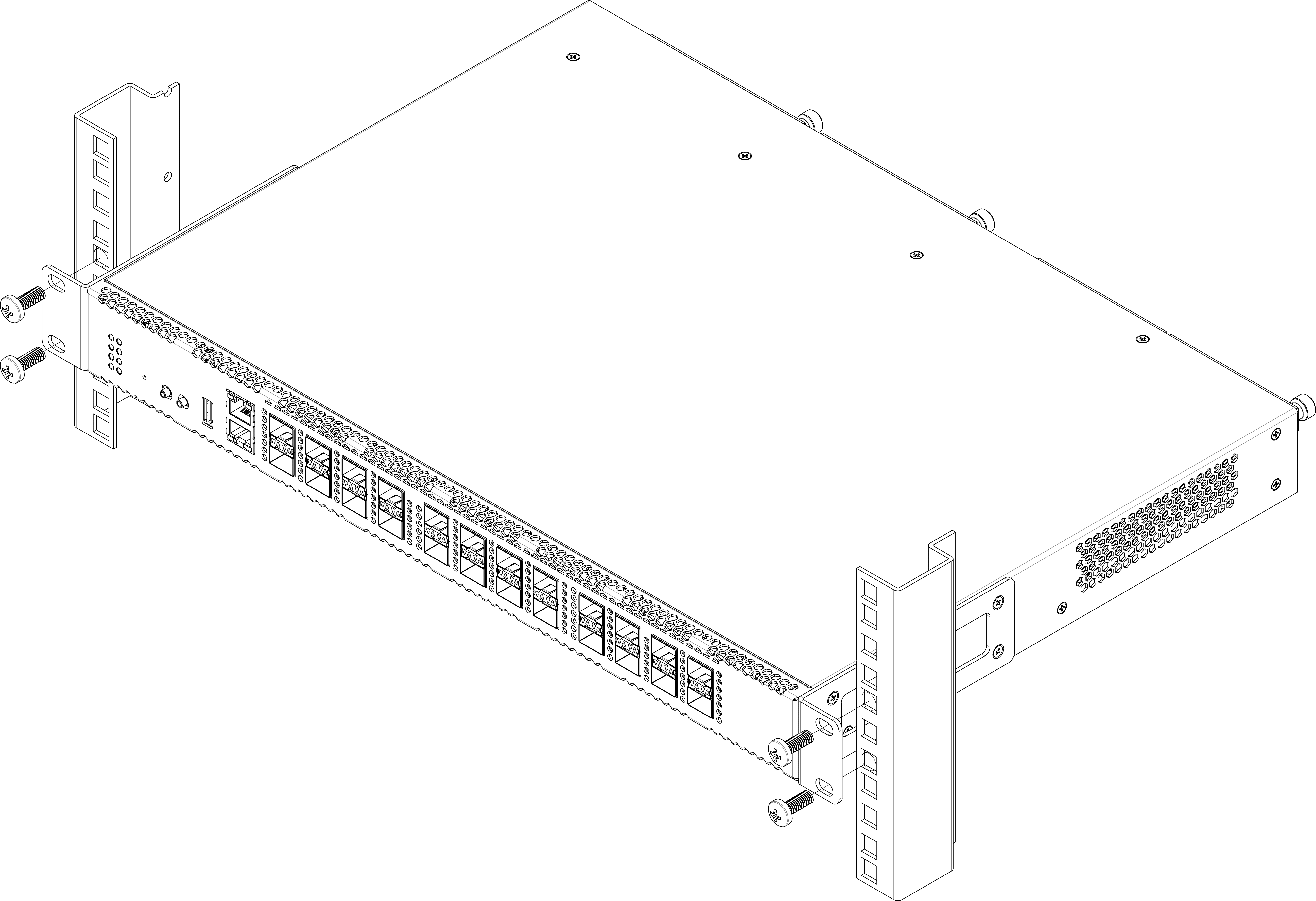
Terminal rack installation
To install the terminal to the rack:
- Step 1. Attach the terminal to the vertical guides of the rack.
- Step 2. Align mounting holes in the support bracket with the corresponding holes in the rack guides. Use the holes of the same level on both sides of the guides to ensure the device horizontal installation.
- Step 3. Use a screwdriver to attach the terminal to the rack.
Figure 6 – Device rack installation
The terminal is horizontally ventilated. The side panels have air vents. Do not block the air vents to avoid components overheating and subsequent terminal malfunction.
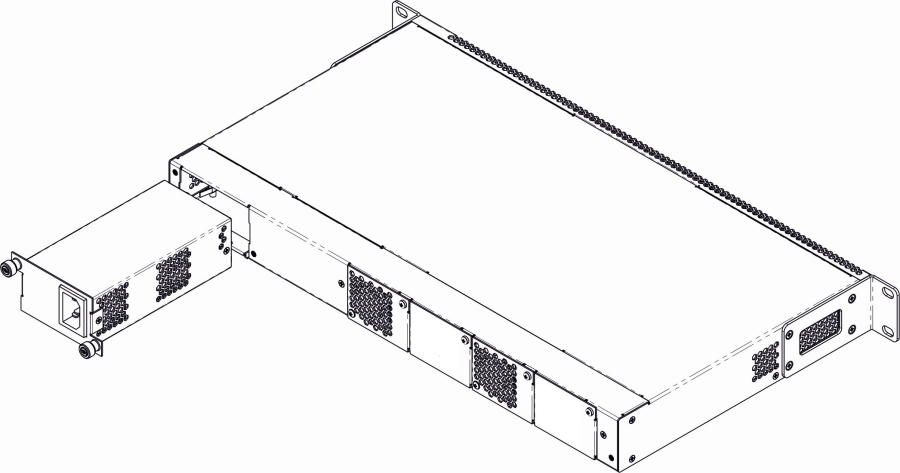
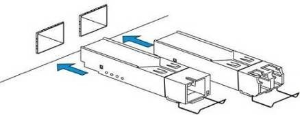
Power module installation
Depending on power supply requirements, terminals can be supplemented with either 220V, 50 Hz AC power module or 48 V DC power supply module. Location of the power module is shown in Figure 7.
Figure 7 – Power module installation
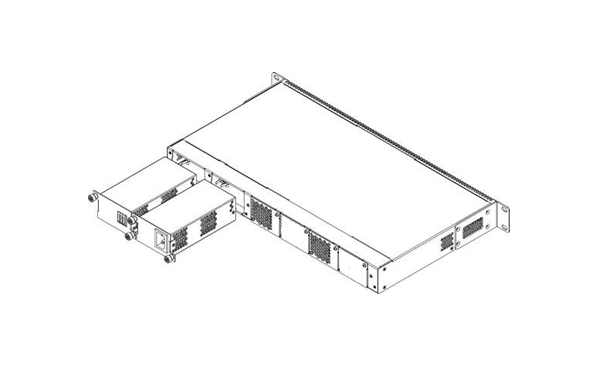
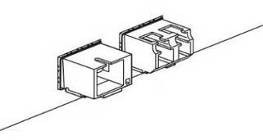
Terminals can operate with one or two power modules. The second power module installation is necessary when greater reliability is required. In case of using two power supply modules, it is allowed to use different power modules for supplying (with different voltage).
Figure 8 – Power module installation
From the electric point of view, both places for power module installation are identical. In the terms of device operation, the power supply module located closer to the edge is considered as the main module, and the one closer to the centre — as the backup module. Power modules can be inserted and removed without powering the device off. When an additional power module is inserted or removed, the device continues to operate without reboot.
To install a power module:
- Step 1. Install the power module into the socket shown in Figure 7 or Figure 8.
- Step 2. Screw the module to the case.
- Step 3. Follow the instructions in Terminal installation to power on.
The device installation order
- Step 1. Mount the device. In case of installation to a 19" form-factor rack, mount the support brackets from the delivery package to the rack.
- Step 2. Ground the case of the device. This should be done prior to connecting the device to the power supply. An insulated multiconductor wire should be used for earthing. The device grounding and the earthing wire section should comply with Electric Installation Code. The ground terminal is on the rear panel, Figure 3.
- Step 3. If you intend to connect a PC or another device to the switch console port, the device must be properly grounded as well.
- Step 4. Connect the power supply cable to the device.
- Step 5. Turn the device on and check the front panel LEDs to make sure the terminal is in normal operating conditions.
Getting started with the terminal
Connecting to the terminal CLI
This section describes various connection methods for Command Line Interface (CLI) of the terminal.
A serial port (hereafter – COM port) is recommended for preliminary adjustment of the terminal.
Connecting to CLI via COM port
This type of connection requires PC either to have an integrated COM port or to be supplied with an USB-COM adapter cable. The PC should also have a terminal program installed, e. g. Hyperterminal.
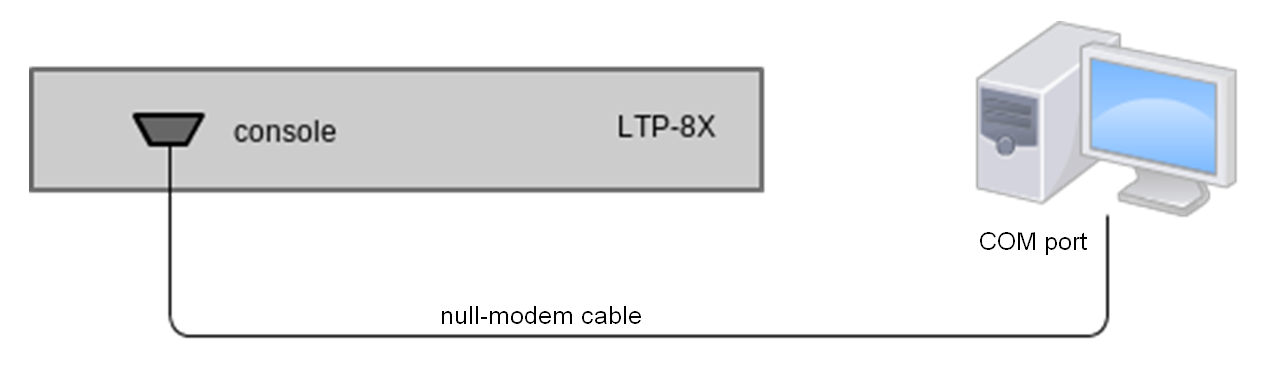
- Step 1. Use the null modem cable from the delivery package to connect the console port of the terminal to the PC COM port as shown in figure below.
Figure 9 – Connecting the terminal to a PC via COM port
Step 2. Launch the terminal program and create a new connection. Select the corresponding COM port in the Connect to drop-down list. Assign the port settings according to the table below. Click <OK>.
Table 8 – Port specifications
Speed
115200
Data bits
8
Parity
No
Stop bits
1
Flow control
None
Step 3. Press <Enter>. Log into the terminal CLI.
Factory default authorization settings:
login: admin, password: password.******************************************** * Optical line terminal LTP-16N * ******************************************** LTP-16N login: admin Password: LTP-16N#
Connecting to CLI via Telnet protocol
The Telnet protocol connection is more flexible than the connection via COM port. Connection to CLI can be established directly at the terminal location or via an IP network with the help of a remote desktop.
This section considers direct connection to CLI at the terminal location. Remote connection is similar, but requires changes in the terminal IP address that will be considered in detail in the Network Settings section.
In order to be connected to the terminal, a PC should have a Network Interface Card (NIC). The connection will additionally require the sufficient amount of network cable (Patching Cord RJ45) as it is not included in the delivery package.
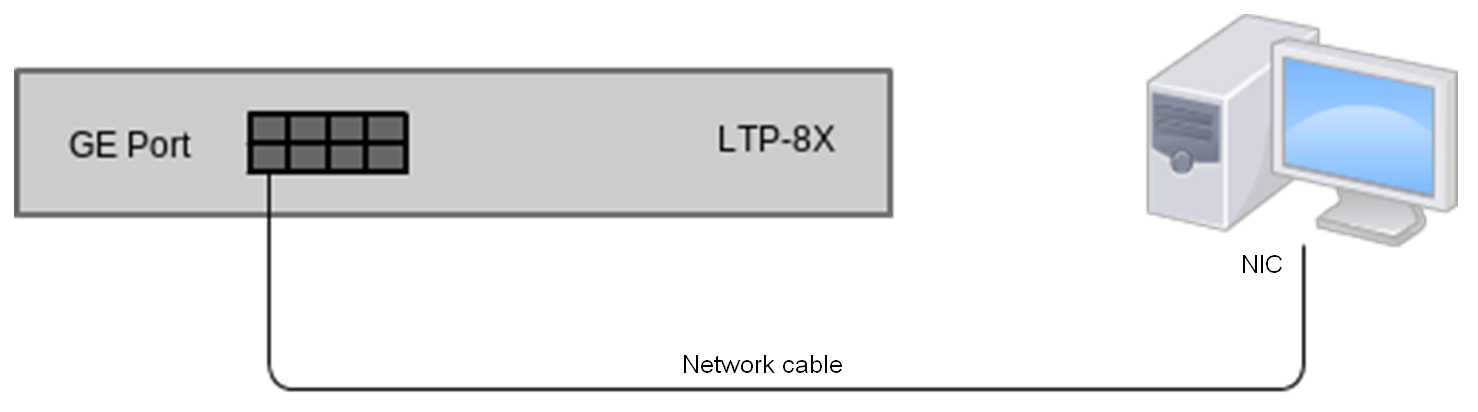
- Step 1. Connect one side of the network cable to any OOB port on the terminal. Connect another end to NIC on the PC as shown in figure below.
Figure 10 – Connecting the terminal to a PC via network cable
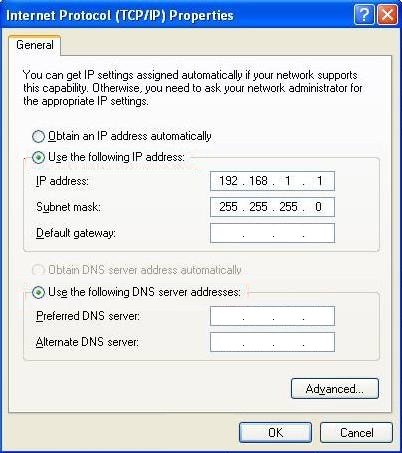
- Step 2. Assign IP settings for network connections. Set 168.1.1 as an IP address and 255.255.255.0 as a subnet mask.
Figure 11 – Network connection configuration
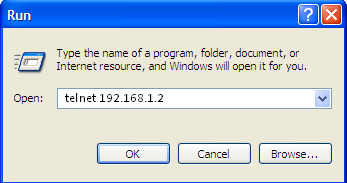
- Step 3. On the PC, click Start > Run. Enter the telnet command and the terminal's IP address. The factory setting for the IP address is 168.1.2. Click <OK>.
Figure 12 – Client startup
Step 4. Log into the terminal CLI.
Factory authorization settings:
login: admin, password: password.Trying 192.168.1.2... Connected to 192.168.1.2. Escape character is ’^]’. ******************************************** * Optical line terminal LTP-16N * ******************************************** LTP-16N login: admin Password: LTP-16N#
Connecting to CLI via Secure Shell protocol
Secure Shell connection (SSH) has functionality similar to the Telnet protocol. However, as opposed to Telnet, Secure Shell encrypts all traffic data, including passwords. This enables secure remote connection via public IP networks.
This section considers direct connection to CLI at the terminal location. Remote connection is similar, but requires changes in the terminal IP address that will be considered in detail in the Network settings section.
In order to connect to the terminal, a PC should have a Network Interface Card (NIC). The PC should have an SSH client installed, e.g. PuTTY. The connection will additionally require the sufficient amount of network cable (Patch Cord RJ-45) as it is not included in the delivery package.
- Step 1. Perform steps 1 and 2 from the Connecting to CLI via COM port
- Step 2. Run PuTTY. Enter IP address of the terminal. The default IP address is 168.1.2. Select port 22 and SSH protocol type. Click <Open>.
Step 3. Log into the terminal CLI. Factory authorization settings:
login: admin, password: password.login: admin Password: ******** LTP-16N#
Getting started with terminal CLI
CLI is the main means of communication between user and the terminal. This section describes general CLI procedures: information on grouping, autocomplete options, and command history is given.
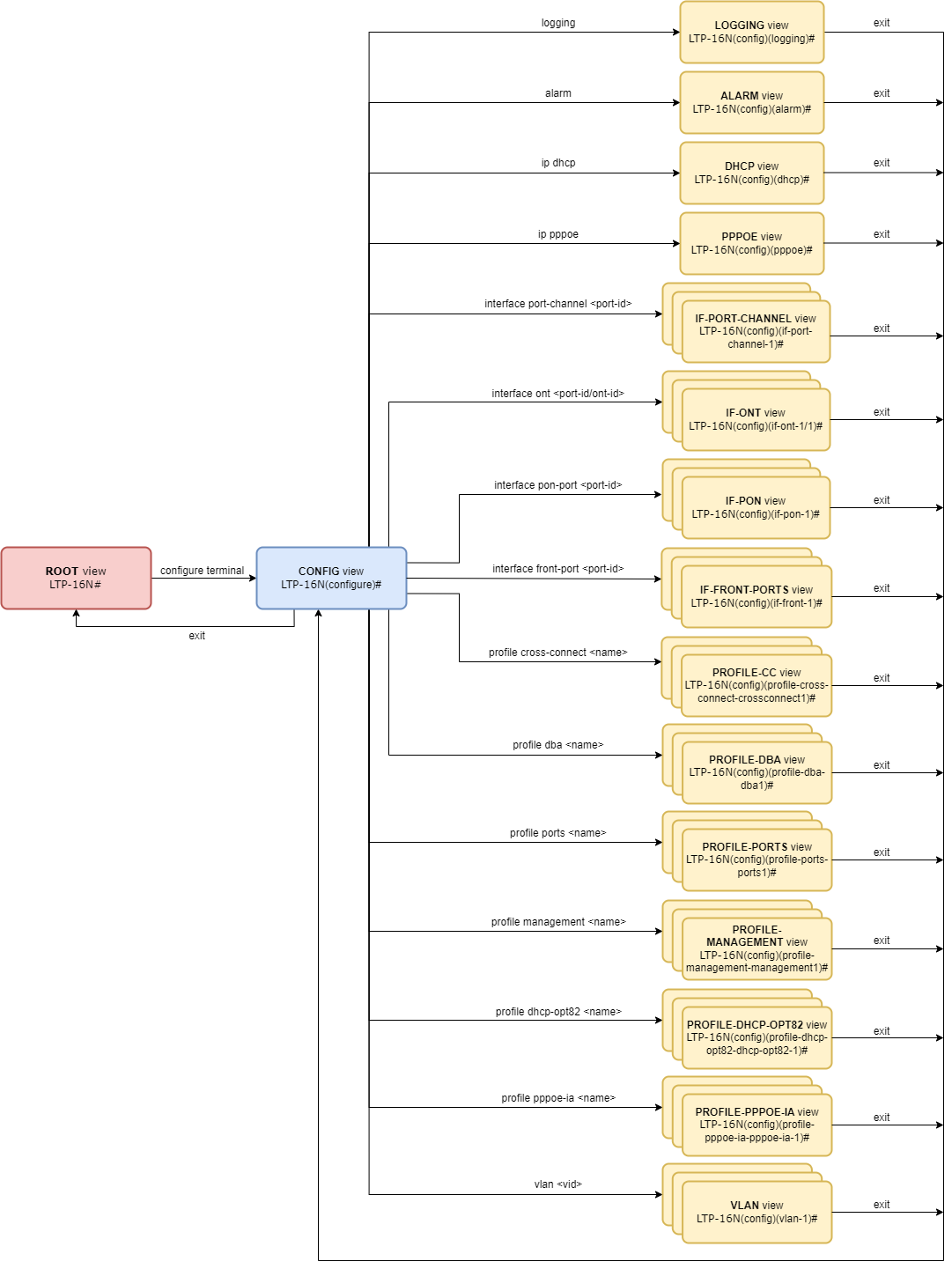
CLI views hierarchy
The command system of the LTP-16N Command Line Interface is divided into views. The transition between views is performed by commands. The exit command is used to return to the previous level. Some views are an array where a unique index must be used to access a specific object.
Figure 13 shows a graphic chart of main views and the commands to switch between them.
Figure 13 – CLI views hierarchy
CLI hotkeys
In order to speed up the operations with the command line, the following hotkeys have been added:
Table 9 – Command line hotkeys
Hotkey | Result |
|---|---|
Ctrl+A | Transition to the beginning of line |
Ctrl+D | In a nested command mode – exit to the previous command mode (exit command), in a root command mode – exit from CLI |
Ctrl+E | Transition to the end of line |
Ctrl+L | Screen clearing |
Ctrl+U | Removal of characters to the left of a cursor |
Ctrl+W | Removal of a word to the left of a cursor |
Ctrl+K | Removal of characters to the right of a cursor |
Ctrl+C | Line clearing, command execution interruption |
CLI automatic code completion
To simplify the use of the command line, the interface supports automatic command completion. This function is activated when the command is incomplete and the <Tab> character is entered.
For example, enter the ex command in the Top view and press <Tab>:
LTP-16N# ex<Tab> LTP-16N# exit
As this mode has only one command with the ex prefix, CLI automatically completes it.
If there are several commands with this prefix, CLI shows hints with possible options:
LTP-16N# co<Tab> commit configure copy LTP-16N# con<Tab> LTP-16N# configure
Group operations
Group operations can be performed on such terminal configuration objects as interfaces and ONTs. It is especially convenient when same actions have to be applied to multiple objects.
To perform a group operation, select the range of object IDs instead of one object ID. This feature is supported by a majority of CLI commands.
For example, enable broadcast-filter for all ONTs in a certain channel.
LTP-16N# configure LTP-16N(configure)# interface ont 1/1-128 LTP-16N(config)(if-ont-1/1-128)# broadcast-filter LTP-16N(config)(if-ont-1/1-128)#
View the list of active ones in the first 3 PON ports:
LTP-16N# show interface ont 1-3 online GPON-port 1 has no online ONTs GPON-port 2 has no online ONTs GPON-port 3 has no online ONTs Total ONT count: 0
Configuring the terminal
Terminal configuration
A collection of all terminal settings is referred to as configuration. This section provides information on the parts which configuration consists of. It also defines lifecycle of configuration and describes main operations, which can be performed.
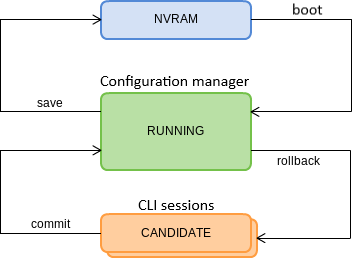
Configuration lifecycle
The terminal configuration may have the following states:
- Running – active configuration. It refers to the current configuration of the terminal.
- Candidate – configuration under review;
- NVRAM – configuration stored in non-volatile memory. This configuration will be used as RUNNING after the device is loaded.
The Running configuration is loaded to a new CLI session and becomes available for editing (Candidate). A different copy of the Candidate configuration is used for each session. After a configuration (Candidate) change in a CLI session, the user can issue a command to apply the changed configuration (the commit command). The save command saves the Running configuration into NVRAM of the terminal.
Figure 14 shows a chart of configuration lifecycle.
Figure 14 – Configuration lifecycle of the terminal chart
Configuration backup
Configuration backups allow the terminal operation to be quickly restored after abnormal situations or replacement. Regular manual backups of the configuration are recommended.
Uploading the terminal configuration is possible to a TFTP/FTP/HTTP server available in the management network. Uploading is carried out by the copy command. Specify as arguments that the fs://config terminal configuration is uploaded, as well as the destination URL.
LTP-16N# copy fs://config tftp://192.168.1.1/config Upload backup file to TFTP-server..
Configuration restore
The terminal configuration is restored from a TFTP/FTP/HTTP server available in the management network. Restoring is carried out by the copy command. Specify as arguments that the fs://config terminal configuration is uploaded, as well as the destination URL.
LTP-16N# copy tftp://10.0.105.1/config fs://config Download file from TFTP-server.. Reading of the configuration file.. Configuration have been successfully restored (all not saved changes was lost)
Configuration reset
To reset a terminal configuration to factory settings, use the default command. After running the command, the default configuration is applied as a Candidate and must be applied using the commit command.
LTP-16N# default
Do you really want to do it? (y/N) y
Configuration has been reset to default
LTP-16N# commit
Resetting a configuration of a remote terminal also resets network settings. The terminal will not be available for operation until the network settings are reconfigured.
Network settings
This section describes adjustment of network settings for the terminal. Adjusting network settings enables remote control and integration with OSS/BSS systems.
Network parameters configuration
It is recommended to adjust network settings via COM port connection. This will prevent issues with connection loss upstream the terminal being adjusted. Be very careful when using remote adjustment.
Step 1. Use the show running-config management command to view the current network settings.
LTP-16N# show running-config management all management ip 192.168.1.2 management mask 255.255.255.0 management gateway 0.0.0.0 management vid 1
Step 2. Enter the configure view. Set the terminal name by using the hostname command.
LTP-16N# configure terminal LTP-16N(configure)# system hostname LTP-16N-test
Step 3. Set the terminal IP address by using the management ip command.
LTP-16N(configure)# management ip 10.0.0.1
Step 4. Set the subnet mask by using the management netmask command.
LTP-16N(configure)# management mask 255.0.0.0
Step 5. Set the default gateway by using the management gateway command.
LTP-16N(configure)# management gateway 10.0.0.254
Step 6. Set the management VLAN of the terminal by using the management vid command if necessary.
LTP-16N(configure)# management vid 10
To operate with the device over the management interface via uplink ports, allow the management vid on the necessary ports.
When connecting to the OOB and the uplink port in management at the same time, a loop can be formed.
Step 7. The network settings will change as soon as the configuration is applied. No terminal reboot is needed.
LTP-16N(configure)# do commit
User management
This section describes the management of the terminal users.
The factory settings provide only one user, i.e. the device administrator.
login: admin
password: password
It is recommended to change the default password of the admin user at the initial stage of configuration.
For security reasons, there is a strictly defined set of permissions, which can be delegated to terminal users. For these purposes, each user gets his own privilege level. Level 0 corresponds to a minimum set of permissions, Level 15 — to a maximum set of permissions. Levels 1 to 14 are fully configurable. For ease of use, these levels are filled with default privileges.
The CLI commands are divided into access levels according to the block they change or let you view. Commands without access level (exit, !) are available to all users. Level 15 commands are available only to Level 15 users. Thus, the level of commands available to a user does not exceed the user's level.
Privilege configuration
Step 1. The default privilege allocation can be viewed by using the show running-config privilege all command.
privilege 6 commands-interface-ont privilege 6 commands-configuration privilege 6 commands-interface-gpon-port privilege 6 commands-interface-front-port privilege 7 view-igmp privilege 7 view-dhcp privilege 7 view-pppoe privilege 7 view-interface-ont privilege 7 view-interface-front-port privilege 7 view-configuration privilege 7 config-general privilege 8 view-igmp privilege 8 view-dhcp privilege 8 view-pppoe privilege 8 view-interface-front-port privilege 8 view-configuration privilege 8 config-vlan privilege 8 config-general privilege 8 config-interface-front-port privilege 8 commands-configuration privilege 9 view-igmp privilege 9 view-dhcp privilege 9 view-pppoe privilege 9 view-interface-ont privilege 9 view-interface-front-port privilege 9 view-configuration privilege 9 config-vlan privilege 9 config-general privilege 9 config-interface-gpon-port privilege 9 config-interface-ont privilege 9 config-interface-ont-profile privilege 9 config-interface-front-port privilege 9 commands-interface-ont privilege 9 commands-configuration privilege 9 commands-interface-gpon-port privilege 9 commands-interface-front-port privilege 10 view-igmp privilege 10 view-dhcp privilege 10 view-pppoe privilege 10 view-alarm privilege 10 view-system privilege 10 view-interface-ont privilege 10 view-interface-front-port privilege 10 view-configuration privilege 10 config-general privilege 11 view-igmp privilege 11 view-dhcp privilege 11 view-pppoe privilege 11 view-alarm privilege 11 view-system privilege 11 view-interface-ont privilege 11 view-interface-front-port privilege 11 view-configuration privilege 11 config-alarm privilege 11 config-general privilege 11 config-logging privilege 11 config-access privilege 11 config-cli privilege 11 commands-configuration privilege 12 view-igmp privilege 12 view-dhcp privilege 12 view-pppoe privilege 12 view-alarm privilege 12 view-system privilege 12 view-interface-ont privilege 12 view-interface-front-port privilege 12 view-configuration privilege 12 view-firmware privilege 12 config-vlan privilege 12 config-igmp privilege 12 config-dhcp privilege 12 config-pppoe privilege 12 config-alarm privilege 12 config-general privilege 12 config-logging privilege 12 config-interface-front-port privilege 12 config-access privilege 12 config-cli privilege 12 config-management privilege 12 commands-configuration privilege 13 view-igmp privilege 13 view-dhcp privilege 13 view-pppoe privilege 13 view-alarm privilege 13 view-system privilege 13 view-interface-ont privilege 13 view-interface-front-port privilege 13 view-configuration privilege 13 view-firmware privilege 13 config-vlan privilege 13 config-igmp privilege 13 config-dhcp privilege 13 config-pppoe privilege 13 config-alarm privilege 13 config-system privilege 13 config-general privilege 13 config-logging privilege 13 config-interface-gpon-port privilege 13 config-interface-ont privilege 13 config-interface-ont-profile privilege 13 config-interface-front-port privilege 13 config-access privilege 13 config-cli privilege 13 config-management privilege 13 commands-interface-ont privilege 13 commands-configuration privilege 13 commands-interface-gpon-port privilege 13 commands-general privilege 13 commands-interface-front-port privilege 15 view-igmp privilege 15 view-dhcp privilege 15 view-pppoe privilege 15 view-alarm privilege 15 view-system privilege 15 view-interface-ont privilege 15 view-interface-front-port privilege 15 view-configuration privilege 15 view-firmware privilege 15 config-vlan privilege 15 config-igmp privilege 15 config-dhcp privilege 15 config-pppoe privilege 15 config-alarm privilege 15 config-system privilege 15 config-general privilege 15 config-logging privilege 15 config-interface-gpon-port privilege 15 config-interface-ont privilege 15 config-interface-ont-profile privilege 15 config-interface-front-port privilege 15 config-access privilege 15 config-cli privilege 15 config-management privilege 15 config-user privilege 15 commands-interface-ont privilege 15 commands-configuration privilege 15 commands-copy privilege 15 commands-firmware privilege 15 commands-interface-gpon-port privilege 15 commands-license privilege 15 commands-general privilege 15 commands-system privilege 15 commands-interface-front-port
Step 2. Enter the configure view. Set the required permissions corresponding to the level by using the privilege command, e.g. set permissions allowing Level 1 to view configuration of the ONT.
LTP-16N# configure terminal LTP-16N(configure)# privilege 1 view-interface-ont
Step 3. Settings of privileges will be applied immediately. No terminal reboot is needed.
LTP-16N(configure)# do commit
User list preview
To view the list of terminal users, enter the show running-config user all command.
LTP-16N# show running-config user all user root encrypted_password $6$FbafrxAp$vY6mRGiEff9zGhaClnJ8muzM.1K1g86.GfW8rDv7mjOpcQcRptx7ZY//WTQDi9QxZSZUkOk02L5IHIZqDX0nL. user root privilege 15 user admin encrypted_password $6$lZBYels7$1sd.B2eherdxsFRFmzIWajADSMNbsL1fjO7PsVCTJJmpDHpz0gZmkX2rZlJhLgRzTvkDwQ1eqF3MwNQiKGwPz/ user admin privilege 15
The admin and root users always exist and cannot be deleted or duplicated. The terminal supports up to 16 users.
Adding a new user
In order to operate effectively and safely, the terminal, as a rule, requires one or several additional users. To add a new user, enter the user command in the configure view.
LTP-16N# configure terminal
LTP-16N(configure)# user operator
User operator successfully created
Pass the name of the new user as a parameter to the user command. The name should not be longer than 32 characters. The name should not contain special characters.
Changing user password
To change user password, enter the user command. Pass the user name and a new password as parameters. Default password is password. In the configuration, the password is stored in encrypted form.
LTP-16N(configure)# user operator password newpassword
User operator successfully changed password
LTP-16N(configure)#
The password should not be longer than 31 characters and shorter than 8 characters. If the password contains a space, use quotations for the password.
Viewing and changing user access rights
To manage user access rights, a user priority system is implemented. A newly created user is granted with a minimal set of permissions.
LTP-16N(configure)# do show running-config user user operator encrypted_password $6$mIwyhgRA$jaxkx6dATExGeT82pzqJME/eEbZI6c9rKWJoXfxLmWXx7mQYiRY0pRNdCupFsg/1gqPfWmqgc1yuR8J1g.IH20 user operator privilege 0
To change the user priority level, enter the user command. Pass the user name and a new priority as parameters.
LTP-16N(configure)# user operator privilege 15
User operator successfully changed privilege
LTP-16N(configure)# do show running-config user
user operator encrypted_password $6$mIwyhgRA$jaxkx6dATExGeT82pzqJME/eEbZI6c9rKWJoXfxLmWXx7mQYiRY0pRNdCupFsg/1gqPfWmqgc1yuR8J1g.IH20
user operator privilege 15
Deleting a user
To delete a user, enter the no user command in the configure view. Pass the user name as a parameter.
LTP-16N# configure terminal
LTP-16N(configure)# no user operator
User operator successfully deleted
Services configuration
This section describes configuration of integrated terminal services.
SNMPD configuration
For the terminal to work via SNMP, the appropriate service should be enabled.
Step 1. Enter the configure view.
LTP-16N# configure terminal
Step 2. Enable the SNMP agent of the terminal by using snmp enable command.
LTP-16N(configure)# ip snmp enable
Step 3. The settings of the SNMP agent change as soon as the configuration is applied. No terminal reboot is needed.
LTP-16N(configure)# do commit
Configure users to operate with SNMPv3.
Step 1. Add users and set the privilege levels.
LTP-16N(configure)# ip snmp user "rwuser" auth-password "rwpassword" enc-password "rwencrpass" access rw LTP-16N(configure)# ip snmp user "rouser" auth-password "ropassword" enc-password "roencrpass" access ro
Step 2. The settings of the SNMP agent change as soon as the configuration is applied. No terminal reboot is needed.
LTP-16N(configure)# do commit
Step 3. Check the configuration using the show running command.
LTP-16N# show running-config ip snmp ip snmp encrypted-user rwuser auth-password GP7dmbXhmcnoGFwUQ== enc-password QKw388vDx+PWTnoiUg= access rw ip snmp encrypted-user rouser auth-password +N02El5KMmJDs/e/w== enc-password uH+sCFAYHDgNlaH5ic= access ro ip snmp engine-id 55e3edafe1c7c92199c28b74b4
The SNMPv3 agent supports authNoPriv and authPriv methods. The encryption of the password performs according to the MD5 algorithm.
Step 4. Configure SNMP trap replication to allow the management system to receive the traps. For example, add 2 replicators and specify to send v2 SNMP traps to 192.168.1.11 and v1 traps to 192.168.1.12. To do this, use the ip snmp traps command.
It is possible to configure several receivers of SNMP traps of the same version.
LTP-16N(configure)# ip snmp traps 192.168.1.11 type v2 LTP-16N(configure)# ip snmp traps 192.168.1.12 type v1
Step 5. The settings of the SNMP agent change as soon as the configuration is applied. No terminal reboot is needed.
LTP-16N(configure)# do commit
Step 6.Check the configuration using the show running command.
LTP-16N# show running-config ip snmp ip snmp encrypted-user rwuser auth-password GP7dmbXhmcnoGFwUQ== enc-password QKw388vDx+PWTnoiUg= access rw ip snmp encrypted-user rouser auth-password +N02El5KMmJDs/e/w== enc-password uH+sCFAYHDgNlaH5ic= access ro ip snmp engine-id 55e3edafe1c7c92199c28b74b4 ip snmp traps 192.168.1.11 type v2 ip snmp traps 192.168.1.12 type v1
The types and purpose of SNMP traps are closely connected with the log of active alarms.
NTP configuration
For terminal to operate via NTP, it is necessary to configure the corresponding service.
Step 1. Enter the configure view.
LTP-16N# configure terminal
Step 2. Specify the NTP server that will be used for time synchronization by the ip ntp server command.
LTP-16N(configure)# ip ntp server 192.168.1.10
The ip ntp enable cannot be executed without first specifying an NTP server.
Step 3. Set the synchronization interval in seconds by the ip ntp interval command.
LTP-16N(configure)# ip ntp interval 4096
Minimum interval is 8 seconds, maximum interval is 65536 seconds.
Step 4. Set the time zone for your region by the ip ntp timezone command.
LTP-16N(configure)# ip ntp timezone hours 7 minutes 0
Hours can be set from -12 to 12, minutes — from 0 to 59.
Step 5. Enable NTP service by the ip ntp enable command.
LTP-16N(configure)# ip ntp enable
Step 6. NTP agent parameters will change immediately after the configuration is applied. No terminal reboot is needed.
LTP-16N(configure)# do commit
Step 7. Check the configuration by the show running ip ntp command.
LTP-16N# show running-config ip ntp ip ntp enable ip ntp server 192.168.1.5 ip ntp interval 16 ip ntp timezone hours 7 minutes 0
Daylight saving time configuration
Step 1. Enter the configure view.
LTP-16N# configure terminal
Step 2. Configure daylight saving time by ip ntp daylightsaving start and ip ntp daylightsaving end commands.
ip ntp daylightsaving start — start of daylight saving time.
ip ntp daylightsaving end — end of daylight saving time.
Both commands have a similar structure. Start and end dates for daylight saving time can be set with a fixed date or a floating date. After entering the month, the user will be given the option to select the type of transition date for each of the settings:
day — parameter that sets a specific date as a day of the month (from 1 to 31).
week and weekday — parameters that specify a floating date that varies depending on the year. The week parameter is ordinal number of the week in a month. May take the following values: First, Second, Third, Fourth, Last. The weekday parameter specifies the day of the week.
LTP-16N(configure)# ip ntp daylightsaving start month March week Last weekday Sunday start-hours 1 start-minutes 00 LTP-16N(configure)# ip ntp daylightsaving end month October day 30 end-hours 1 end-minutes 00
After entering these commands, the transition to daylight saving time will be carried out annually at 1 am on the last Sunday in March, and back at 1 am on October 30th.
Step 3. The daylight saving time settings will change immediately after the configuration is applied. No terminal reboot is needed.
LTP-16N(configure)# do commit
The ip ntp daylightsaving start and ip ntp daylightsaving end settings of daylight saving time start and end cannot be applied separately. These settings only work in conjunction.
The difference between ip ntp daylightsaving start and ip ntp daylightsaving end daylight saving time start and end should not be less than an hour.
Step 4. Check the configuration by show running ip ntp command.
LTP-16N# show running-config ip ntp ip ntp daylightsaving start month March week Last weekday Sunday start-hours 1 start-minutes 0 ip ntp daylightsaving end month October day 30 end-hours 1 end-minutes 0
LOGD configuration
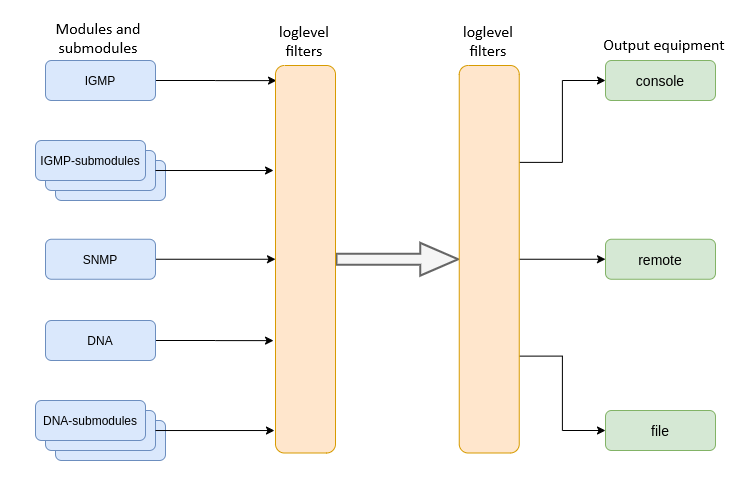
System log collects terminal history data and allows its further display. Adjustment of system log operates with such terms as module, filter level, and output device.
Figure 15 – Terminal system log
Messages of the system log are grouped into modules according to their functions. Configuration of the following modules is possible:
Table 10 – System log modules
Module | Description |
|---|---|
cli | CLI module service messages |
snmp | Messages from the SNMP agent |
dna | Primary network module messages |
fsm-pon | PON state machine messages |
igmp | Messages from IGMP operation module |
logmgr | Log control module service messages |
usermgr | Log control module service messages |
| dhcp | Service messages by DHCP module |
| pppoe | Service messages by PPPoE module |
| lldp | Service messages by LLDP module |
For more flexible logging configuration, the level of filtering, as well as sub-module settings, can be selected for each module.
The filtering level sets the minimum importance level of the messages to be displayed in the log. The used filtering levels are listed in Table 11.
Table 11 – System log filtering levels
Level | Description |
|---|---|
critical | Critical events |
error | Operation errors |
warning | Warnings |
notice | Important events during normal operation. Default values for all modules |
info | Information messages |
debug | Debug messages |
The critical level is the maximum level, the debug level is the minimum one.
The log subsystem allows display of the terminal operation log on different devices. All output devices can be used simultaneously.
Table 12 – System log output devices
Output device | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
System log | system | The system log allows the log to be displayed locally or with the help of the syslog server. |
Console | console | Being used for log display, the console allows system messages to be visible as soon as they are received in the terminal connected to the Console port. |
File | file | Logging into a file allows system messages to be written directly to the file, which can be sent to support specialists for further analysis. |
The log is saved in non-volatile memory by default. The system has 3 log rotated files of 1M each.
Module configuration
Consider the configuration using the dna module and the ont sub-module, which is responsible for displaying logs for the ONT. Other modules have similar configuration process.
Step 1. Enter the logging view.
LTP-16N(configure)# logging
Step 2. Set the level of log display with the ONT index for which the logs will be displayed. To do this use the module dna <port-id>[/ont-id] loglevel command.
LTP-16N(config)(logging)# module dna interface ont 1/1 loglevel debug
Step 3. Apply the configuration by using the commit command.
LTP-16N(config)(logging)# do commit
Configuring the log storage
Use the following command to record logs to non-volatile memory:
LTP-16N(config)(logging)# permanent
If you enter "no" before the command, the logs will be recorded to RAM. In this case, the logs will be erased after reboot.
System log configuration
Step 1. Use the file size command to specify the memory size in bytes to be used for system log storage.
LTP-16N(config)(logging)# file size 30000
Step 2. If necessary, use the remote server ip command to specify the IP address of the remote SYSLOG server to be used to display system log.
LTP-16N(config)(logging)# remote server ip 192.168.1.43
Step 3. Configure the output devices by using the logging command.
Each output device may have its own filtering level or have the output disabled.
For example, enable the display of debug messages to a file and to a remote service:LTP-16N(config)(logging)# remote loglevel debug LTP-16N(config)(logging)# file loglevel debug
Step 5. Apply the configuration by using the commit command.
LTP-16N(config)(logging)# do commit
Step 6. To view SYSLOG configuration information, use the do show running-config logging command.
LTP-16N(config)(logging)# do show running-config logging logging module dna ont 1/1 loglevel debug permanent file size 30000 file loglevel debug remote server ip 192.168.1.43 remote loglevel debug exit
ALARMD configuration
ALARMD is a terminal alarms manager. Alarms manager enables troubleshooting and provides information about important events related to terminal operation.
A record in active alarms log (an event) corresponds to an event, which happened in the terminal. Types of events and their descriptions are provided in the following table.
Table 13 – Types of events in the active alarms log
Event | Description | Threshold |
|---|---|---|
system-ram | Free RAM size decreased to the threshold | 12% 1 |
system-login | User tried to log in or logged in using their credentials | - |
system-logout | User logged out | - |
config-save | User saved the configuration | - |
config-change | OLT configuration changed | - |
system-load-average | Average CPU load reached the threshold, estimated time is 1 minute | 0 1 |
system-temperature | Temperature of one of the four temperature sensors has exceeded the threshold | 70 1 |
system-fan | Fan rotation speed exceeded the safe operating limits | 2000 < X < 12000 1 |
pon-alarm-los | Translation of Loss of Signal PLOAM alarms | - |
pon-alarm-lofi | Translation of Loss of Frame PLOAM alarms from ONT | - |
pon-alarm-loami | Translation of PLOAM loss PLOAM alarms from ONT | - |
pon-alarm-dowi | Translation of Drift of Window PLOAM alarms from ONT | - |
pon-alarm-sdi | Translation of Signal Degraded PLOAM alarms from ONT | - |
pon-alarm-sufi | Translation of Start-up Failure PLOAM alarms from ONT | - |
pon-alarm-loai | Translation of Loss of Acknowledge PLOAM alarms from ONT | - |
pon-alarm-dgi | Translation of Dying-Gasp PLOAM alarms from ONT | - |
pon-alarm-dfi | Translation of Deactivate Failure PLOAM alarms from ONT | - |
pon-alarm-tiwi | Translation of Transmission Interference Warning PLOAM alarms from ONT | - |
pon-alarm-loki | Translation of Loss of Key PLOAM alarms from ONT | - |
pon-alarm-lcdgi | Translation of Loss of GEM Channel Delineation PLOAM alarms from ONT | - |
pon-alarm-rdii | Translation of Remote Defect Indication PLOAM alarms from ONT | - |
1 The value can be adjusted.
Every record in the active alarms log has the parameters specified in Table 14 that are specified for each event type.
Table 14 – Parameters of events in the active alarms log
Token | Description |
|---|---|
severity | Describes event severity. Has four states:
|
in | Specifies whether an SNMP trap should be sent when an event is added to the log. Has two states:
|
out | Specifies whether an SNMP trap should be sent when an event is deleted from the log (normalization). Has two states: |
| ttl | Alarm lifetime in seconds. There are special options:
|
Active alarms log configuration
Step 1. To configure the active alarm log, go to configure view and then to alarm view.
LTP-16N# configure terminal LTP-16N(configure)# alarm LTP-16N(config)(alarm)#
Step 2. For example, configure the alarm system-fan. To do this use the system-fan command. The other alarms are configured similarly.
LTP-16N(config)(alarm)# system-fan min-rpm 5000 LTP-16N(config)(alarm)# system-fan severity critical LTP-16N(config)(alarm)# system-fan in true
Step 3. Apply the changes by using the do commit command.
LTP-16N(config)(alarm)# do commit
AAA configuration
This section describes the procedure for configuring services and protocols related to authentication, authorization, and accounting.
For AAA operation, RADIUS and TACACS+ protocols are supported. Table 15 lists these protocols functionality.
Table 15 – RADIUS and TACACS+ functionality
| Functionality and a protocol | TACACS+ | RADIUS |
|---|---|---|
| Authentication | + | + |
| Authorization | + | - |
| CLI session start and end accounting (accounting start-stop) | + | - |
| CLI commands accounting (accounting commands) | + | - |
For supported protocols, server configuration principles are common. For each server, the following can be configured:
- IP address;
- key;
- timeout;
- port for connection to a server.
Up to 3 servers can be specified for RADIUS. They will be accessed according to the specified priority. If the priority is not specified, then the first priority, which is the highest, will be used by default.
Step 1. Set RADIUS/TACACS+ server IP address and specify authentication and authorization via TACACS+. Authentication and authorization will be executed through the specified servers, the privilege level for the user is specified through the TACACS+ server.
LTP-16N# configure terminal LTP-16N(configure)# aaa LTP-16N(config)(aaa)# tacacs-server host 192.168.1.1 LTP-16N(config)(aaa)# tacacs-server host 192.168.1.2 LTP-16N(config)(aaa)# tacacs-server host 192.168.1.3 LTP-16N(config)(aaa)# authentication tacacs+ LTP-16N(config)(aaa)# authorization tacacs+ privilege LTP-16N(config)(aaa)# enable
Step 2. Set the encryption key used when communicating with the server.
LTP-16N(config)(aaa)# tacacs-server host 192.168.1.1 key 1234567-r0 LTP-16N(config)(aaa)# tacacs-server host 192.168.1.2 key 1234567-r1 LTP-16N(config)(aaa)# tacacs-server host 192.168.1.3 key 1234567-r2
Step 3. Set the time to wait for the server to respond.
LTP-16N(config)(aaa)# tacacs-server timeout 3
Step 4. Set the port to use to connect to the server (if necessary).
LTP-16N(config)(aaa)# tacacs-server host 192.168.1.2 port 444
Step 5. Apply changes.
LTP-16N(config)(aaa)# do commit
VLAN configuration
This section describes VLAN configuration.
VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network) is a group of devices, which communicate on the channel level and are combined into a virtual network, connected to one or more network devices (GPON terminals or switches). VLAN is a very important tool for creating a flexible and configurable logical network topology over the physical topology of a GPON network.
Step 1. To configure VLAN, go to the configure view.
LTP-16N# configure terminal LTP-16N(configure)#
Step 2. Enter the VLAN configuration mode with the vlan command. Pass VID as a parameter.
LTP-16N(configure)# vlan 5 LTP-16N(config)(vlan-5)#
VLAN configuration
To configure VLAN permission on interfaces, see Interface configuration.
Step 1. For convenience, specify a VLAN name by using the name command. To clear the name, use the no name command.
LTP-16N(config)(vlan-5)# name IpTV
Step 2. If you need to process IGMP packets on a specified VLAN, use the ip igmp snooping enable command to enable IGMP-snooping.
LTP-16N(config)(vlan-5)# ip igmp snooping enable
Step 3. Configure the IGMP querier if needed. It can be enabled with the help of the ip igmp snooping querier enable command.
The fast-leave mode is enabled by means of the ip igmp snooping querier fast-leave command. By default, this mode is disabled.
DSCP and 802.1P marking for IGMP query is configured by means of the ip igmp snooping querier user-prio and ip igmp snooping querier dscp commands.LTP-16N(config)(vlan-5)# ip igmp snooping querier enable LTP-16N(config)(vlan-5)# ip igmp snooping querier fast-leave LTP-16N(config)(vlan-5)# ip igmp snooping querier dscp 40
Step 4. Configure IGMP if needed.
Compatible versions (v1, v2, v3, or their combination):
LTP-16N(config)(vlan-5)# ip igmp version v2-v3
Interval between queries:
LTP-16N(config)(vlan-5)# ip igmp query-interval 125
Maximum query response time:
LTP-16N(config)(vlan-5)# ip igmp query-response-interval 10
Interval between Group-Specific Queries:
LTP-16N(config)(vlan-5)# ip igmp last-member-query-interval 1
Robustness:
LTP-16N(config)(vlan-5)# ip igmp robustness 2
Step 5. Apply the configuration by using the commit command.
LTP-16N(config)(vlan-5)# do commit
VLAN deletion
Step 1. Delete a VLAN by using the no vlan command. Pass VID (or its range) as a parameter.
LTP-16N(configure)# no vlan 5
Step 2. Apply the configuration by using the commit command.
LTP-16N(configure)# do commit
IGMP configuration
This section describes general IGMP configuration.
Enabling snooping
Step 1. The global snooping configuration is performed in the configure view.
LTP-16N# configure terminal LTP-16N(configure)#
Step 2. Enable IGMP snooping by using the ip igmp snooping command.
LTP-16N(configure)# ip igmp snooping enable
Step 3. Apply the configuration by using the commit command.
LTP-16N(configure)# do commit
Report proxying
Step 1. Proxying is configured in configure view.
LTP-16N# configure terminal LTP-16N(configure)#
Step 2. Enable IGMP report proxying between VLAN by the ip igmp proxy report enable command.
LTP-16N(configure)# ip igmp proxy report enable
Step 3. Set IGMP report proxying rules by the ip igmp proxy report range command. As parameters, specify the range of allowed groups, as well as the direction of proxying as a pair of VIDs. It is possible to set general proxy rules for all VLANs, for this use the from all keyword.
LTP-16N(configure)# ip igmp proxy report range 224.0.0.1 226.255.255.255 from 30 to 90
Step 4. Apply the configuration by using the commit command.
LTP-16N(configure)# do commit
IGMP Proxy cannot be enabled without specifying a proxy range. Both settings are required.
DHCP configuration
This section describes the procedure for operating the terminal with the DHCP. The operation of the protocol can be divided into blocks:
- DHCP snooping. Used to intercept DHCP traffic, control and monitor sessions.
- DHCP opt82. Functionality to insert service option 82 in DHCP packets.
- DHCP relay. Functionality to redirect DHCP to another subnet.
DHCP snooping
This functionality is used to intercept and process traffic on the terminal CPU.
Currently, this functionality must be enabled if you want to control and monitor DHCP sessions and to operate with option 82 in DHCP packets.
DHCP snooping enabling
Step 1. The global snooping configuration is performed in the ip dhcp view, section configure view.
LTP-16N# configure terminal LTP-16N(configure)# ip dhcp LTP-16N(config)(dhcp)#
Step 2. Enable DHCP snooping using the snooping enable command.
LTP-16N(config)(dhcp)# snooping enable
DHCP option 82
DHCP option 82 is used to provide a DHCP server with additional information about a received DHCP request. This may include information about the terminal running DHCP option 82 as well as information about the ONT which sent the DHCP request. DHCP packets are modified by interception and further processing in the terminal CPU, i.e. DHCP snooping must be enabled.
The DHCP server analyses DHCP option 82 and identifies the ONT. Terminal allows the option to be both transparently transmitted from the ONT and formed/rewritten according to a specified format. DHCP option 82 is especially useful for networks, which have no private VLANs dedicated for each user.
DHCP option 82 supports configurable formats for both Circuit ID and Remote ID. The format of the suboptions is configured with the help of the tokens listed in Table 16. The placeholders will be replaced with corresponding values, while the rest of the words will be passed as is.
Table 16 – List of tokens for configuring the DHCP option 82 suboption format
Token | Description |
|---|---|
%HOSTNAME% | Terminal network name |
%MNGIP% | Terminal IP address |
%GPON-PORT% | Number of the OLT channel the DHCP request arrived from |
%ONTID% | ID of the ONT, which sent the DHCP request |
%PONSERIAL% | Serial number of the ONT, which sent the DHCP request |
%GEMID% | ID of the GEM port the DHCP request arrived to |
%VLAN0% | External VID |
%VLAN1% | Internal VID |
%MAC% | MAC address of the ONT, which sent the request |
%OLTMAC% | OLT`s MAC address |
%OPT60% | DHCP option 60 received from the ONT |
%OPT82_CID% | Circuit ID received from the ONT |
%OPT82_RID% | Remote ID received from the ONT |
%DESCR% | First 20 characters of ONT description |
DHCP option 82 management
The DHCP option 82 is configured via the profile system – profile dhcp-opt82. The system allows creating several different profiles and assigning them not only globally to all DHCP packets in general, but also separating profiles by VLAN.
Step 1.Create DHCP option 82 profile using the profile dhcp-opt82 command. Pass profile name as a parameter.
LTP-16N# configure terminal LTP-16N(configure)# profile dhcp-opt82 test LTP-16N(config)(profile-dhcp-opt82-test)#
Step 2. Assign the global profile, using the opt82 profile command in ip dhcp view.
LTP-16N(configure)# ip dhcp LTP-16N(config)(dhcp)# opt82 profile test
Step 3. Assign another profile to the VLAN if needed.
LTP-16N(config)(dhcp)# opt82 profile test_vlan_100 vid 100
Step 4. Enable DHCP packet capture using the snooping enable command.
LTP-16N(config)(dhcp)# snooping enable
Step 5. Apply the configuration using the commit command.
LTP-16N(config)(dhcp)# do commit
DHCP option 82 profile configuration
Step 1. Create or switch to dhcp-opt82 profile.
LTP-16N# configure terminal LTP-16N(configure)# profile dhcp-opt82 test LTP-16N(config)(profile-dhcp-opt82-test)#
Step 2. Enable insert/overwrite of DHCP option 82 with the help of the overwrite-opt82 command if needed.
LTP-16N(config)(profile-dhcp-opt82-test)# overwrite-opt82 enable
Step 3. Set the DHCP option 82 format with the circuit-id and remote-id commands if necessary. A list of possible tokens is given in Table 15.
LTP-16N(config)(profile-dhcp-opt82-test)# circuit-id format %PONSERIAL%/%ONTID% LTP-16N(config)(profile-dhcp-opt82-test)# remote-id format %OPT82_RID%
Step 4. Apply the configuration by using the commit command.
LTP-16N(config)(dhcp)# do commit
DHCP relay
The DHCP relay functionality is a relay of DHCP packets from a client network through a routed network to a DHCP server.
DHCP-Relay works only through the management VLAN. The DHCP server is in one OLT-managed VLAN, and the subscriber traffic is in another. With this scheme of operation, DHCP broadcast requests from the client VLAN are transferred to the management VLAN and sent as unicast.
DHCP Relay configuration
Step 1. Go to DHCP settings.
LTP-16N# configure terminal LTP-16N(configure)# LTP-16N(configure)# ip dhcp LTP-16N(config)(dhcp)#
Step 2. Enable DHCP snooping. Snooping can be activated for all VLANs or for the necessary ones. In case with relay, it should be client (100) and management (200) VLAN.
LTP-16N(config)(dhcp)# snooping enable vlan 100,200
Step 3. Enable DHCP relay.
LTP-16N(config)(dhcp)# relay enable
Step 4. Specify servers address and client VLAN, from which the redirect will take place. Several servers can be specified, then redirection will be made to all servers at once, but the session will be built only through the first responder.
LTP-16N(config)(dhcp)# relay server-ip 192.168.200.5 vid 100 LTP-16N(config)(dhcp)# relay server-ip 192.168.200.200 vid 100
Step 5. Apply the configuration by using the commit command.
LTP-16N(config)(dhcp)# do commit
Active DHCP leases monitoring
When enabled, DHCP snooping allows monitoring of DHCP leases. To view the list of sessions use the show ip dhcp sessions command:
LTP-16N# show ip dhcp sessions
DHCP sessions (2):
## Serial GPON-port ONT-ID Service IP MAC Vid GEM Life time
---- ------------ --------- ------ ------- --------------- ----------------- --- ---- ---------
1 ELTX6C000090 1 1 1 192.168.101.75 E0:D9:E3:6A:28:F0 100 129 3503
2 ELTX71000030 1 3 1 192.168.101.143 70:8B:CD:BD:A5:32 100 189 3597
LTP-16N#
PPPoE configuration
This section describes the terminal operating procedure with the PPPoE. The operation of the protocol can be divided into two blocks:
- PPPoE snooping. Used to intercept PPPoE traffic, control and monitor PPPoE sessions.
- PPPoE intermediate agent. Functionality for inserting service information into PPPoE packets.
PPPoE snooping
This functionality is used to intercept and process traffic on the terminal CPU.
Currently, this functionality must be enabled if you want to control and monitor PPPoE sessions and to operate with option 82 in packets.
PPPoE snooping enabling
Step 1. The global snooping configuration is performed in the ip pppoe view, which in turn is in the configure view.
LTP-16N# configure terminal LTP-16N(configure)# ip pppoe LTP-16N(config)(pppoe)#
Step 2. Enable PPPoE snooping using the snooping enable command.
LTP-16N(config)(pppoe)# snooping enable
PPPoE intermediate agent
PPPoE Intermediate Agent is used to provide BRAS with additional information about a received PADI request. This may include information about the terminal running PPPoE Intermediate Agent as well as information about the ONT, which sent the PADI request. PADI packets are modified by interception and further processing in the terminal CPU.
BRAS analyses the Vendor Specific tag and identifies the ONT. PPPoE Intermediate Agent forms or rewrites the Vendor Specific tag using a specified format. Vendor Specific tags are especially useful for networks, which have no private VLANs dedicated for each user. PPPoE Intermediate Agent supports configurable formats for Circuit ID and Remote ID. The format of the suboptions is configured with the help of the tokens listed in Table 17. The placeholders will be replaced with corresponding values, while the rest of the words will be passed as is.
Table 17 – List of tokens to configure the PPPoE Intermediate Agent suboption format
Token | Description |
|---|---|
%HOSTNAME% | Terminal network name |
%MNGIP% | Terminal IP address |
%GPON-PORT% | Number of the OLT channel the PADI request arrived from |
%ONTID% | ID of the ONT, which sent the PADI request |
%PONSERIAL% | Serial number of the ONT, which sent the PADI |
%GEMID% | ID of the GEM port the PADI request arrived to |
%VLAN0% | External VID |
%VLAN1% | Internal VID |
%MAC% | MAC address of the ONT, which sent the request |
%OLTMAC% | MAC address of the OLT |
%DESCR% | First 20 characters of ONT description |
PPPoE Intermediate Agent management
The PPPoE Intermediate Agent is configured through the profile system – profile pppoe-ia. The system allows creating several different profiles and assign them globally to all PPPoE traffic.
Step 1. Create the PPPoE Intermediate Agent profile using the profile pppoe-ia command. Pass profile name as a parameter.
LTP-16N# configure terminal LTP-16N(configure)# profile pppoe-ia test LTP-16N(config)(profile-pppoe-ia-test)#
Step 2. Assign the global profile using the pppoe-ia profile command in ip pppoe view.
LTP-16N(configure)# ip pppoe LTP-16N(config)(pppoe)# pppoe-ia profile test LTP-16N(config)(pppoe)#
Step 3. Enable PPPoE packet capture using the snooping enable command.
LTP-16N(config)(pppoe)# snooping enable
Step 4. Apply the configuration using the commit command.
LTP-16N(config)(pppoe)# do commit
PPPoE Intermediate Agent profile configuration
Step 1. Create or switch to pppoe-ia profile.
LTP-16N# configure terminal LTP-16N(configure)# profile pppoe-ia test LTP-16N(config)(profile-pppoe-ia-test)#
Step 2. Set the PPPoE Intermediate Agent format with the circuit-id and remote-id commands if necessary. A list of possible tokens is given in Table 16.
LTP-16N(config)(profile-pppoe-ia-test)# circuit-id format %PONSERIAL%/%ONTID% LTP-16N(config)(profile-pppoe-ia-test)# remote-id format %GEMID%
Step 3. Apply the configuration by using the commit command.
LTP-16N(config)(pppoe-ia)# do commit
Active PPPoE sessions monitoring
When PPPoE snooping is enabled, sessions can be monitored. To view the list of sessions use the show ip pppoe sessions command:
LTP-16N(config)(pppoe)# do show ip pppoe sessions PPPoE sessions (1): ## Serial GPON-port ONT ID GEM Client MAC Session ID Duration Unblock ---- ------------ --------- ------ ---- ----------------- ---------- --------- --------- 1 ELTX6C000090 1 1 129 E0:D9:E3:6A:28:F0 0x0001 0:06:00 0:00:00
Interface configuration
This section describes configuration of terminal interfaces.
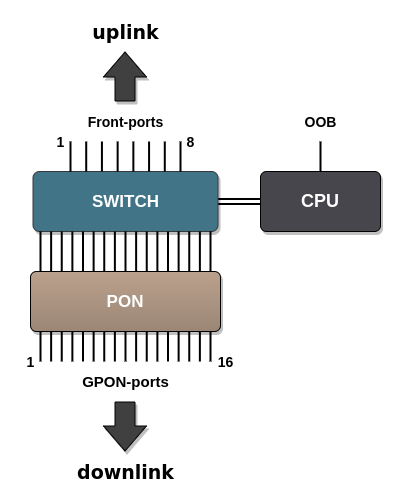
Terminal interfaces can be divided into three groups:
- front-ports – to connect the OLT to the operator's core network;
GPON-ports – to connect ONT;
OOB – to manage and configure the OLT.
Figure 16 – Set of terminal interfaces
Table 18 lists types of terminal switch interfaces.
Table 18 – Interfaces types and numbers
Interface | Quantity | Range |
|---|---|---|
front-port | 8 | [1..8] |
pon-port | 16 | [1..16] |
oob | 1 | - |
front-ports configuration
Step 1. Enter the view of the interface (of interface group) settings of which to be changed.
LTP-16N# configure terminal LTP-16N(configure)# interface front-port 1 LTP-16N(config)(if-front-1)#
Step 2. Enable the interface by using the no shutdown command. The shutdown command disables the interface.
LTP-16N(config)(if-front-1)# shutdown
Step 3. Set the list of allowed VLANs on the port, using the vlan allow command.
LTP-16N(config)(if-front-1)# vlan allow 100,200,300
Step 4. Apply the configuration by using commit command.
LTP-16N(config)(if-front-1)# do commit
PON interfaces configuration
Step 1. Enter the view of the interface (of interface group), which settings should be changed.
LTP-16N# configure terminal LTP-16N(configure)# interface pon-port 13 LTP-16N(config)(if-pon-13)#
Step 2. Enable or disable interfaces with the no shutdown or shutdown command respectively if necessary.
LTP-16N(config)(if-pon-13)# shutdown
Step 3. Apply the configuration by using the commit command.
LTP-16N(config)(if-pon-13)# do commit
LAG configuration
This section describes configuration of uplink interfaces aggregation. Link aggregation (IEEE 802.3ad) is a technology that allows multiple physical links to be combined into one logical link (aggregation group). Aggregation group has a higher throughput and is very reliable.
The terminal supports one mode of interface aggregation – static. All communication channels in the group are always active.
Balancing configuration
It is possible to configure parameters for traffic balancing functions in port-channel. It is possible to configure the polynomial to be used in the interface selection function with the interface port-channel load-balance polynomial command. You can also configure which of the header fields will be used in calculations. Possible options: src-mac, dst-mac, vlan, ether-type. It is allowed to use a combination of up to 3 fields.
LTP-16N# configure terminal LTP-16N(configure)# interface port-channel load-balance hash src-mac dst-mac vlan LTP-16N(configure)# interface port-channel load-balance polynomial 0x9019
Port-channel configuration
Step 1. Create an interface port-channel and pass the index as a parameter.
LTP-16N# configure terminal LTP-16N(configure)# interface port-channel 1 LTP-16N(config)(if-port-channel-1)#
Step 2. The port-channel settings are mostly similar to the front-port settings. For example, allow VLANs passing:
LTP-16N(config)(if-port-channel-1)# vlan allow 100,200,300
Step 3. Apply the configuration by using the commit command.
LTP-16N(config)(if-port-channel-1)# do commit
Adding ports to port-channel
Step 1.To aggregate ports in a port-channel, go to the ports to be aggregated:
LTP-16N(configure)# interface front-port 3-4 LTP-16N(config)(if-front-3-4)#
Step 2. Set the port-channel on the interfaces using the channel-group command
LTP-16N(config)(if-front-3-4)# channel-group port-channel 1
Interface and port-channel configurations should be the same. If the configurations are different, an error will occur when trying to aggregate the interfaces. If you want to force the aggregation, you can use the force option for the channel-group command. In this case, the interfaces will be configured from the port-channel and the current configuration will be reset.
An interface can belong to only one aggregation group.
Step 3. Apply the configuration by using the commit command.
LTP-16N(config)(if-front-3-4)# do commit
After changing the port-channel settings, the terminal will be automatically reconfigured. There may be a temporary stoppage of services.
LLDP configuration
Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP) — link layer protocol, which allows network devices advertising their identity, capabilities, as well as gathering this information about neighboring devices. There is support for standard RFC mib 1.0.8802 in SNMP agent.
Global LLDP configuration
Step 1. Global LLDP settings are located in configure view. Go to this section by using configure terminal command.
LTP-16N# configure terminal LTP-16N(configure)#
Step 2. Enable LLDP processing by using lldp enable command.
LTP-16N(configure)# lldp enable
Step 3. Specify how often the device will send LLDP information updates.
LTP-16N(configure)# lldp timer 10
Step 4. Set the amount of time for the receiving device to hold received LLDP packets before dropping them. This value is sent to the received side in LLDP update packets and is a multiplicity for a LLDP timer (lldp timer). Thus, the lifetime of LLDP packets is calculated by the formula:
TTL = min(65535, LLDP-Timer * LLDP-HoldMultiplier)
LTP-16N(configure)# lldp hold-multiplier 5
Step 5. Apply the configuration by using the commit command.
LTP-16N(configure)# do commit
LLDP configuration for interfaces
Step 1. Configuring LLDP on interfaces in corresponding interface-front-port view. Go to the interfaces section for which LLDP needs to be configured.
LTP-16N# configure terminal LTP-16N(configure)# interface front-port 1-3 LTP-16N(config)(if-front-1-3)#
Step 2. Change the port operation mode from LLDP, if necessary.
LTP-16N(config)(if-front-1-3)# lldp mode transmit-receive
Step 3. Set optional parameters to be sent in LLDP packets:
LTP-16N(config)(if-front-1-3)# lldp optional-tlv system-name port-description
Step 4. Apply the configuration by using the commit command.
LTP-16N(config)(if-front-1-3)# do commit
IP source-guard configuration
IP source-guard allows limiting an unauthorized use of IP addresses on the network by binding source IP and MAC addresses to a specific service on a specific ONT. There are two operation modes:
- Static –to pass any traffic from the client, explicitly set the IP and MAC addresses of the client equipment.
- Dynamic – obtaining an address by client equipment via DHCP protocol. Based on the exchange of client equipment with the DHCP server, a DHCP snooping table containing the MAC-IP-GEM-port correspondence as well as information about the lease time is formed on the OLT. Only those packets from the client are allowed, in which the "MAC source" and "IP source" fields match the entries in the DHCP snooping table. To ensure the operation of client equipment, the IP address of which was set statically, it is possible to create static entries in dynamic mode.
For IP source-guard operation, enable DHCP snooping on this VLAN. For more information, see the DHCP snooping section.
Step 1. Enable IP source-guard.
LTP-16N# configure terminal LTP-16N(configure)#ip source-guard enable
The ip source-guard enable command enables agent operation for all VLANs. If IP source-guard operation is needed only in a certain VLAN, then enable the agent only for this VLAN.LTP-16N(configure)#ip source-guard enable vlan 100
Step 2. Apply the configuration by using the commit command.
LTP-16N(configure)# do commit
The following command is used to enable a DHCP session to be re-established for a device with the same MAC address:
LTP-16N(configure)# ip source-guard one-dynamic-binding-for-mac enable
It will automatically overwrite an old session with a new one.
The following command is used to add static bindings:
LTP-16N(configure)# ip source-guard bind ip <IP> mac <MAC> interface-ont <ONT> service <NUM>
where:
- IP – IP address of client equipment in Х.Х.Х.Х format;
- MAC – MAC address of client equipment in ХХ:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX format;
- ONT – ONT ID in X/Y format (CNANNEL_ID/ONT_ID);
- NUM – service number on the ONT through which traffic with specified addresses in the range 1-30 will pass.
Use the show command to view status, mode, and static binding information:
LTP-16N# show ip source-guard binds
By default, the dynamic mode is used – dynamic and static entries work simultaneously. If only static entries are needed, configure the following:
LTP-16N(configure)# ip source-guard mode static
Port mirroring configuration
Port mirroring allows you to duplicate the traffic on monitored ports by forwarding incoming and/or outgoing packets to the controlling port. The user has the ability to set the controlling and controlled ports and select the type of traffic (inbound and/or outbound) that will be sent to the controlling port.
Step 1. Port mirroring is performed in mirror view section. In total, up to 15 mirrors with a unique destination interface can be created. To enter the mirror view, run the command:
LTP-16N# configure terminal LTP-16N(configure)# mirror 1 LTP-16N(config)(mirror-1)#
Step 2. Specify the interface to which the mirrored traffic will be sent. There can be only one interface for all created mirrors.
LTP-16N(config)(mirror-1)# destination interface front-port 1
Step 3. If necessary, an additional label for mirrored traffic can be set.
LTP-16N(config)(mirror-1)# destination interface front-port 1 add-tag 777
Step 4. Add ports from which traffic will be listened. If necessary to listen specific VLANs, add the vlan keyword to the command. If only one of the traffic directions needs to be listened to, add rx or tx.
LTP-16N(config)(mirror-1)# source interface pon-port 9
Step 5. Apply the configuration by using the commit command.
LTP-16N(config)(mirror-1)# do commit
Packets mirrored from the PON port will have an additional label. This label is equal to the value of the GEM port from which the packet was received.
QoS
QoS is currently supported only via IEEE 802.1p.
General QoS configuration
Step 1. QoS configuration is performed in configure view section.
LTP-16N# configure terminal LTP-16N(configure)#
Step 2. Enable QoS processing according to priorities. By default, all packets are directed to 0, the non-priority queue.
LTP-16N(configure)# qos enable
Step 3. Select QoS operation mode. Currently only 802.1p is supported.
LTP-16N(configure)# qos type 802.1p
Step 4. Apply the configuration by using the commit command.
LTP-16N(configure)# do commit
After changing the QoS settings, the terminal will be automatically reconfigured. Services may be temporarily suspended.
L2 QoS configuration
Step 1. Select the queue scheduler operation mode. SP is a Strict priority mode. Strict priority ensures packet processing according to queue priority. WFQ — Weighted Fair Queue. This mode focuses on the weights of each queue and their ratios. Packets are processed according to the weight of the queue.
LTP-16N(configure)# qos 802.1p mode sp
Step 2. Use the qos map command to set the 802.1p translation rules to the appropriate queue:
LTP-16N(configure)# qos 802.1p map 0 to 1
Step 3. When using the WFQ mode, distribute the weights of each queue as necessary:
LTP-16N(configure)# qos 802.1p wfq queues-weight 10 23 11 40 0 63 2 60
Step 4. Apply the configuration by using the commit command.
LTP-16N(configure)# do commit
Weighted Fair Queue operates based on queue weight. For example, two queues with weights 10 and 20 are used. The bandwidth for these queues will be calculated using the following formula: (queue weight\(sum of queue weights). That is, in this example, the bandwidth will be divided into 10\30 and 20\30.
ONT configuration
Service models
This section considers main terms and classification of service models.
The service model can generally be based on one of the service principles: N-to-1, 1-to-1 and multicast. The "VLAN for Service" (N-to-1) architecture means that a service VLAN (S-VLAN) is used to provide all users with a certain service. The "VLAN for Subscriber" (1-to-1) architecture implies that a client VLAN (C-VLAN) is used to provide a user with multiple services. These methods are often combined in practice and form a hybrid model, which uses S-VLAN and C-VLAN simultaneously.
1-to-1 architecture
A separate VLAN is used for each subscriber in the C-VLAN model. In this operation scheme a channel from the uplink port to the GEM port of the ONT, in a given S-VLAN is built for the subscriber. And all traffic (including broadcast), goes to this GEM-port.
N-to-1 architecture
The S-VLAN model has dedicated S-VLANs for each service. Traffic is distributed among the GEM ports of the clients, based on the MAC table. If the MAC address is not learnt, the packet is sent to the broadcast GEM-port and replicated to all subscribers.
Multicast architecture
This architecture is similar to N-to-1, except that a dedicated multicast GEM port is used.
VLAN ID replacement
The transfer of traffic from the service S-VLAN to the client C-VLAN can be done either on the OLT or on the ONT. To configure the replacement place, the vlan-replace option is used. The option is configured in the cross-connect profile, which allows configuring the label replacement scheme for each service. By default, the replacement occurs on ONT.
Operating principle
The model traffic concept is used for implementation of different service models in the terminal. The model is configured in a cross-connect profile, which allows the configuration of combined circuits within a single ONT. The detailed example is given below.
1-to-1
Below is an example of operation of the service configured according to the 1-to-1 model.
The scheme of this service model is shown in the Figure 17.
Figure 17 – 1-to-1 traffic model operation scheme
A C-VLAN is used between an ONT and service routers (BRAS, VoIP SR) that encapsulate services for one subscriber (one ONT service), such as VoIP, Internet, and IPTV. In this case, all traffic is routed to one common GEM port.
N-to-1
Below is an example of the implementation of a service model that falls under the N-to-1 structure. This scheme is best considered using the example of two ONTs.
The scheme of this model is shown in the Figure 18.
Figure 18 – N-to-1 model scheme
Dedicated S-VLANs are used between the OLT and service routers (BRAS, VoIP SR) for each of the following services (here – Internet). The destination of the packet is defined by the MAC table, which explicitly stores the MAC address and GEM port correspondence. If no entry is found, the packet is sent to the broadcast GEM port and replicated to all ONTs using the service.
Multicast
The multicast scheme is similar to the N-to-1 scheme, except that a multicast GEM port is used and the MAC table is involved only in IGMP exchange. Multicast is sent directly to the multicast GEM port. This mechanism is closely related to IGMP snooping.
ONT licensing
By default, only ONT manufactured by ELTEX Enterprise LLC is allowed to work on the OLT. To enable any third-party ONTs, OLT requires a license. To purchase the license, contact ELTEX Marketing Department.
Loading a license file to OLT
A license is a text file of the following format:
{
"version":"<VER>",
"type":"all",
"count":"<count>",
"sn":"<SN>",
"mac":"<MAC>",
"sign":"<hash>"
}
Where:
- VER – license file version number;
- count – number of third-party ONTs enabled on the OLT;
- SN – LTP serial number;
- MAC – LTP MAC address;
- hash – license file digital signature.
There are two ways to load a license to OLT.
Use the copy command:
LTP-16N# copy tftp://<IP>/<PATH> fs://license Download file from TFTP-server.. License successfully installed.
Where:
IP – IP address of TFTP server;
PATH – path to the license file on TFTP server.Use CLI:
LTP-16N# license set """<license>""" License saved. License successfully installed.
Where:
<license> – full content of the license file including curly brackets.
To view information about the license on the device, use the show command.LTP-16N# show license Active license information: License valid: yes Version: 1.2 Board SN: GP2B000022 Licensed vendor: all Licensed ONT count: 10 Licensed ONT online: 3The license file remains after device reload, firmware update, and configuration load. If OLT is reset to factory settings, the license is also deleted.
LTP-16N# copy tftp://<IP>/<PATH> fs://license Download file from TFTP-server.. License successfully installed.
LTP-16N# copy tftp://<IP>/<PATH> fs://license Download file from TFTP-server.. License successfully installed.
Deleting a license file from OLT
If necessary, previously installed license can be deleted using the no license command.
LTP-16N# no license License file removed. License successfully deleted from system. LTP-16N# show license Active license information: No license installed
At license upload and removal, the terminal will be automatically reconfigured. This will interrupt all ONT services.
ONT general configuration principles
This section describes general principles of ONT configuration. It also defines configuration profiles.
ONT is configured with the help of a profile, which defines high-level expression of data communication channels. All operations related to channel creation are performed automatically. The way data communication channels are created depends on the selected service model.
ONT configuration includes assignment of configuration profiles and specification of ONT specific parameters. Configuration profiles allow general parameters to be set for all or for a range of ONTs. Profile parameters may include, for instance, DBA settings, configuration of VLAN operations in OLT and ONT, settings of Ethernet ports in ONT. Specific ONT parameters allow each separate ONT to have its own settings specified. Such settings include, for example, GPON password, subscriber's VLAN, etc.
ONT operation modes
Introduce the concept of Bridged and Routed services. For this, consider the concept of OMCI and RG management domains. In terms of management domains, an ONT is considered as a device, which operates in the OMCI domain only. The devices, which operate in both management domains (i. e. have an integrated router), are denoted as ONT/RG.
For more information on protocol operation, see TR-142 Issue 2.
Everything that refers to the OMCI domain can be applied to both ONT and ONT/RG devices. For this reason, we will further denote ONT/RG as ONT. If an ONT is configured without the RG domain (without a router), skip all steps concerning RG.
Bridged service is a service, which configuration requires the OMCI management domain only, i. e. it can be completely configured with the help of the OMCI protocol in ONT. Routed service is a service, which configuration requires both the OMCI and RG management domains.
In addition to configuration in terminal, a routed service requires the RG domain to be configured by using one of the following methods:
- Pre-defined configuration – subscriber is provided with an ONT having fixed configuration.
- Local ONT configuration using WEB interface.
- ONT configuration using the TR-069 protocol and auto configuration server (ACS).
ONT is connected to RG using a Virtual Ethernet interface point (VEIP), which corresponds to the TR-069 WAN interface (described in TR-098) on the RG side. VEIP is represented by a virtual port in terminal parameters. The port has the same configuration procedure as Ethernet ports in the ports profile.
General principles of configuration
Service is the key term of ONT configuration. This term completely includes a communication channel, through which data is transferred from the interfaces located on the front panel of the terminal (see section Interface configuration) to users ONT ports. There are two service profiles: cross-connect and dba. The cross-connect profile creates a GEM service port, the dba profile allocates an Alloc-ID for this ONT and associates a corresponding GEM port to the Alloc-ID.
Table 19 – ONT profiles
Profile | Description |
|---|---|
cross-connect | Defines VLAN transformation on OLT and ONT, service delivery model and ONT operation mode |
dba | Defines upstream traffic parameters |
ports | Defines user port groups in ONT as well as IGMP and multicast parameters for user ports |
management | Defines TR-69 management service parameters |
| shaping | Defines ONT bandwidth shaping |
| template | Defines ONT configuration template |
ONT profiles configuration
Cross-connect profile configuration
- Step 1. When configuring the cross-connect profile, first of all define the service delivery model, the traffic-model parameter is responsible for this.
- Step 2. Then define the ONT mode – ont-mode bridge or ont-mode router. For bridge, select a group by using the bridge group command.
- Step 3. Configure the outer vid, user vid and inner vid.
- Step 4. The tag mode parameter is responsible for enabling Q-in-Q mode in the upstream direction, outer vid and inner vid set respectively the outer and inner tag in Q-in-Q mode.
- Step 5. If the service will be used for management, iphost must be enabled. And if necessary, set an iphost id for it.
- Step 6. By default, the n-to-1 scheme is used, if necessary, it is possible to change it to the 1-to-1 scheme. For more information, see Service models.
- Step 7. By default, multicast is forbidden. If multicast is needed, use the multicast enable command.
DBA profile configuration
This profile configures dynamic bandwidth allocation (DBA). These parameters allow specification of any T-CONT type described in G.984.3.
- Step 1. First, define the allocation-scheme — in one T-CONT or in different ones.
- Step 2. After that, configure status-reporting to define the type of ONT queues status report.
- Step 3. The bandwidth guaranteed, and bandwidth besteffort parameters define the guaranteed and best-effort bandwidth correspondingly.
Ports profile configuration
The ports profile allows to group ports in ONT. The profile also contains IGMP and multicast setting as they are separately adjusted for each port.
Up to 4 Ethernet ports can be configured.
- Step 1. Ethernet port grouping (applicable to bridge mode only) is done with the bridge-group. These values mean port association with the OMCI domain, i. e. the port can be directly used in OLT to establish a data communication channel.
- Step 2. IGMP and multicast configuration is described in details in Section IGMP configuration.
- Step 3. Configure Dynamic entry. Specify multicast VLAN allowed range of multicast addresses. Dynamic entry is used to filter multicast by VLAN range of allowed multicast addresses.
- Step 4. Configure veip multicast enable (applicable only for router operating mode). Specify VLAN that will be used for multicast in upstream and downstream direction, also specify the operation to be performed with the tag (pass, replace-tag, replace-vid). The replace-tag, replace-vid settings are used to change VLAN tag or 802.1Q, for example, if it is necessary to get two services through one service from different VLANs.
Management profile configuration
In the management profile, it is possible to configure parameters to control a device configured in the RG domain. There are two options for transmitting the configuration for ACS settings – via OMCI; receive in other ways (for example via DHCP opt43).
- Step 1. Set the iphost id to the value set in the cross-connect profile.
- Step 2. Set the ACS configuration obtainment mode by using the omci-configuration enable command.
- Step 3. When transmitting parameters via OMCI, set parameters for ACS: username, password and url.
Shaping profile configuration
In the shaping profile, it is possible to configure parameters for limiting the transmission rate in upstream. The restriction is possible by the type of traffic – unicast\broadcast\multicast for each service separately.
- Step 1. Enable shaping for a specific service.
- Step 2. Set the peak speed.
- Step 3. Set shaping.
ONT configuration procedure
Figure below shows a step-by-step procedure of ONT configuration.
Figure 19 – ONT configuration procedure
Step 1. Prior to proceed to ONT configuration, add an ONT into the OLT configuration. For an ONT to be added and configured, it does not need to be physically connected to the OLT. You can view the list of inactive ONTs with the help of the show interface ont <pon-port> unactivated command.
LTP-16N# show interface ont 1 unactivated ----------------------------------- GPON-port 5 ONT unactivated list ----------------------------------- ## Serial ONT ID PON-port RSSI Status 1 ELTX0600003D n/a 5 n/a unactivatedStep 2. To specify ONT settings, go to the corresponding view with the help of the interface ont command. Specify ONT serial number.
LTP-16N# configure terminal LTP-16N(configure)# interface ont 1/1 LTP-16N(config)(if-ont-1/1)# serial ELTX0600003D
Step 3. Apply the configuration by using the commit command.
LTP-16N(config)(if-ont-1/1)# do commit
Service configuration in the ont-mode bridge mode
Consider configuring a mixed scheme of services built on different traffic-model. ONT will be configured in the bridge mode.
Configure 3 services:
- HSI and IPTV unicast, by traffic model N-to-1, the service VLAN is 200, the tag will be taken on the ONT, untagged traffic will come from the ONT port.
- Multicast, packets will come on OLT with tag 98, from the ONT port — also not tagged.
- On the 1-to-1 model, with a service VLAN 100, in a separate bridge group, the ONT port will come out with a tag 10. Tag replacement will take place on the OLT.
Figure 20 – Abstract representation of the test configuration
Step 1. Create a cross-connect profile named Internet. Configure the bridged service specifying the bridge group the ONT port will be connected to (in this case, it is equal to 10 for the first service). Set the outer-vid to 200, replacing the label is not necessary and the traffic from the port comes without the tag, so leave the vlan-replace and user vid unchanged.
LTP-16N# configure terminal LTP-16N(configure)# profile cross-connect Internet LTP-16N(config)(profile-cross-connect-Internet)# ont-mode bridge LTP-16N(config)(profile-cross-connect-Internet)# bridge group 10 LTP-16N(config)(profile-cross-connect-Internet)# outer vid 200
Step 2. Analogically with the described above, create another cross-connect profile named IPTV for the second service and configure the bridge group. Additionally, configure the traffic-model for the multicast service type.
LTP-16N(config)(profile-cross-connect-IPTV)# ont-mode bridge LTP-16N(config)(profile-cross-connect-IPTV)# bridge group 11 LTP-16N(config)(profile-cross-connect-IPTV)# outer vid 98 LTP-16N(config)(profile-cross-connect-IPTV)# traffic-model multicast
Step 3. Create profile for the third service. Configure another group for it. And also configure tag replacement on the OLT and tagging traffic from the ONT port. For this set the values vlan-replace olt-side and user vid to 10.
LTP-16N(configure)# profile cross-connect UNI_TAG LTP-16N(config)(profile-cross-connect-UNI_TAG)# ont-mode bridge LTP-16N(config)(profile-cross-connect-UNI_TAG)# bridge group 12 LTP-16N(config)(profile-cross-connect-UNI_TAG)# outer vid 100 LTP-16N(config)(profile-cross-connect-UNI_TAG)# vlan-replace olt-side LTP-16N(config)(profile-cross-connect-UNI_TAG)# user vid 10 LTP-16N(config)(profile-cross-connect-UNI_TAG)# traffic-model 1-to-1
Step 4. Specify DBA parameters. To do this, create a dba profile and adjust the corresponding settings. Set a value of a guaranteed bandwidth and allocation scheme in this example:
LTP-16N(configure)# profile dba AllService LTP-16N(config)(profile-dba-AllService)# allocation-scheme share-t-cont LTP-16N(config)(profile-dba-AllService)# bandwidth guaranteed 1024
Step 5. Associate bridge group with ONT port. To do this, create a ports profile and set the bridge group parameter to 10 for the eth1, eth2 port and to 11 for the eth3 port. Set the rules of multicast traffic processing for port 2 and multicast restriction rules on ONT:
LTP-16N(configure)# profile ports PP LTP-16N(config)(profile-ports-PP)# port 1 bridge group 10 LTP-16N(config)(profile-ports-PP)# port 2 bridge group 11 LTP-16N(config)(profile-ports-PP)# port 2 multicast LTP-16N(config)(profile-ports-PP)# port 2 igmp downstream tag-control remove-tag LTP-16N(config)(profile-ports-PP)# port 2 igmp upstream tag-control add-tag LTP-16N(config)(profile-ports-PP)# port 2 igmp upstream vid 98 LTP-16N(config)(profile-ports-PP)# port 2 igmp downstream vid 98 LTP-16N(config)(profile-ports-PP)# port 3 bridge group 12 LTP-16N(config)(profile-ports-PP)# igmp multicast dynamic-entry 1 group 224.0.0.1 239.255.255.255 vid 98
Step 6. Assign the created profiles in the ONT.
LTP-16N(configure)# interface ont 1/1 LTP-16N(config)(if-ont-1/1)# service 1 profile cross-connect Internet dba AllService LTP-16N(config)(if-ont-1/1)# service 2 profile cross-connect IPTV dba AllService LTP-16N(config)(if-ont-1/1)# service 3 profile cross-connect UNI_TAG dba AllService LTP-16N(config)(if-ont-1/1)# profile ports PP
Step 7. Allow the required VLAN to pass on the uplink interface (see section Interface configuration).
LTP-16N# configure terminal LTP-16N(configure)# interface front-port 1 LTP-16N(config)(if-front-1)# vlan allow 200,100,98
Step 8. For VLAN 98, configure IGMP snooping. By default, IGMP snooping is enabled for all VLANs, but disabled globally. It is necessary to enable IGMP snooping globally:
LTP-16N(configure)# vlan 98 LTP-16N(config)(vlan-98)# ip igmp snooping enable LTP-16N(config)(vlan-98)# exit LTP-16N(configure)# ip igmp snooping enable
Step 9. Apply the configuration by using the commit command.
LTP-16N# commit
Service configuration in the ont-mode router mode
Consider a typical configuration of services for ONT configured the in router mode: HSI, IPTV, VoIP and ACS.
To do this, configure 5 services:
- HSI service. N-to-1 traffic model, the service VLAN is 200, there will be a tag replacement on the OLT and it will arrive to 10 on the OLT.
- IPTV service. Service for multicast traffic. Multicast traffic model. The stream passes without replacing the VLAN 30 tag.
- STB service. The service is required for unicast traffic for STBs. The tag is replaced to ONT. VLAN 250.
- VoIP service. Service for telephony, similar in settings to HSI. VLAN 100.
- ACS service. This service is used to control the ONT via ACS. Service VLAN 2000.
Step 1. Create a cross-connect profile named HSI. The ont-mode router mode is configured by default, so it is not necessary to set it. Set the service VLAN to 200 and user to 10. The tag will be replaced on OLT.
LTP-16N# configure terminal LTP-16N(configure)# profile cross-connect HSI LTP-16N(config)(profile-cross-connect-HSI)# outer vid 200 LTP-16N(config)(profile-cross-connect-HSI)# vlan-replace olt-side LTP-16N(config)(profile-cross-connect-HSI)# user vid 10
Step 2. Similarly to the described above, create another cross-connect profile named IPTV for the second service and configure traffic-model for multicast service.
LTP-16N(configure)# profile cross-connect IPTV LTP-16N(config)(profile-cross-connect-IPTV)# outer vid 30 LTP-16N(config)(profile-cross-connect-IPTV)# user vid 30 LTP-16N(config)(profile-cross-connect-IPTV)# traffic-model multicast
Step 3. Create a cross-connect profile named STB similarly to HSI. Set the service VLAN to 250. On the terminal, the traffic will go to 40 VLAN.
LTP-16N(configure)# profile cross-connect STB LTP-16N(config)(profile-cross-connect-STB)# outer vid 250 LTP-16N(config)(profile-cross-connect-STB)# vlan-replace olt-side LTP-16N(config)(profile-cross-connect-STB)# user vid 40
Step 4. Create a cross-connect profile named VOIP similar to HSI. Set the service VLAN to 100. On the terminal, the traffic will go to 20 VLAN.
LTP-16N(configure)# profile cross-connect VOIP LTP-16N(config)(profile-cross-connect-VOIP)# outer vid 100 LTP-16N(config)(profile-cross-connect-VOIP)# vlan-replace olt-side LTP-16N(config)(profile-cross-connect-VOIP)# user vid 20
Step 5. Create a cross-connect profile named ACS. Set the service VLAN to 2000. Also enable iphost in this service. Leave the default index value for iphost.
LTP-16N(configure)# profile cross-connect ACS LTP-16N(config)(profile-cross-connect-ACS)# outer vid 2000 LTP-16N(config)(profile-cross-connect-ACS)# iphost enable
Step 6. Specify DBA parameters. To do this, create a dba profile and adjust the corresponding settings. Set a value of a guaranteed bandwidth and allocation scheme in this example:
LTP-16N(configure)# profile dba AllService LTP-16N(config)(profile-dba-AllService)# allocation-scheme share-t-cont LTP-16N(config)(profile-dba-AllService)# bandwidth guaranteed 1024
Step 7. Create ports profile. Add the settings to allow multicast traffic to pass through VeIP:
LTP-16N(configure)# profile ports veip LTP-16N(config)(profile-ports-veip)# veip multicast enable LTP-16N(config)(profile-ports-veip)# veip igmp downstream vid 30 LTP-16N(config)(profile-ports-veip)# veip igmp upstream vid 30
Step 8. Create management profile. Add the configuration for authorization on the ACS server:
LTP-16N(configure)# profile management ACS LTP-16N(config)(profile-management-ACS)# username test LTP-16N(config)(profile-management-ACS)# password test_pass LTP-16N(config)(profile-management-ACS)# url http://192.168.100.100
Step 9. Assign the created profiles on the ONT
LTP-16N(configure)# interface ont 1/1 LTP-16N(config)(if-ont-1/1)# service 1 profile cross-connect HSI dba AllService LTP-16N(config)(if-ont-1/1)# service 2 profile cross-connect IPTV dba AllService LTP-16N(config)(if-ont-1/1)# service 3 profile cross-connect STB dba AllService LTP-16N(config)(if-ont-1/1)# service 4 profile cross-connect VOIP dba AllService LTP-16N(config)(if-ont-1/1)# service 5 profile cross-connect ACS dba AllService LTP-16N(config)(if-ont-1/1)# profile ports veip LTP-16N(config)(if-ont-1/1)# profile management ACS
Step 10. Allow the required VLAN to pass on the uplink interface (see section Interface configuration).
LTP-16N# configure terminal LTP-16N(configure)# interface front-port 1 LTP-16N(config)(if-front-1)# vlan allow 100,200,250,2000
Step 11. For VLAN 30, configure IGMP snooping. Also, enable IGMP snooping globally:
LTP-16N(configure)# vlan 30 LTP-16N(config)(vlan-30)# ip igmp snooping enable LTP-16N(config)(vlan-30)# exit LTP-16N(configure)# ip igmp snooping enable
Step 12. Apply the configuration by using the commit command.
LTP-16N# commit
Configuration templates
It is not always convenient for carriers, especially large ones, to assemble ONT configuration from profiles for each subscriber. This is time-consuming and, in a certain sense, risky, since it increases the likelihood of carrier errors. As a rule, companies use one or more service plans, under which ONT profiles are defined.
This section describes ONT templates. The mechanics of configuration templates is very simple. The network administrator prepares in advance the required number of templates according to the number of service plans. The configuration template specifies a list of profiles, as well as a set of ONT parameters with maximum detail. The subscriber department engineer or the OSS/BSS system assigns the template to the ONT and redefines some additional configuration parameters, if necessary. As a rule, the assignment of a configuration through templates occurs in one click or in one command.
Step 1. Create ONT configuration template.
LTP-16N# configure terminal LTP-16N(configure)# template one_service LTP-16N(config)(template-one_service)#
Step 2. Assign previously created ONT profiles to the required services. As an example, cross-connect profile with PPPoE name and dba profile with dba1 name.
LTP-16N(config)(template-one_service)# LTP-16N(config)(template-one_service)# service 1 profile cross-connect PPPoE dba dba1
Step 3. Enable redefining parameters assigned from templates. By default, all parameters in template are undefine (parameters will use settings not from the template, but only those that were assigned to the interface ont). To use configuration specified in template, configure define for this parameter.
LTP-16N(config)(template-one_service)# define service 1
Step 4. Apply the configuration by using the commit command.
LTP-16N(config)(template-one_service)# do commit
Assigning ONT configuration template
Step 1. Switch to ONT configuration. If necessary, ONT ID range can be used for group operations.
LTP-16N# configure terminal LTP-16N(configure)# interface ont 1/1 LTP-16N(config)(if-ont-1/1)#
Step 2. Assign configuration template to ONT.
LTP-16N(config)(if-ont-1/1)# template one_service
Step 3. If necessary, set individual options for ONT that are not specified in template.
LTP-16N(config)(if-ont-1/1)# rf-port-state enable
Step 4. Apply the configuration by using the commit command.
LTP-16N(config)(if-ont-1/1)# do commit
Disabling ONT
Starting with 1.4.0 firmware version, the ability to remotely disable the interface ONT has been added.
LTP-16N# configure terminal LTP-16N(config)# interface ont 1/1 LTP-16N(config)(if-ont-1/1)# shutdown LTP-16N(config)(if-ont-1/1)# do commit
ONT firmware update
This section describes the procedure of ONT firmware update via OMCI.
Uploading firmware for ONT update
Step 1. To upload a file with ONT firmware to the terminal, use the copy command.
LTP-16N# copy tftp://192.168.1.5/ntu-rg-3.50.0.1342.fw.bin fs://ont-firmware
Step 2. To view uploaded files, use the show firmware ont list command.
LTP-16N# show firmware ont list N | Firmware 1 ntu-rg-3.50.0.1342.fw.bin
Step 3. If necessary to remove the firmware file from the terminal, use the delete firmware ont command.
LTP-16N# delete firmware ont * All ONT firmwares deleted successfully
ONT firmware management
Currently, only manual start and stop of ONT updates are supported.
Step 1. To start firmware update, use the firmware update start command. The system will write about the current ONT update statuses. Upon completion of the update, the ONT will automatically reboot and start operating with the new firmware version.
LTP-16N# firmware update start interface ont 7/1-10 filename ntu-rg-3.50.0.1342.fw.bin ONT 7/1 is not connected ONT 7/2 is currently being updated ONT 7/3 is currently in the update queue ONT 7/4 firmware will be updated ONT 7/5 not ready for firmware updateStep 2. To stop firmware update, use the firmware update start command.
LTP-16N# firmware update stop interface ont 7/1-10 ONT 7/1 is not connected ONT 7/2 firmware updating will be stopped ONT 7/3 firmware updating will be removed from the update queue ONT 7/4 does not need to stop updating
OLT configuration
S-VLAN ethertype configuration
By default, ethertype 0x8100 is used. Ethertype for S-VLAN can be changed using the following command:
LTP-16N# configure terminal LTP-16N(configure)# pon network svlan-ethertype 0x88A8 LTP-16N(configure)# do commit
ONT block time configuration
When MAC duplication is detected (when the same MAC address is trained on two ports of the OLT), the ONT is blocked for the set timer, by default 60 seconds. The value of this timer can be configured:
LTP-16N# configure terminal LTP-16N(configure)# pon olt ont-block-time 200 LTP-16N(configure)# do commit
Unactivated-timeout configuration
Unactivated-timeout is a timer after which the ONT will be removed from monitoring if no connection messages were received from it.
Terminal monitoring
General information
Information on current terminal firmware version
To view information on the current version of terminal firmware, use the show version command.
LTP-16N# show version
Eltex LTP-16N: software version 1.0.0 build 1699 on 05.11.2020 11:59
Terminal information preview
To view information about the terminal, use the show system environment command.
LTP-16N# show system environment
System information:
CPU load average (1m, 5m, 15m): 0.11, 0.22, 0.25
Free RAM/Total RAM (Gb): 6.26/7.76
Free disk space/Total disk space(Gb)): 5.77/6.13
Temperature:
Sensor PON SFP 1 (*C): 36
Sensor PON SFP 2 (*C): 34
Sensor Front SFP (*C): 31
Sensor Switch (*C): 36
Fan state:
Fan configured speed: auto
Fan minimum speed (%): 15
Fan speed levels (%): 15-100
Fan 1 (rpm): 6420
Fan 2 (rpm): 6420
Fan 3 (rpm): 6420
Fan 4 (rpm): 6540
Power supply information:
Module 1: PM160 220/12 1vX
Type: AC
Intact: true
Module 2: offline
HW information
FPGA version: 3.0
PLD version: 2.0
Factory
Type: LTP-16N
Revision: 1v3
SN: GP3D000041
MAC: E4:5A:D4:1A:05:60
Table 20 – Terminal parameters
Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
CPU load average | Average processor load |
Free RAM/Total RAM | Free/total RAM |
Free disk space/Total disk space | Free/total non-volatile memory |
Temperature | Temperature from sensors |
Fan configured speed | Set fan rotation speed |
Fan minimum speed | Minimum fan rotation speed |
Fan speed levels | Set fan rotation speed for each level |
Fan state | Fans state and rpm value |
FPGA version | FPGA firmware version |
PLD version | PLD firmware version |
Power supply information | Information about installed power modules |
Factory | Device unique information |
Network connection check
To check network connection, use the ping command. As a parameter, pass the IP address of the node to be checked.
LTP-16N# ping 192.168.1.5 PING 192.168.1.5 (192.168.1.5): 56 data bytes 64 bytes from 192.168.1.5: seq=0 ttl=64 time=0.311 ms 64 bytes from 192.168.1.5: seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.223 ms 64 bytes from 192.168.1.5: seq=2 ttl=64 time=0.276 ms --- 192.168.1.5 ping statistics --- 3 packets transmitted, 3 packets received, 0% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max = 0.223/0.270/0.311 ms
Terminal operation log
Use the show log command to view log files.
LTP-16N# show log files
## Name Size in bytes Date of last modification
1 LTP.log 4073 Mon Nov 16 15:57:04 2020
Total files: 1
Use the show log buffer command to view a local terminal operation log buffer.
LTP-16N# show log buffer syslog-ng starting up; version='3.20.1' 16 Nov 15:55:41 NOTICE USRMGR - User-manager started. 16 Nov 15:55:41 NOTICE NETWORK-MGR - Network-manager started. 16 Nov 15:55:41 NOTICE LOGMGR - Log-manager started. 16 Nov 15:56:20 NOTICE DNA - DNA start 16 Nov 15:56:51 NOTICE DNA - front-port 4 changed state to active_working ...
When using a remote syslog server, use the log display tools provided by the syslog server.
Enter show log <filename> command to view the files.
LTP-16N# show log LTP.log
Active alarms log
To view the active alarms log, use the show alarms command. Pass the type of events and/or their importance as parameters. You can view all active alarms by using the show alarm active all command.
LTP-16N# show alarms active all
Active alarms (2):
## type severity description
1 fan critical fan slot 1
2 fan critical fan slot 2
Event log
To view events, use the show alarm history command. Pass the type of events and/or their severity as parameters. You can view all events with the show alarm history all command.
LTP-16N# show alarms history all Datetime Severity Type Norm Description ------------------- -------- ------------------ ---- ---------------------------------------------------------------------- 13.05.2022 08:18:01 info fan Fan 1 speed 6360 rpm 13.05.2022 08:18:31 info fan * Fan 1 speed 6540 rpm is back to normal 13.05.2022 08:19:54 major ont-link-up ONT6/2 (ELTX660421C4) link up 13.05.2022 08:19:59 info ont-state-changed ELTX660421C4 6 2 OK "NTU-RG-1421G-Wac" "3.40.1.1655" "2v6" "-19.83"
front-port monitoring
View port statistics
For front-port statistics, use the show interface front-port 1 counters command. If you want advanced statistics, enter the verbose parameter.
LTP-16N# show interface front-port 1 counters Port UC packet recv MC packet recv BC packet recv Octets recv UC packet sent MC packet sent BC packet sent Octets sent ---- -------------- -------------- -------------- -------------- -------------- -------------- -------------- -------------- 1 0 0 0 0 0 3828 0 806192
View port state
To view port information such as status and SFP type, use the show interface front-port <id> state command.
LTP-16N# show interface front-port 1 state
Front-port Status Speed Media
-------------------- -------------------- -------------------- --------------------
1 up 1G copper
pon-port monitoring
View port state
To view information about the gpon-port and SFP state for this port, use the show interface pon-port <id> state command.
LTP-16N# show interface pon-port 1 state Port State ONT count SFP vendor SFP product number SFP vendor revision SFP temperature [C] SFP voltage [V] SFP tx bias current [mA] SFP tx power [dBm] ---- -------- --------- ------------------ ------------------ ------------------- ------------------- --------------- ------------------------ ------------------ 1 OK 3 Ligent LTE3680M-BC 1.0 45 3.27 16.84 3.72
MAC table monitoring
To view MAC tables, use the show mac command.
LTP-16N# show mac
Loading MAC table...
MAC port svid
------------------- ----------------- ------
A8:F9:4B:81:43:00 front-port 1 30
A8:F9:4B:82:8B:80 front-port 1 30
2C:56:DC:99:8E:63 pon-port 6 1100
50:3E:AA:0D:13:64 front-port 1 1100
48:5B:39:02:55:84 front-port 1 1100
00:15:17:E4:27:CA front-port 1 1100
A8:F9:4B:84:F5:40 front-port 1 30
7 MAC entries
It is also possible to use include/exclude filters for MAC table by interface, mac, svid, cvid, gem, type. To query a MAC table without filters, use the show mac verbose command.
LTP-16N# show mac verbose
Loading MAC table...
MAC port svid cvid ONT gem type
------------------- ----------------- ------ ------ ----- ------- ---------
A8:F9:4B:81:43:00 front-port 1 30 Dynamic
A8:F9:4B:82:8B:80 front-port 1 30 Dynamic
2C:56:DC:99:8E:63 pon-port 6 1100 6/2 181 Dynamic
50:3E:AA:0D:13:64 front-port 1 1100 Dynamic
48:5B:39:02:55:84 front-port 1 1100 Dynamic
00:15:17:E4:27:CA front-port 1 1100 Dynamic
A8:F9:4B:84:F5:40 front-port 1 30 Dynamic
7 MAC entries
ONT monitoring
ONT configurations list
Step 1. To view active ONT configurations, use the show interface ont <ID> configured command. As an ID, pass the PON port number or a range of numbers.
LTP-16N# show interface ont 2 configured ----------------------------------- pon-port 2 ONT configured list ----------------------------------- ## Serial ONT ID PON-port Status 1 ELTX6201CD9C 1 2 OK 2 ELTX6201C610 2 2 OK 3 ELTX62015240 3 2 OK 4 ELTX6201CD6C 4 2 OK 5 ELTX62015458 5 2 OK 6 ELTX6201A8F4 6 2 OK 7 ELTX6201C848 7 2 OK 8 ELTX62013B8C 8 2 OK 9 ELTX6201C830 9 2 OK 10 ELTX62015230 10 2 OK 11 ELTX62014758 11 2 OK 12 ELTX62013BE0 12 2 OK 13 ELTX6201A904 13 2 OK 14 ELTX62015214 14 2 OK 15 ELTX6201420C 15 2 OK 16 ELTX6201CD88 16 2 OK 17 ELTX6201CA0C 17 2 OK 18 ELTX6201AB04 18 2 OK 19 ELTX62018E48 19 2 OK20 ELTX62014658 20 2 OK 21 ELTX6201AB14 21 2 OK 22 ELTX62014280 22 2 OK 23 ELTX6201CD8C 23 2 OK 24 ELTX6201B700 24 2 OK 25 ELTX6201C74C 25 2 OK 26 ELTX620141F0 26 2 OK 27 ELTX62014664 27 2 OK 28 ELTX6201CADC 28 2 OK 29 ELTX620190E8 29 2 OK 30 ELTX62018E84 30 2 OK 31 ELTX6201B714 31 2 OK 32 ELTX6201D384 32 2 OK
List of empty ONT configurations
Step 1. To view empty ONT configurations (vacant ONT IDs), use the show interface ont <ID> unconfigured command.
LTP-16N# show interface ont 1-16 unconfigured pon-port 1 ONT unconfigured: 33-128 pon-port 2 ONT unconfigured: 33-128 pon-port 3 ONT unconfigured: 33-128 pon-port 4 ONT unconfigured: 33-128 pon-port 5 ONT unconfigured: 33-128 pon-port 6 ONT unconfigured: 33-128 pon-port 7 ONT unconfigured: 33-128 pon-port 8 ONT unconfigured: 33-128 pon-port 9 ONT unconfigured: 33-128 pon-port 10 ONT unconfigured: 33-128 pon-port 11 ONT unconfigured: 33-128 pon-port 12 ONT unconfigured: 1-128 pon-port 13 ONT unconfigured: 1-128 pon-port 14 ONT unconfigured: 1-128 pon-port 15 ONT unconfigured: 2-128 pon-port 16 ONT unconfigured: 2-19,30-128
View the list of unactivated ONTs
Step 1. To view the list of ONTs that are connected but not activated, use the show interface ont <ID> unactivated command. As an argument, specify the PON interface number or a range of numbers.
LTP-16N# show interface ont 11 unactivated ----------------------------------- pon-port 11 ONT unactivated list ----------------------------------- ## Serial ONT ID PON-port RSSI Version EquipmentID Status 1 ELTX70000010 n/a 11 n/a n/a n/a UNACTIVATED 2 ELTX77000230 n/a 11 n/a n/a n/a UNACTIVATED
List of connected ONTs
Step 1. To view the list of online ONTs, use the show interface ont <ID> online command. As an argument, specify the GPON interface number or a range of numbers.
LTP-16N# show interface ont 2,16 online ----------------------------------- pon-port 2 ONT online list ----------------------------------- ## Serial ONT ID GPON-port RSSI Status 1 ELTX6201CD9C 1 2 -21.74 OK 2 ELTX6201C610 2 2 -19.07 OK 3 ELTX62015240 3 2 -20.09 OK 4 ELTX6201CD6C 4 2 -21.14 OK 5 ELTX62015458 5 2 -21.19 OK 6 ELTX6201A8F4 6 2 -20.00 OK7 ELTX6201C848 7 2 -20.51 OK 8 ELTX62013B8C 8 2 -20.76 OK 9 ELTX6201C830 9 2 -20.97 OK 10 ELTX62015230 10 2 -20.04 OK 11 ELTX62014758 11 2 -20.81 OK 12 ELTX62013BE0 12 2 -20.13 OK 13 ELTX6201A904 13 2 -19.91 OK 14 ELTX62015214 14 2 -20.51 OK 15 ELTX6201420C 15 2 -20.76 OK 16 ELTX6201CD88 16 2 -21.08 OK 17 ELTX6201CA0C 17 2 -21.31 OK 18 ELTX6201AB04 18 2 -21.55 OK 19 ELTX62018E48 19 2 -21.67 OK 20 ELTX62014658 20 2 -21.08 OK 21 ELTX6201AB14 21 2 -21.43 OK 22 ELTX62014280 22 2 -21.49 OK 23 ELTX6201CD8C 23 2 -23.01 OK 24 ELTX6201B700 24 2 -21.49 OK 25 ELTX6201C74C 25 2 -21.67 OK 26 ELTX620141F0 26 2 -20.22 OK 27 ELTX62014664 27 2 -23.47 OK 28 ELTX6201CADC 28 2 -22.01 OK 29 ELTX620190E8 29 2 -20.46 OK 30 ELTX62018E84 30 2 -21.55 OK 31 ELTX6201B714 31 2 -20.13 OK 32 ELTX6201D384 32 2 -21.14 OK ----------------------------------- pon-port 16 ONT online list ----------------------------------- ## Serial ONT ID PON-port RSSI StatusTable 21 – ONT status description
ONT status
Description
UNACTIVATED
ONT has no configuration
INIT ONT initialization AUTH
ONT authentication
MIBUPLOAD
MIB ONT upload
CONFIG ONT configuration OK
ONT is in operation
FWUPDATING
ONT firmware update is in progress
FAIL
ONT has a critical failure
OFFLINE
ONT is disabled
List of disconnected ONTs
Step 1. To view the list of offline ONTs, use the show interface ont <ID> offline command. As an argument, specify the PON interface number or a range of numbers.
LLTP-16N# show interface ont 3 offline ----------------------------------- pon-port 3 ONT offline list ----------------------------------- ## Serial ONT ID PON-port Status 1 ELTX5F000F1C 1 3 OFFLINE 2 ELTX5F00056C 2 3 OFFLINE 3 ELTX5F0009E0 3 3 OFFLINE 4 ELTX5F001134 4 3 OFFLINE 5 ELTX5F000120 5 3 OFFLINE 6 ELTX5F000140 6 3 OFFLINE 7 ELTX5F000144 7 3 OFFLINE
View ONT statistics
To view ONT statistics, use the show interface ont 0/0 counters command. As parameters, specify the ONT ID and the type of requested statistics. Two types of pon and gem-ports counters outputs are available:
- pon – shows total ONT packet statistics, including service packets;
- gem-ports – statistics on user traffic within each gem-port.
LTP-16N# show interface ont 2/1 counters gem-port
ONT [2/1] GEM port statistics
GEM port id Rx Packet Rx Bytes Tx Packet Tx Bytes
129 985 66980 0 0
Broadcast 0 0 0 0
Multicast 0 0 186912 255316584
LTP-16N# show interface ont 2/1 counters pon
[ONT 2/1] PON statistics
Drift Positive: 0
Drift Negative: 0
Delimiter Miss Detection: 0
BIP Errors: 0
BIP Units: 284296791264
FEC Corrected symbols: 0
FEC Codewords Uncorrected: 0
FEC Codewords Uncorrected: 0
FEC Codewords: 0
FEC Corrected Units: 0
Rx PLOAMs Errors: 0
Rx PLOAMs Non Idle: 74
Rx OMCI: 292
Rx OMCI Packets CRC Error: 0
Rx Bytes: 128484
Rx Packets: 2233
Tx Bytes: 45504
Tx Packets: 948
BER Reported: 2
System environment configuration
The system has the ability to configure the fans.
Enter show system environment to view the system status.
Fans configuration
Step 1.Set the rotation speed, the default mode is auto.
LTP-16N(configure)# system fan speed 70
Terminal maintenance
SFP transceivers replacement
SFP transceivers can be installed both with the terminal turned off and on. The front panel has pairs of slots: even slots are in the upper line, uneven slots are at the bottom. SFP transceivers are symmetrically installed for each pair of slots.
- Step 1. Insert an SFP transceiver into a slot with its open side down (open side up for the bottom line of slots).
Figure 21 – SFP transceivers installation
- Step 2. Push the module. When it is in place, a distinctive 'click' should be heard.
Figure 22 – installed SFP transceivers
Transceiver removal
- Step 1. Unlock the module latch.
Figure 23 – Opening SFP transceiver latch
- Step 2. Remove the module from the slot.
Figure 24 – SFP transceivers removal
Ventilation units replacement
The terminal design allows ventilation units replacement without powering off the device.
Figure 25 – Ventilation unit. Installation to the case
To remove a ventilation unit:
- Step 1. Use a screwdriver to remove the screws for securing the ventilation unit on the rear panel (Figure 25).
- Step 2. Carefully pull the unit until it is removed from the case.
To install a ventilation unit:
- Step 1. Insert the unit into the terminal case.
- Step 2. Fix the ventilation unit on the rear panel with screws (Figure 25).
Power module replacement
The design of the terminal provides the possibility of replacing one of the power supply units without disconnecting power to the second.
To remove a ventilation unit:
- Step 1. Use a screwdriver to remove the right screw fixing the power supply unit to the rear panel (see Figure 25).
- Step 2. Carefully pull the unit until it is removed from the case.
To install a ventilation unit, perform the following actions:
- Step 1. Insert the unit into the device housing until you hear it click into place.
- Step 2. Secure the power supply unit to the rear panel with the mounting screws (Figure 25).
OLT firmware update
This section describes the terminal firmware update procedure. To download a firmware file, use the TFTP server available in the terminal management network. The device has two areas for firmware files, with the ability to boot from the selected one.
- Step 1. Copy the firmware file into the root folder (or any other known folder) of the TFTP server.
Step 2. Update the firmware by using the copy command.
copy tftp://192.168.1.5/ltp-16n-1.0.0-build1699.fw.bin fs://firmware
Step 3. To view the firmware versions in the sections, use the show firmware
LTP-16N# show firmware Image Running Boot Version Build Date ----- ------- ---- ------- ----- ---------------- 1 yes * 1.4.0 673 12.05.2022 09:25 2 no 1.4.0 672 12.05.2022 07:26 "*" designates that the image was selected for the next boot
Step 4. Select the section that will be applied after reboot.
LTP-16N# firmware select-image alternate
Step 5. Reboot the device.
LTP-16N# reboot
The list of changes
Firmware version | Document version | Issue date | Revisions |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.4.0 | Issue 5 | 22.07.2022 | Synchronization with firmware version 1.4.0 Sections added:
Sections changed:
|
| 1.3.1 | Issue 4 | 28.02.2022 | Synchronization with firmware version 1.3.1 |
| 1.3.0 | Issue 3 | 02.11.2021 | Sections added:
|
1.2.0 | Issue 2 | 28.05.2021 | Synchronization with firmware version 1.2.0 |
1.0.0 | Issue 1 | 30.11.2020 | First issue |