Optical network terminal
NTU-52V
NTU-52VC
Firmware version 1.3.2
IP address: http://192.168.1.1
Login: user
Password: user
Introduction
A GPON is a network of passive optical networks (PON) type. It is one of the most effective state-of-the-art solutions of the last mile issue that enables cable economy and provides information transfer downlink rate up to 2.5 Gbps and uplink rate up to 1.25 Gbps. Being used in access networks, GPON-based solutions allow end users to have access to new services based on IP protocol in addition to more common ones.
The key GPON advantage is the use of one optical line terminal (OLT) for multiple optical network terminals (ONT). OLT converts Gigabit Ethernet and GPON interfaces and is used to connect a PON network with data communication networks of a higher level. ONT device is designed to connect user terminal equipment to broadband access services. It can be used in residential areas and office buildings.
The range of ONT NTU equipment produced by ELTEX comprises of terminals with two UNI interfaces of 10/100/1000Base-T and supports for FXS, USB1, RF2 interfaces:
- NTU-52V, NTU-52VC
This user manual describes intended use, main specifications, configuration, monitoring, and firmware update for NTU-52V/VC optical terminals.
Notes and warnings
Notes contain important information, tips, or recommendations on device operation and setup.
Warnings inform users about hazardous conditions which may cause injuries or device damage and may lead to the device malfunctioning or data loss.
1For NTU-52V
2For NTU-52VC
Product Description
Purpose
NTU-52V/VC GPON ONT (Gigabit Ethernet Passive Optical Network) devices represent high-performance user terminals designed to establish a connection with upstream passive optical network equipment and to provide broadband access services to the end user. GPON connection is established through the PON interface, while Ethernet interfaces are used for connection of terminal equipment.
The key GPON advantage is the optimal use of bandwidth. This technology is considered as the next step in provisioning of new high-speed Internet applications at home and office. Being developed for network deployment inside houses or buildings, these ONT devices provide robust connection with high throughput and at long distances for users living and working at remote apartment and office buildings.
An integrated router allows local network equipment to be connected to a broadband access network. The terminals protect PCs from DoS and virus attacks with the help of firewall and filter packets to control access based on ports and MAC/IP addresses of source and target. Users can configure a home or office web site by adding a LAN port into DMZ. The 'Parental Control' feature provides filtering of Web sites with inappropriate content, domain blocking. Virtual private network (VPN) provides mobile users and branch offices with a protected communication channel for connection to a corporate network.
FXS port enable IP telephony and provide various useful features such as display of caller ID, three-way conference call, phone book, and speed dialling. This makes dialling and call pick-up user friendly.
USB ports can be used for USB-enabled devices (USB flash drives, external HDD).
NTU-52VC device has an integrated RF output, to which a TV is connected to watch analog or digital cable television (if the service is provided by the carrier).
Models
NTU-52V/VC series devices are designed to support various interfaces and features, see Table 1.
Table 1 – Models
| Model name | WAN | LAN | FXS | TV | USB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NTU-52V | 1xGPON | 1xFastEthernet, 1xGigabit Ethernet | 1 | - | 1 |
| NTU-52VC | 1xGPON | 1xFastEthernet, 1xGigabit Ethernet | 1 | 1 | - |
Device Specification
Device is equipped with the following interfaces:
- Ports to connect network devices (FXS):
- 1xPON SC/APC port for connection to provider's network (WAN);
- Ethernet RJ-45 LAN ports for connection of network devices (LAN):
- 1 port of RJ-45 10/100Base-T (for details see Section 3. Design);
- 1 port of RJ-45 10/100/1000Base-T (for details see Section 3. Design);
- 1 USB 2.0 port for external USB or HDD storages2.
- 1 RF port for cable television (CaTV) connection1.
1Only for NTU-52VC
2Only for NTU-52V
The device supports the following functions: The terminal uses an external adapter for 220V/12V power supply.
- Network functions:
- bridge or router operation mode;
- PPPoE (auto, PAP, CHAP, MSCHAP authorization);
- IPoE (DHCP-client and static);
- static IP address and DHCP (DHCP client on WAN side, DHCP server on LAN side);
- DNS (Domain Name System);
- DynDNS (Dynamic DNS);
- UPnP (Universal Plug and Play);
- IPsec (IP Security);
- NAT (Network Address Translation);
- Firewall;
- NTP (Network Time Protocol);
- QoS;
- IGMP snooping;
- IGMP proxy;
- Parental Control;
- Storage service;
- SMB, FTP, Print Server;
- VLAN in accordance with IEEE 802.1Q.
- VoIP
- SIP
- audio codecs: G.729 (A), G.711(A/U), G.723.1;
- echo cancellation (G.164 and G.165 guidelines);
- Voice activity detection (VAD);
- Comfort noise generator (CNG);
- DTMF signal detection and generation
- DTMF transmission (INBAND, RFC2833, SIP INFO)
- Fax transmission: G.711, T.38
- Caller ID display.
- Firmware updates via web interface, TR-069, OMCI.
- Remote monitoring, configuration and setup:
- TR-069;
- Web interface;
- OMCI.
- CaTV1.
1Only for NTU-52VC
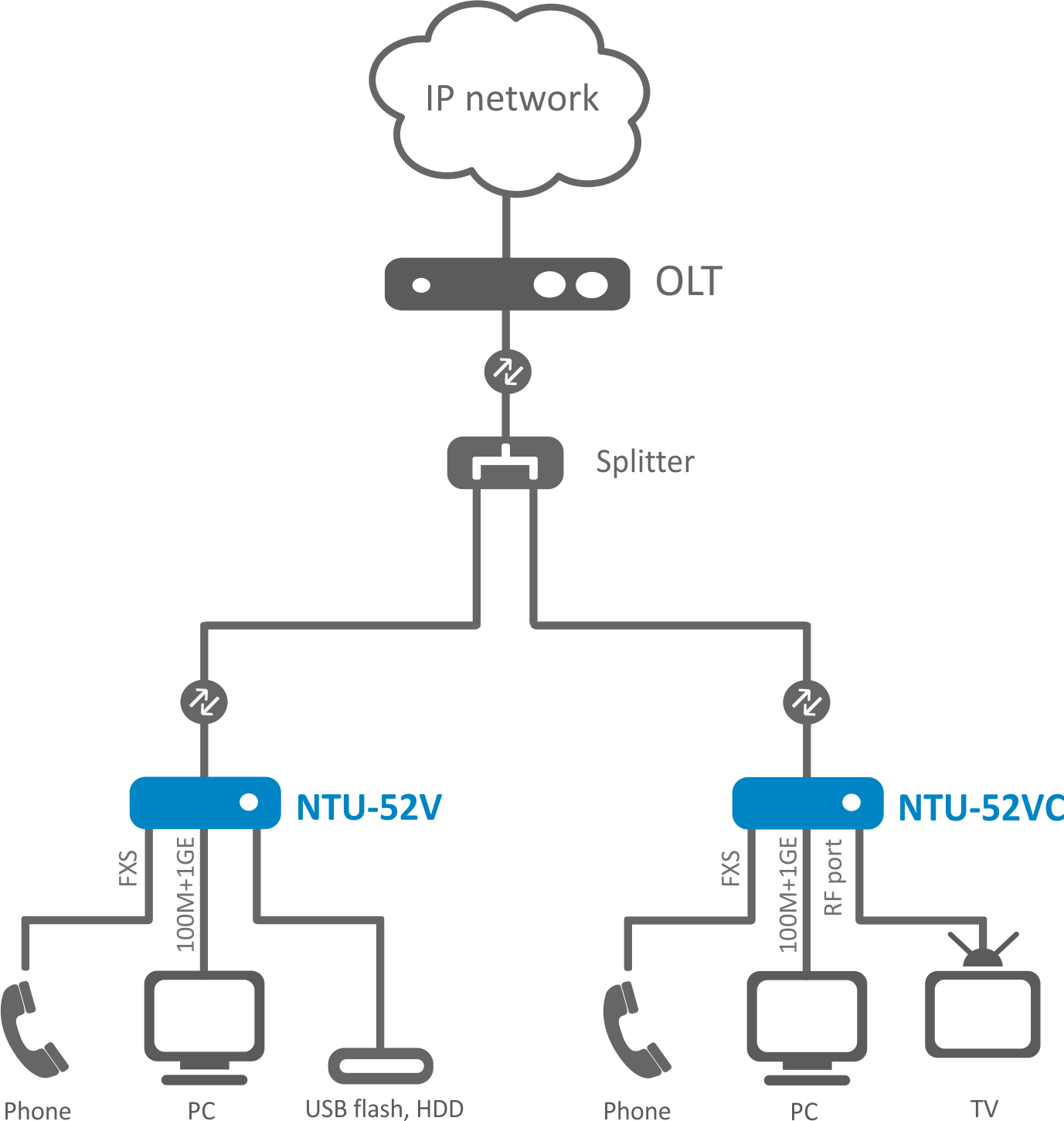
The figures below illustrate applications schemes of NTU-52V/VC.
Figure 1 – NTU-52V and NTU-52VC application diagram
Key Specifications
Table 2 shows main specifications of the terminals:
Table 2 — Main Specifications
VoIP protocols
Supported protocols | SIP |
|---|
Audiocodecs
Codecs | G.729, annex A |
|---|
Ethernet LAN interface parameters
Number of interfaces | 2 |
|---|---|
Socket | RJ-45 |
Data rate | Auto-negotiation, 10/100/1000 Mbps, |
Standards | IEEE 802.3i 10Base-T Ethernet |
PON interface parameters
Number of interfaces | 1 |
|---|---|
| Standards | ITU-T G.984.x Gigabit-capable passive optical networks (GPON) ITU-T G.988 ONU management and control interface (OMCI) specification IEEE 802.1Q Tagged VLAN (The following VLANs are used for internal operation and cannot be used to create WAN services: 0, 4032, 4039, 4022, 4023, 4024, 4027, 4026, 4000~4005, 4095) IEEE 802.1P Priority Queues IEEE 802.1D Spanning Tree Protocol |
| Connector type | SC/APC in accordance with ITU-T G.984.2, ITU-T G.984.5 Filter, FSAN Class B+, SFF-8472 |
| Transmission environment | Fiber optical cable SMF—9/125, G.652 |
| Splitting ratio | Up to 1:128 |
| Maximum range of coverage | 20 km |
| Transmitter: | 1310 nm |
| 1244 Mbps |
| +0,5 to +5 dBm |
| 1 nm |
| Receiver: | 1490 nm |
| 2488 Mbps |
| from -8 to -28, BER≤1.0x10-10 |
| Receiver optical congestion | -4 dBm |
Subscriber analogue ports parameters
| Number of ports | NTU-52V | NTU-52VC |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | |
| Loop resistance | Up to 2 kΩ | |
| Call reception | Pulse/frequency (DTMF) | |
| Caller ID display | Yes | |
Control
| Local control | Web interface |
|---|---|
| Remote control | Telnet, TR-069, OMCI |
| Firmware update | OMCI, TR-069, HTTP |
| Acces restriction | By password |
General parameters
| Model | NTU-52V | NTU-52VC | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Power supply | 12 VDC/220 VAC power adapter | 12 VDC/220 VAC power adapter | |
| RF port | - | 1 | |
| Max. power consumption | 10 W | ||
| Operating temperature | From +5 to +40°С | ||
| Relative humidity | 80% max. | ||
| Dimensions | 147×110×24 mm | 160×120×40 mm | |
| Weight | 0,3 kg | ||
Design
Subscriber terminal is designed as desktop device in plastic housing.
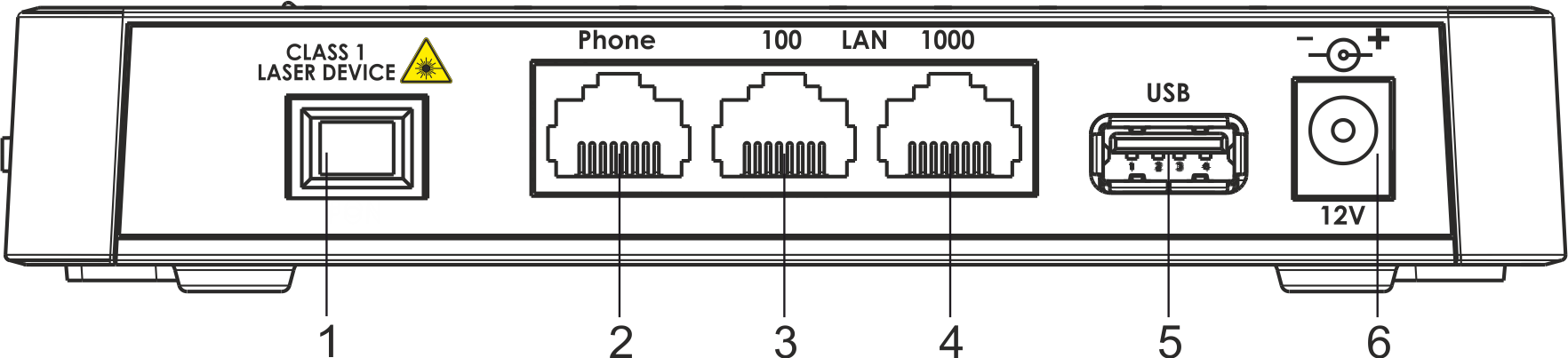
The rear panel layout of the devices is depicted in Fig. 2, 3.
Figure 2 — NTU-52V rear panel layout
Connectors and controls located on the rear panel of 52V are listed in Table 3.
Table 3 – Description of the connectors and controls on the rear panel
# | Rear panel element | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | PON | SC port (socket) for PON with GPON interface |
2 | Phone | RJ-45 connector for analogue phone connection |
| 3 | LAN 10/100 | RJ-45 port for network devices connection (Ethernet/Fast Ethernet) |
4 | LAN 10/100/1000 | RJ-45 port for network devices connection (Gigabit Ethernet) |
5 | USB | Connector for external drives and other USB devices |
6 | 12V | Power adapter connector |
Connectors and controls located on the rear panel of 52VC are listed in Table 4.
Table 4 – Description of the connectors and controls on the rear panel
# | Rear panel element | Description |
|---|---|---|
1 | On/Off | Power button |
| 2 | 12V | Power adapter connector |
| 3 | F | A functional key that reboots the device and resets it to factory settings |
| 4 | TV | RF port for connecting a coaxial cable |
| 5 | LAN 10/100 | RJ-45 port for network devices connection (Ethernet/Fast Ethernet) |
| 6 | LAN 10/100/1000 | RJ-45 port for network devices connection (Gigabit Ethernet) |
| 7 | Phone | RJ-11 connector for analogue phone connection |
| 8 | PON | SC port (socket) for PON with GPON interface |
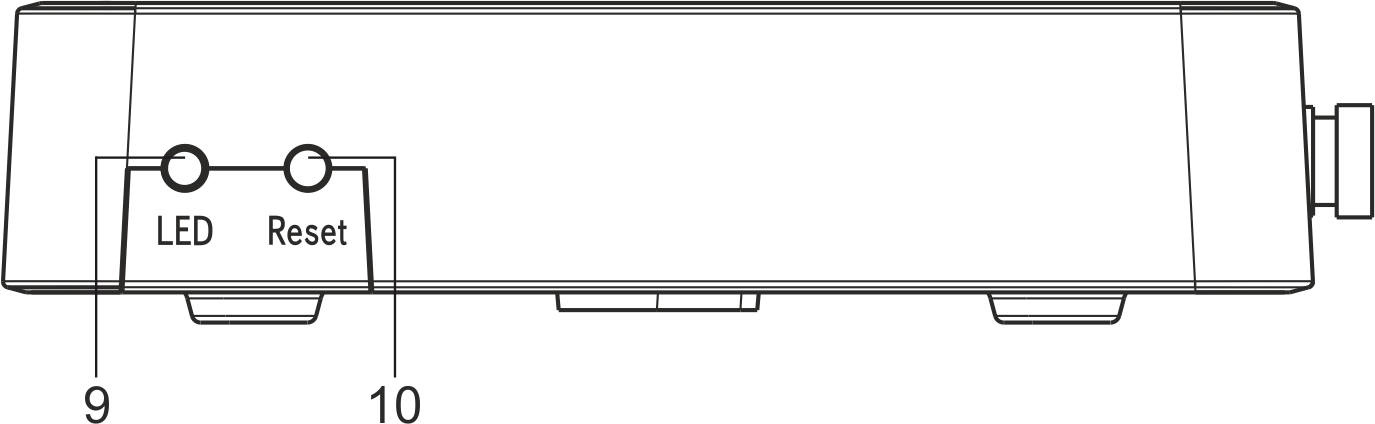
The side panel layout of the NTU-52V is depicted in figure below.
Figure 4 — NTU-52V side panel layout
See Table 5 for detailed information about buttons located on the side panel of the device.
Table 5 – Description of the side panel LED indicators
# | Side panel element | Description |
|---|---|---|
1 | LED | LED on/off button |
2 | Reset/restore | A functional key that reboots the device and resets it to factory settings |
Light Indication
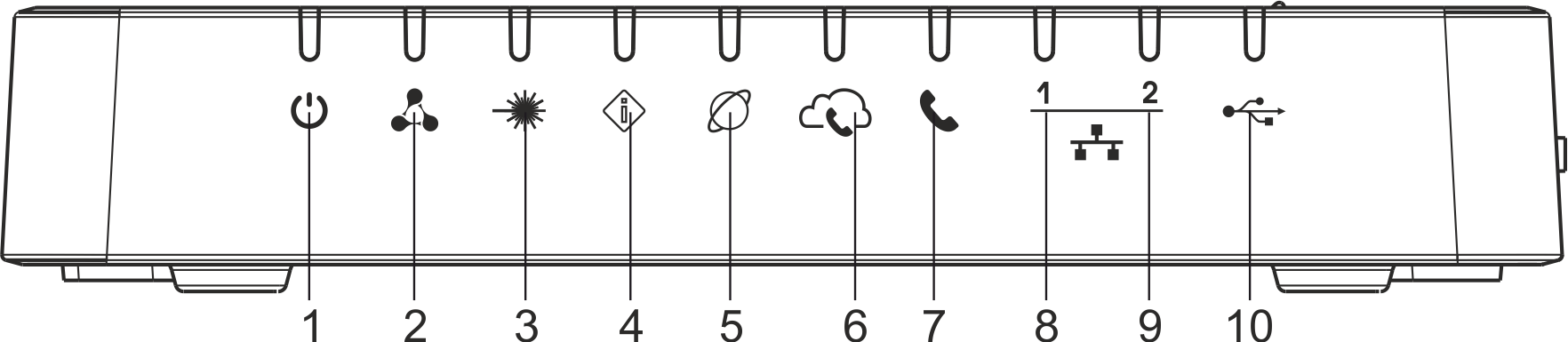
The top panel layout of the NTU-52V is depicted in Fig. 5, the front panel layout is depicted in Fig. 6.
Figure 5 — NTU-52V top panel layout
Figure 6 — NTU-52V front panel layout
The LED indicators located on the top and front panels show the current device status. Table 6 lists possible statuses of the LEDs.
Table 6 – Description of NTU-52V front and top panel LEDs
# | Front panel element | LED Status | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
1 | - power indicator | green | power is connected |
| off | power is not connected | ||
| 2 | - operation status indicator | flashes slowly | the firmware update process is in progress |
| orange | device startup is completed, the default configuration is set | ||
| green | device startup completed, the current device configuration differs from the default | ||
3 | - optical interface operation indicator | off | the device is not connected to OLT |
| flashes green | the device is in the registration process on OLT | ||
| green | the device is connected and registered on OLT | ||
| 4 | - optical interface status indicator | off | the device is connected to OLT |
| flashes red | laser is off at LT side | ||
| red | there is no signal from OLT | ||
5 | - 'Internet' status indicator | off | there is no active connection to Internet |
| green | the device is ready, connection established | ||
| flashes green | the device is in connection process | ||
| 6 | - SIP registration indicator | off | VoIP service is not configured |
| green | VoIP service is successfully activated | ||
| flashes green | port is not registered or SIP authentication is not completed on server | ||
7 | - FXS port activity indicator | off | phone is off hook |
| flashes green | receiving a call | ||
| green | phone is on hook | ||
8-9 | - 1..2 – Ethernet port activity indicator | green | established 10/100 Mbps connection |
| orange | established 1000 Mbps connection | ||
| flashes green/orange rapidly | data transfer is in progress | ||
| 10 | - USB port operation indicator | off | USB device is not connected |
| green | USB device is connected | ||
| flashes green | data transfer is in progress |
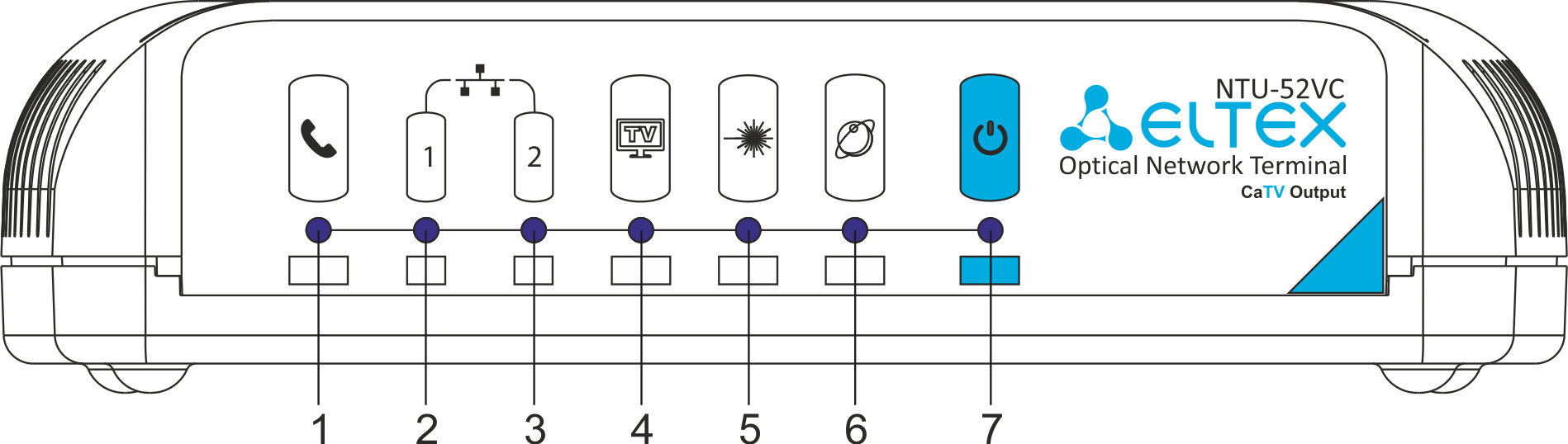
The front panel layout of the NTU-52VC is depicted in Figure 7.
Figure 7 — NTU-52VC front panel layout
The LED indicators located on the front panel show the current state of the device. Table 7 provides possible statuses of the LEDs.
Table 7 – Description of NTU-52VC front panel LEDs
| # | Front panel element | LED Status | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | – FXS port activity indicator | off | phone is off hook |
| flashes green | receiving a call | ||
| green | phone is on hook | ||
| 2-3 | -1 – 10/100 Mbps Ethernet port operation indicator | green | established 10/100 Mbps connection |
| flashes green rapidly | data transfer is in progress | ||
-2 – 10/100/1000 Mbps Ethernet port operation indicator | green | established 10/100 Mbps connection | |
| orange | established 1000 Mbps connection | ||
| flashes green/orange rapidly | data transfer is in progress | ||
| 4 | – TV operation status indicator | off | RF port is disabled |
| orange | CaTV signal power is in the range from -10 dBm..-8 dBm or +2 dBm..+3 dBm | ||
| green | -8dBm < CaTV signal power < +2dBm | ||
| 5 | – optical interface activity indicator | off | device is rebooting |
| flashes red | the device is not connected to OLT | ||
| flashes green | the device is in the registration process on OLT | ||
| green | the device is connected and registered on OLT | ||
| 6 | – 'Internet' operation status indicator | off | there is no active connection to Internet |
| green | the device is ready, connection established | ||
| orange | the device is in connection process | ||
| 7 | – power indicator | off | power is disconnected or device is fault |
| green | device startup completed, the current device configuration differs from default | ||
| orange | device startup is completed, the default configuration is set | ||
| red | device is booting | ||
| flashes slowly | the firmware update process is in progress |
Reboot and Reset to Factory Settings
To reboot the device, press the 'Reset' button located on its side panel. In order to reset the device to the factory settings, press the 'Reset' button and hold it for 7-10 seconds until the indicator glows red and all other LEDs go out. Factory settings for IP address are: LAN - 192.168.1.1, subnet mask – 255.255.255.0. Access can be provided from LAN 1 and LAN 2.
Delivery Package
The NTU-52V/VC standard delivery package includes:
- NTU-52V/VC optical network terminal;
- 220V/12V power adapter;
- User manual.
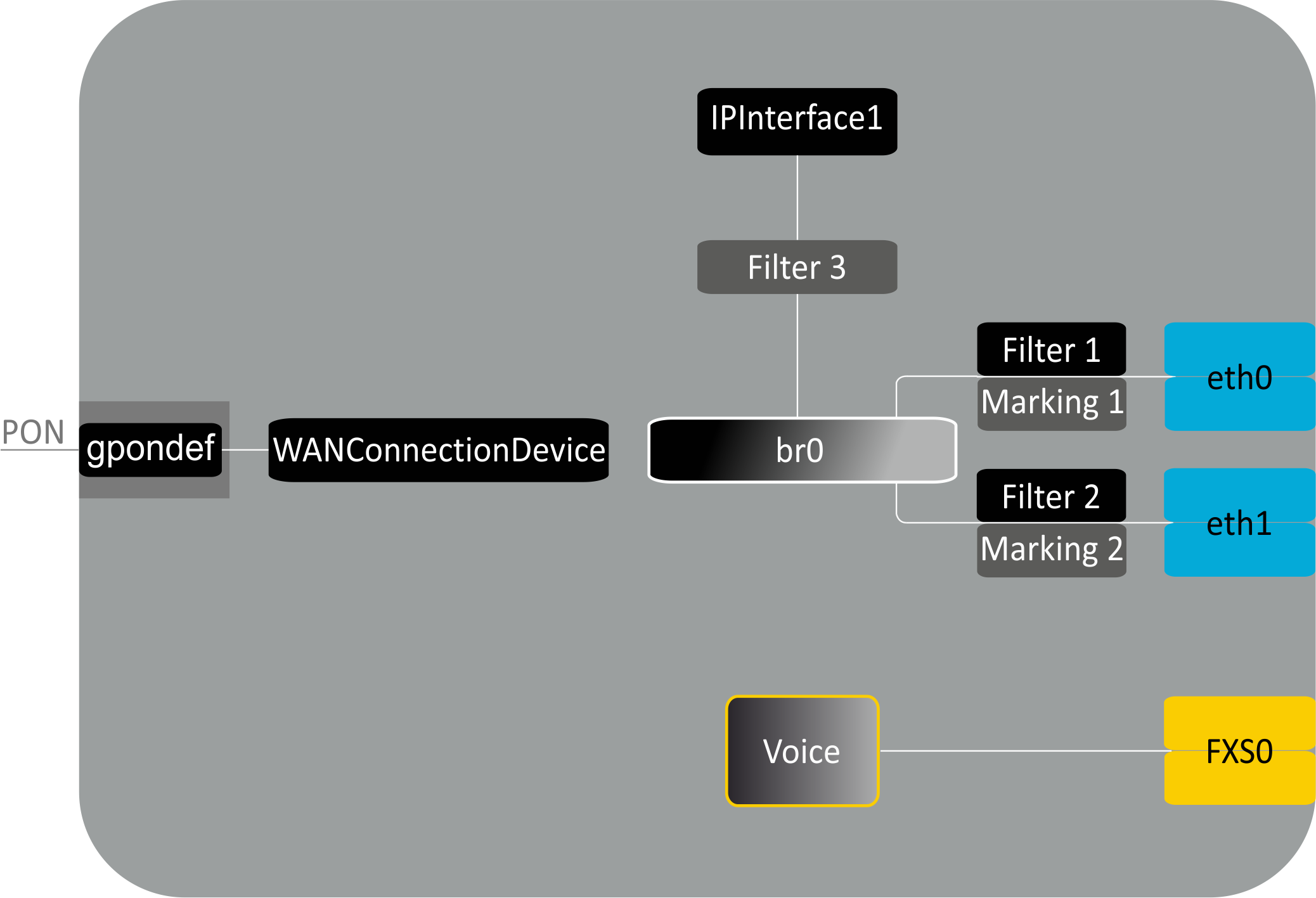
NTU-52V/VC architecture
Figure 8 – Logical architecture of a device with factory settings
Main Components of the Device:
- Optical receiver/transmitter (SFF module) for conversion of an optical signal into an electric one;
- Processor (PON chip) which converts Ethernet and GPON interfaces;
A device with factory (initial) settings have the following logical blocks (see Fig.8):
- Br0;
- Voice (VoIP block);
- eth0…1;
- FXS0;
- IPInterface1.
Br0 block here is used to combine LAN ports into a single group.
The eth0..1 blocks physically represent Ethernet ports with RJ-45 connector for connection of PC, STB, or other network devices. They are logically included into br0 block
FXS0 block is a port with RJ-11 connectors for connection of analogue phone. It is logically included into the Voice block. The Voice block can be controlled through web interface or remotely with ACS server via TR-069 standard. The block specifies VoIP service parameters (SIP server address, phone number, VAS, etc.).
Filter and Marking blocks enable inclusion of local interfaces into a single group (to br0 block). They deal with the traffic transmission rules, Filter blocks are responsible for the incoming traffic on the interface, Marking blocks – for the outgoing one.
IPInterface1 block is a logical entity on which IP address providing the access in LAN and DHCP server distributing addresses to clients are located.
Device configuration via Web interface. Administrator Access
Getting Started
To configure the device, it is necessary to connect to it through Web browser:
1. Open the Web browser (program for viewing hypertext documents), for example, Firefox, Google Chrome and etc.
2. Enter the device IP address in the browser address line
Factory default IP address: 192.168.1.1, subnet mask: 255.255.255.0
When the device is successfully connected, username and password request page will be shown in the browser window:
3. Enter your username into ‘User Name’ and password into ‘Password’ field.
Username: user, password: user.
4. Click the ‘Login’ button. In the browser window, the home page of the device’s web interface will open.
Password changing
To prevent unauthorized access to device in the future, it is recommended to change password. To change the password enter the new password in the 'Admin' menu, 'Password' section in the 'New Password' and 'Confirm new password' fields.
Main elements of the web interface
General view of the device configuration window is depicted below.
The user interface window can be divided into 3 parts:
- The navigation tree on the device settings menu.
- The main settings window for the selected section.
- User change button.
The 'Status' menu. Device Information
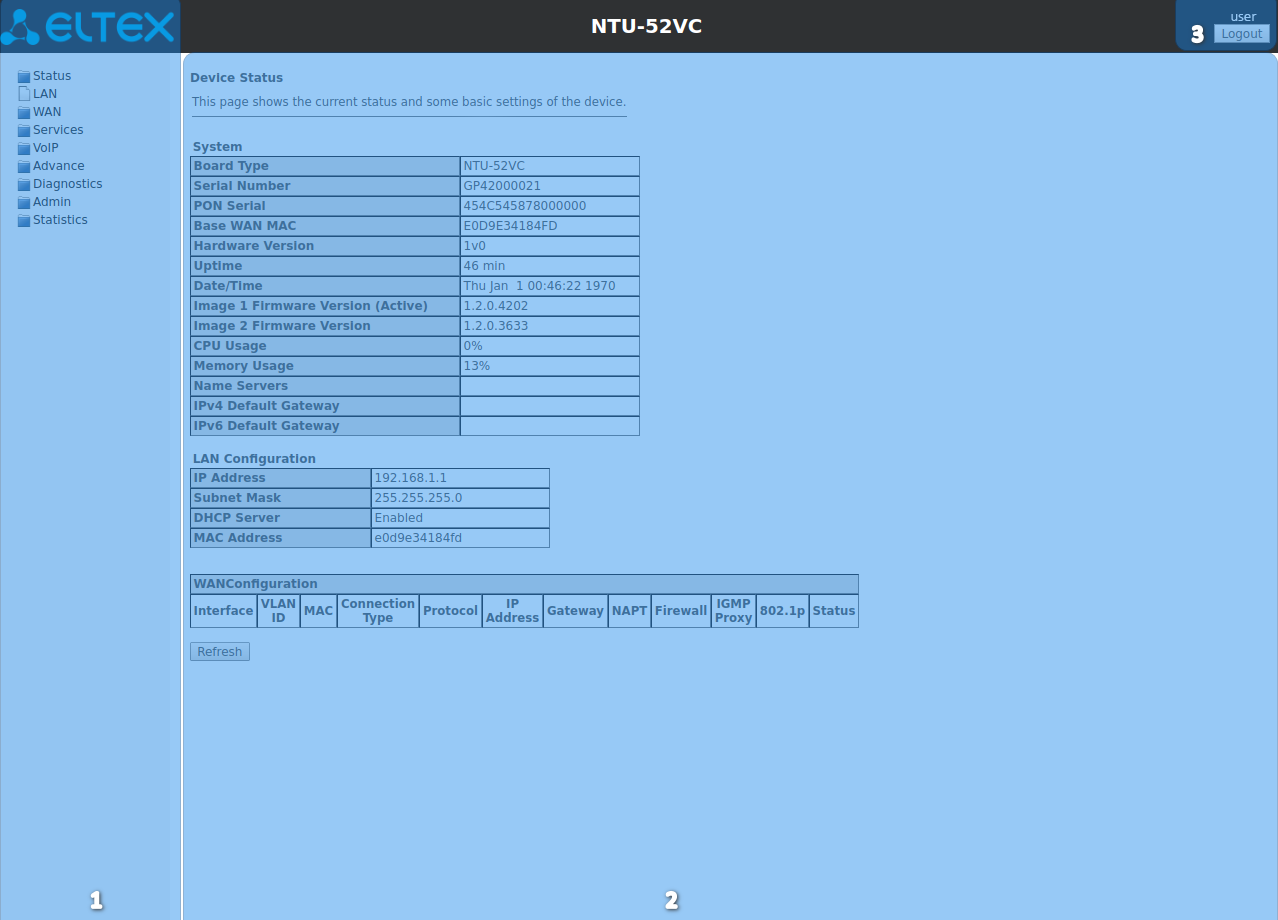
The 'Device status' submenu. Device General Information
This section displays general information about the device, the main parameters of the LAN and WAN interfaces.
Status → Device status
System
- Board Type – device model;
- Serial Number – device serial number;
- PON Serial – device serial number in the PON network;
- Base WAN MAC – WAN MAC address of the device;
- Hardware Version – hardware version;
- Uptime – device uptime;
- Date/Time – current time on the device;
- Image 1 Firmware Version (Active) – current firmware version;
- Image 2 Firmware Version – backup firmware version;
- CPU Usage – CPU utilization percent;
- Memory Usage – memory utilization percent;
- Name Servers – DNS server name;
- IPv4 Default Gateway – IPv4 default gateway;
- IPv6 Default Gateway – IPv6 default gateway.
LAN Configuration
- IP Address – device IP address;
- Subnet Mask – device subnet mask;
- DHCP Server – DHCP server state;
- MAC Address – device MAC address.
WAN Configuration
- Interface – interface name;
- VLAN ID – interface VLAN ID;
- MAC – interface MAC address;
- Connection Type – connection type;
- Protocol – protocol used;
- IP Address – Interface IP address;
- Gateway – gateway;
- Status – interface status.
Click the 'Refresh' button to update the page.
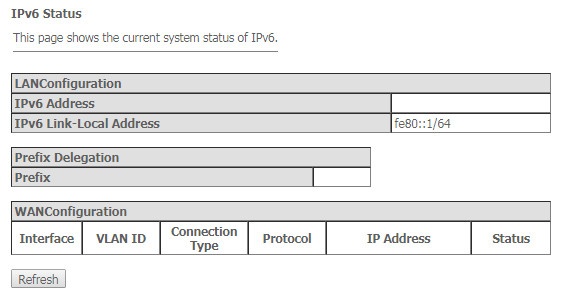
The 'IPv6 Status' submenu. Information about IPv6 system
The tab displays the current status of IPv6 system.
Status → IPv6
LAN Configuration
- IPv6 Address – IPv6 address;
- IPv6 Link-Local Address – local IPv6 address.
Prefix Delegation
- Prefix – IPv6 address prefix.
WAN Configuration
- Interface – interface name;
- VLAN ID – interface VLAN ID;
- Connection Type – connection type;
- Protocol – protocol used;
- IP Address – interface IP address;
- Status – interface status.
Click the 'Refresh' button to update the page.
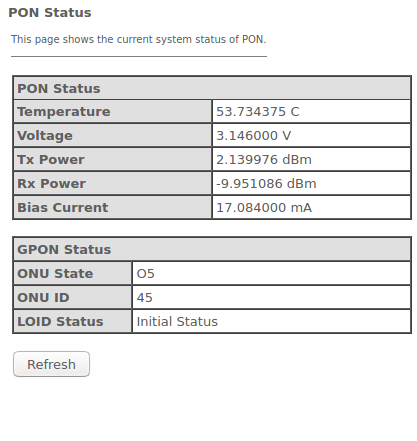
The 'PON' submenu. Optical module status information
The tab displays the current status of PON interface system.
Status → PON
PON Status
- Temperature – current temperature;
- Voltage – voltage;
- Tx Power – transmission signal power;
- Rx Power – reception signal power;
- Bias Current – bias current;
- Video Power – video signal power.
PON Status
- ONU State – ONU status;
- ONU ID – ONU ID;
- LOID Status – LOID status.
Click the 'Refresh' button to update the page.
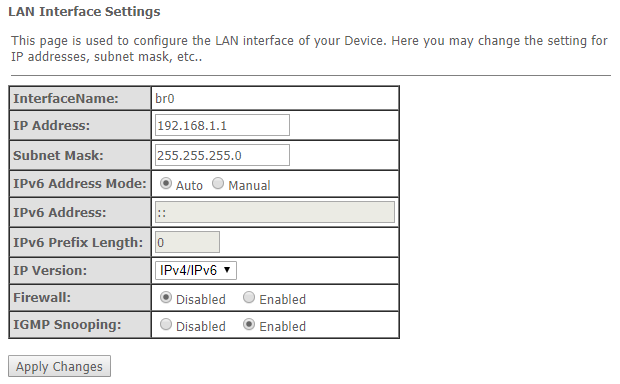
The 'LAN' menu LAN interface configuration
You can configure main parameters of LAN interfaces in this section.
LAN
- Interface name – interface name;
- IP Address – interface IP address;
- Subnet Mask – interface subnet mask;
- IPv6 Address Mode – access to the device via IPv6 address:
- Auto – when checked, the access to the device via IPv6 address will be granted automatically;
- Manual – when checked, you need to specify the IPv6 address manually :
- IPv6 Address – IPv6 address;
- IPv6 Prefix Length – length of the IPv6 address;
- IP Version – IP protocol version used (IPv4 or IPv4/IPv6);
- Firewall (Enabled/Disabled) – enable/disable firewall for LAN interface;
- IGMP Snooping (Enabled/Disabled) – enable/disable IGMP Snooping.
The Services menu. Service configuration
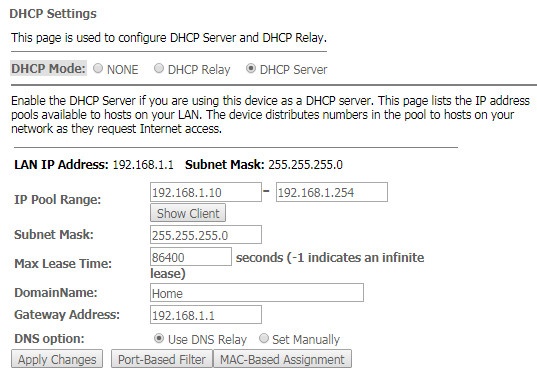
The 'DHCP Setting' submenu. DHCP configuration
The menu allows DHCP server and DHCP repeater configuration.
Services → DHCP (Server)
- DHCP Mode– select operation mode:
- NONE – DHCP disabled;
- DHCP Server – operation in DHCP server mode;
- DHCP Relay – operation in DHCP repeater mode.
- IP Pool Range – range of addresses distributed among clients;
- Show Client – button to view clients who leased the addresses. When clicking, a table with information about DHCP clients leased by a DHCP server is displayed;
- Subnet Mask – subnet mask;
- Max Lease Time – maximum lease time, -1 for endless lease;
- DomainName– domain name;
- Gateway Address – gateway address;
- DNS option – defines DNS operation:
- Use DNS relay – ONT address will be returned as DNS and all queries will be relayed via ONT;
- Set manually – set DNS manually.
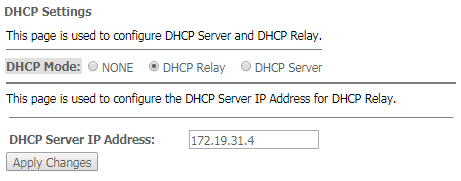
Services → DHCP (Relay)
- DHCP Server IP Address – IP address of the remote DHCP server.
To save the changes, click the 'Apply Changes' button. 'Port-Based Filter' and 'MAC-Based Assignment' buttons allow configuring port-based and MAC-based filtering, respectively.
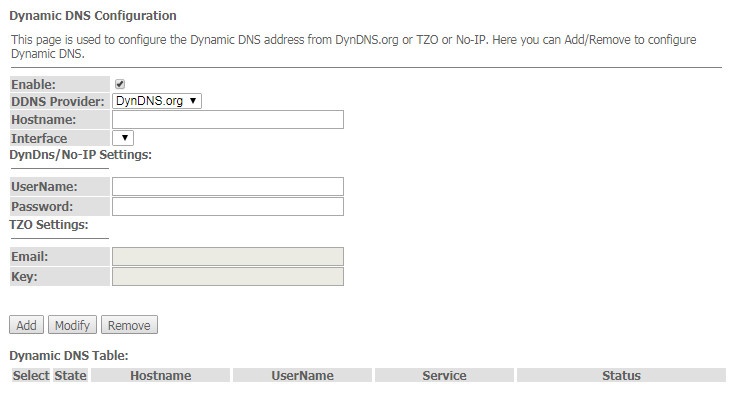
The 'Dynamic DNS' submenu. Dynamic DNS Configuration
Dynamic DNS (domain name system) allows information to be updated on DNS server in real time and (optionally) automatically. It is applied for assignment of a constant domain name to a device (computer, router, e.g. NTU-52V/VC) having a dynamic IP address. The IP address can be assigned by IPCP in PPP connections or in DHCP.
Dynamic DNS is frequently used in local networks where clients are obtaining IP addresses through DHCP and then are registering their names on a local DNS server.
Services → DNS → Dynamic DNS
- Enable – when selected, enable DHCP server (IP addresses from the following range will be dynamically assigned to network devices);
- D-DNS Provider – select the type of D-DNS service (provider): DynDNS.org, TZO.com, No-IP.com
- Custom – another provider selected by user. In this case, you need to specify the provider's name (Hostname) and address (Interface).
DynDns/No-IP Settings:
- UserName – user name;
- Password – authorization password on the service selected for operation with D-DNS.
'Dynamic DNS Table' table with the list of available DNS displayed in this section. To add a record, click the 'Add' button. To remove/modify a record, click the 'Remove'/'Modify' button for the selected record.
The 'Firewall' submenu. Firewall configuration
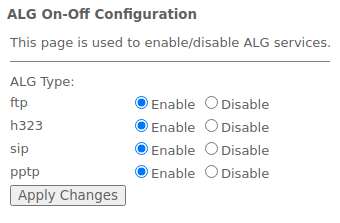
The 'ALG' submenu. Enable/disable ALG services
This section is used to enable/disable ALG services.
Application-level gateway ( ALG) — NAT router component that understands an application protocol and, when packets of that protocol pass through, modifies them so that users behind the NAT can use the protocol.
Services → Firewall → ALG
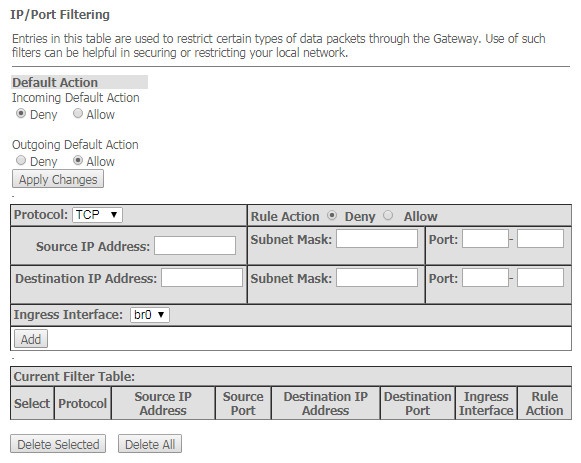
The 'IP/Port Filtering' submenu. Address Filtering Settings
This section is used to configure address filtering. The IP Filtering function filters router traffic by IP addresses and ports.Using these filters can be useful to protect or restrict the local network.
Services → Firewall → IP/Port Filtering
Default action
- Incoming Default Action Deny/Allow – filtering for incoming packets;
- Outgoing Default Action Deny/Allow – filtering for outgoing packets.
To save the changes, click the 'Apply Changes' button.
To add a filter, fill in the appropriate fields and click the 'Add' button:
- Protocol – filtering protocol;
- Rule Action Deny/Allow – packet processing policy (deny/allow);
- Source IP Address – source IP address;
- Destination IP Address – destination IP address;
- Subnet mask – subnet mask;
- Port – port.
- Ingress Interface – ingress interface.
Added filters are displayed in the 'Current Filter Table' located below. The entries in this table are used to restrict certain types of data packets pass through the gateway. To delete a specific filter, select the position and click the 'Delete selected' button, to delete all filters click 'Delete All'.
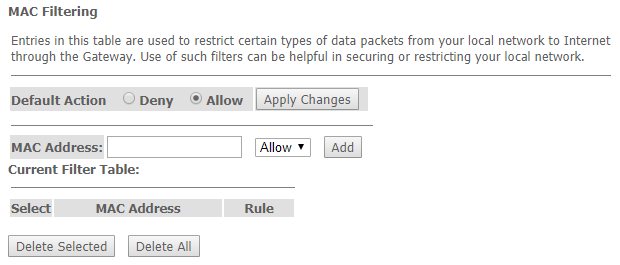
The 'MAC Filtering' submenu. Filtering Settings for MAC Addresses
MAC filtering allows traffic to be forwarded or blocked depending on source and destination MAC addresses. To change the mode click the 'Apply Changes' button.
Services → Firewall → MAC Filtering
- Default Action – default settings:
- Deny – when checked, traffic pass is prohibited by default;
- Allow – when checked, traffic pass is allowed by default;
- MAC Address – MAC address for which limitation/access should be imposed.
Added filters are displayed in the 'Current Filter Table' located below. The 'Rule' field displays the type of created rule ('Allow' - allowing or 'Deny' - forbidding). To remove selected items in the list, click 'Delete Selected'; click 'Delete All' to remove the whole list.
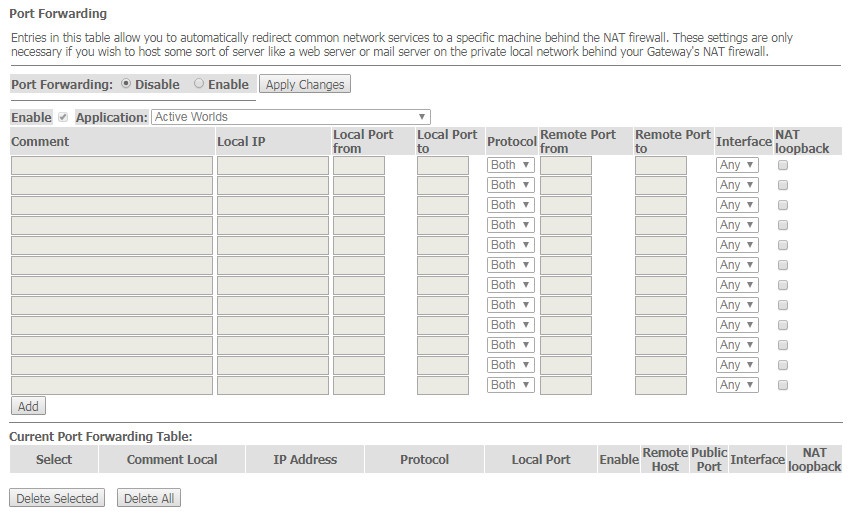
The 'Port Forwarding' submenu. Port forwarding configuration
'Current Port Forwarding Table' with port forwarding information is displayed in this section. Entries in this table allow you to automatically redirect common network services to a specific machine behind the NAT firewall. These settings are only necessary if you wish to host some sort of server like a web server or mail server on the private local network behind your router's NAT firewall. To save the changes, click the 'Apply Changes' button.
Services → Firewall → Port Forwarding
To add the entry in the 'Current Port Forwarding Table' check the Enable flag and fill in the corresponding fields:
- Port Forwarding (Enable/Disable) – enable/disable port forwarding feature;
- Application – this menu has pre-settings for various applications port forwarding;
- Comment – comment;
- Local IP – local IP address to which forwarding is performed;
- Local port from/to – specify the range of local device ports for forwarding;
- Protocol – select protocol (TCP, UDP or both);
- Remote port from/to – specify the initial port of incoming connection. The 'Remote port to' field will be filled automatically;
- Interface – select interface;
- NAT-loopback – NAT loop allows transferring queries from LAN to the router, thus, for example, you can check the work of rules created.
After filling the fields click the 'Add' button to add the entry. To delete a selected position, click the 'Delete Selected' button; to delete the whole table, click the 'Delete All' button.
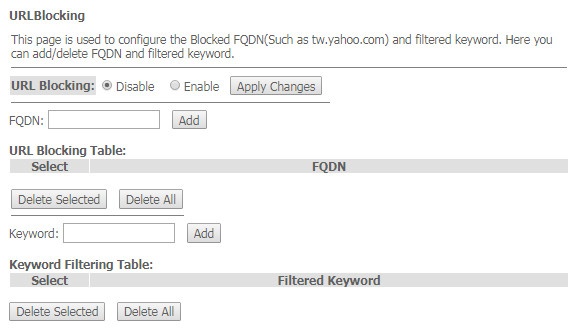
The 'URL Blocking' submenu. Internet access restriction configuration
URL filter performs complete analysis and provides access control to specific Internet resources. This section sets and displays a list of forbidden/allowed URLs to visit. Here you can add the forbidden/allowed FQDN (Fully Qualified Domain Name) with the 'Add' button, filtering by keywords is also possible. The added restrictions are displayed in the 'URL Blocking Table' and the 'Keyword Filtering Table'. To remove a specific URL or keyword from the table, click on it and then on the 'Delete Selected' button. To delete all restrictions click the 'Delete All' button.
Services → Firewall → URL Blocking
- URL Blocking (Enable/Disable) – enable/disable URL Blocking operation;
- FQDN – Fully Qualified Domain Name;
- Keyword – keyword.
To save the changes, click the 'Apply Changes' button.
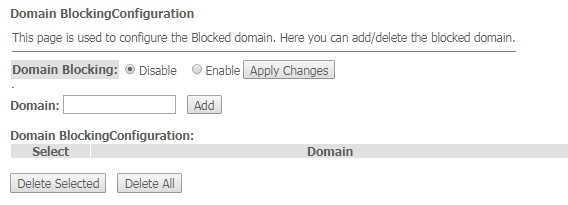
The 'Domain Blocking' submenu. Domain blocking configuration
This section is used to set domain blocking.
Services → Firewall → Domain blocking
To block the domain check Enable, fill the Domain field and click the 'Add' button.
- Domain Blocking (Enable/Disable) – enable/disable blocking;
- Domain – domain name.
To save the changes, click the 'Apply Changes' button. All blocked domains are listed in the 'Domain BlockingConfiguration' table, to remove a blocking for one domain, select it and click the 'Delete Selected' button, to remove all restrictions, click the 'Delete All' button.
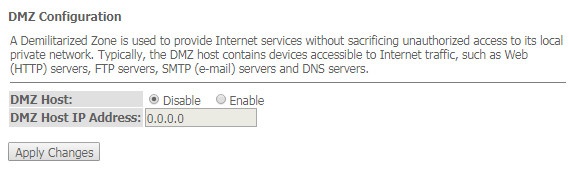
The 'DMZ' submenu. Demilitarized Zone configuration
When an IP address is set in the 'DMZ host IP address field', all requests from external network, that do not satisfy the 'Port Forwarding' rules, will be redirected to a DMZ host (a trusted host with the specified address in the local network).
Services → Firewall → DMZ
- DMZ Host (Enable/Disable) – enable/disable the host;
- DMZ Host IP Address – IP address.
To save the changes, click the 'Apply Changes' button.
The 'UPnP' submenu. Automated Setup of Network Devices
In this section you can configure Universal Plug and Play (UPnP™) function. UPnP ensures compatibility with network equipment, software and peripheral devices.
Services → UPnP
The use of UPnP requires NAT setup on an active WAN interface.
- UPnP (Enable/Disable) – enable/disable the UPnP function;
- WAN Interface – WAN interface on which the UPnP function will operate;
To save the settings, click the 'Apply Changes' button.
The 'RIP' submenu. Dynamic routing configuration
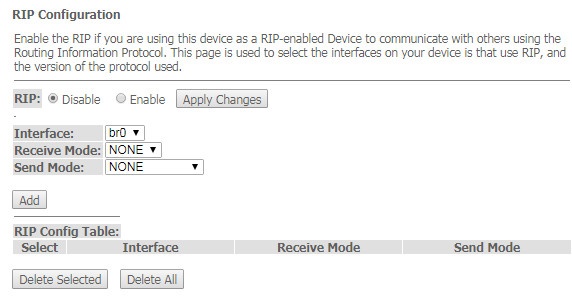
This section is used to select the interfaces on your device is that use RIP, and the version of the protocol used. Enable the RIP if you are using this device as a RIP-enabled Device to communicate with others using the Routing Information Protocol.
Services → RIP
- RIP (Enable/Disable) – enable/disable the use of dynamic routing protocol RIP;
To accept and save the settings, click the 'Apply Changes' button.
- Interface – interface on which RIP will be started;
- Receive Mode – incoming packets processing mode (NONE, RIP1, RIP2, both);
- Send Mode – sending mode (NONE, RIP1, RIP2, RIP1 COMPAT).
Interfaces with the support for RIP are displayed in the 'RIP Config Table'. To delete all entries in the table click the 'Delete All' button; to delete one position from the list select it and click 'Delete Selected'.
The 'Samba' submenu. Configuration of Samba users
In this submenu you can configure Samba users.
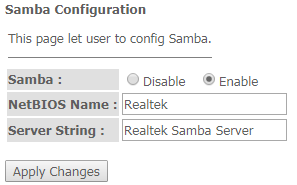
Services → Samba → Samba
- Samba Enable/Disable – enable/disable Samba configuration;
- Server String – server name.
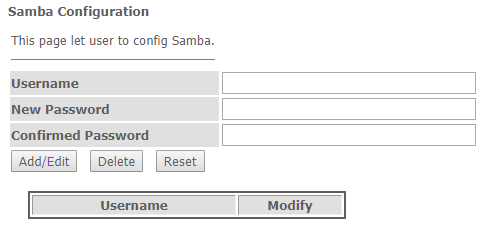
In the 'Accounts' section you can create personal Samba accounts.
Services → Samba → Accounts
- Username – account name;
- New password – password;
- Confirmed Password – password confirmation.
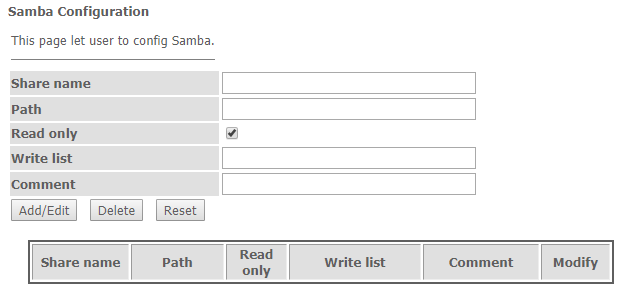
The 'Shares' section is used to add Samba library.
Services → Samba → Shares
- Share name – library name;
- Path – path to library;
- Read only – read only;
- Write list – list of accounts who can change files in the library;
- Comment – comment for the library.
The 'Advance' menu. Advanced settings
The 'ARP Table' menu. View ARP cache
This section shows a list of learned MAC addresses. The ARP efficiency depends a lot on ARP cache presented in every host. The cache contains Internet addresses and corresponding hardware addresses. Every record created in the cache is stored for 5 minutes.
Advance → ARP table
- IP Address – IP address of the client;
- MAC Address – МАС address of the client.
To update the information, click the 'Refresh' button.
The 'Bridging' submenu. Bridging parameters configuration
In this section you can configure bridge parameters. Here you can configure aging time of addresses in MAC table as well as to enable/disable 802.1d Spanning Tree.
Advance → Bridging
- Ageing Time – address lifetime (s);
- 802.1d Spanning Tree (Enable/Disable) – enable/disable 802.1d Spanning Tree protocol.
To save the changes, click the 'Apply Changes' button.
To view the information about bridge and its connected ports click the 'Show MACs' button.
Advance → Bridging → Show MACs
- Port – port number;
- MAC Address – MAC address;
- Is Local – local address;
- Ageing Timer – address lifetime.
To update the information in the table, click the 'Refresh' button, to close the table, click 'Close'.
The 'Routing' submenu. Routing configuration
This submenu is used to configure static routing.
Advance → Routing
To add the static route check 'Enable', fill the corresponding fields and click 'Add Route'.
- Enable – flag for route adding;
- Destination – destination address;
- Subnet Mask – subnet mask;
- Next Hop – next host;
- Metric – metric;
- Interface – interface.
Added static routes are displayed in the 'Static Route Table'. To update the information in the table, click the 'Update' button, to delete the position from the table select it and click 'Delete Selected''.
To view the routes that the device often accesses, click the 'Show Routes' button, then the 'IP Route Table' will be displayed.
Advance → Routing → Show Routes
To update the information in the table, click the 'Refresh' button, to close the table, click 'Close'.
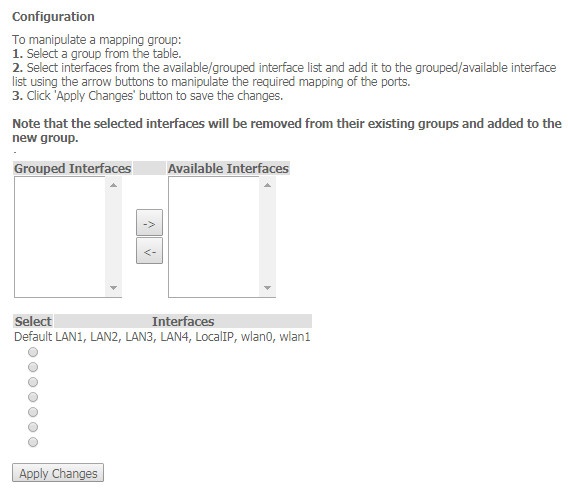
The 'Bridging grouping' submenu. Interface grouping
In this section you can group the interfaces. By default all interfaces are in the same group. To place an interface to a new group, you should:
- Select a new group from the list below;
- Select interfaces from the 'Available Interface' list;
- Click the arrow ← to transfer the interfaces into the group;
- Apply the actions by clicking the 'Apply Changes' button
Advance → Bridge grouping
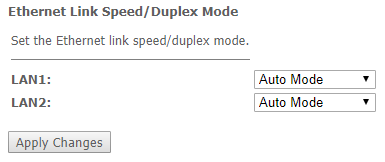
The 'Link mode' submenu. LAN ports configuration
In this submenu you can set the LAN ports operation mode. LAN1/2 – operation mode configuration; available modes: 10M Half Mode, 10M Full Mode, 100M Half Mode, 100M Full Mode and Auto Mode (auto-negotiation mode).
Advance → Link mode
To save the changes, click the 'Apply Changes' button.
The 'IPv6' submenu. IPv6 configuration
In this section you can enable/disable IPv6 operation. For this you should check 'Enable/Disable'.
Advance → IPv6 → IPv6
To save the changes, click the 'Apply Changes' button.
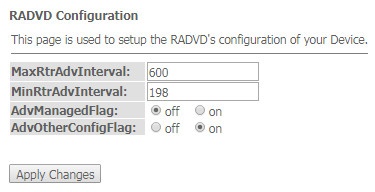
The 'RADVD' submenu. RADVD configuration
In this submenu you can configure RADVD (Router Advertisement Daemon).
Advance → IPv6 → RADVD
- MaxRtrAdvInterval – maximum RA (Router Advertisement) sending interval;
- MinRtrAdvInterval – minimum RA sending interval;
- AdvManagedFlag – enable/disable 'Managed' flag sending in RA;
- AdvOtherFlag – enable/disable Other RA flag sending.
To save the changes, click the 'Apply Changes' button.
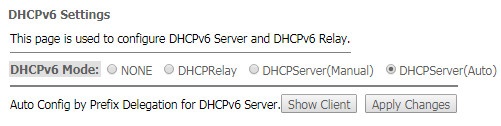
The 'DHCPv6 setting' submenu. DHCPv6 server configuration
This submenu is used to configure DHCPv6 server. By default, it operates in auto configuration mode (DHCPServer(Auto)) via prefix delegation.
Advance → IPv6 → DHCPv6
- DHCPv6 Mode – select mode:
- NONE – operation without DHCP server;
- DHCPRelay – DHCP repeater operation mode;
- DHCPServer (Manual) – manual configuration of DHCP server;
- DHCPServer(Auto) – DHCP server auto-provisioning.
To save the changes, click the 'Apply Changes' button. After clicking on the 'Show Client' button, a table of active DHCPv6 server IP addresses will be displayed.
Advance → IPv6 → DHCPv6 → Show Client
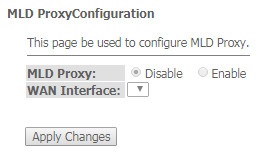
The 'MLD proxy' submenu. MLD proxy function configuration
In this section you can enable/disable MLD-proxy operation. For this you should check 'Enable/Disable'.
Advance → IPv6 → MLD proxy
To save the changes, click the 'Apply Changes' button.
The 'MLD snooping' submenu. MLD snooping function configuration
In this section you can enable/disable MLD-snooping operation. For this you should check 'Enable/Disable'.
Advance → IPv6 → MLD snooping
To save the changes, click the 'Apply Changes' button.
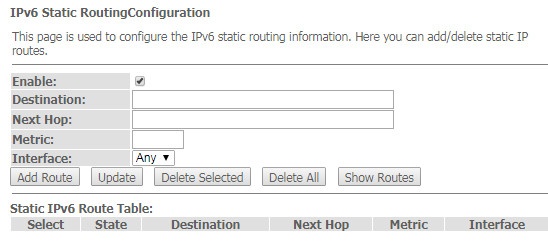
The 'IPv6 routing' routing. IPv6 routes configuration
This section configures static IPv6 routes.
Advance → IPv6 → IPv6 routing
- Enable – flag for route adding;
- Destination – destination address;
- Next Hop – next host;
- Metric – metric;
- Interface – interface.
To add IPv6 Routing, fill in the appropriate fields and click the 'Add Route' button: Added routes are displayed in the 'Static IPv6 Route Table', to update the information click the 'Update' button. To delete the whole table, click the 'Delete All' button; To delete one route, select it and click the 'Delete Selected' button. The 'Show Routes' button displays a table of static IPv6 routes that the network typically accesses.
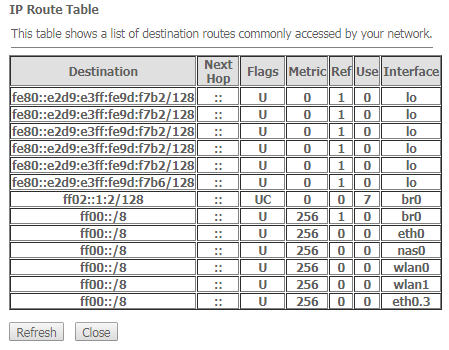
Advance → IPv6 → IPv6 routing → Show Routes
- Destination – destination network;
- Next Hop – nest host
- Flags – flags;
- Metric – metric;
- Ref – route source;
- Use – route usage;
- Interface – interface through which the specified route is available.
To update the table click 'Refresh'; to close it click 'Close'
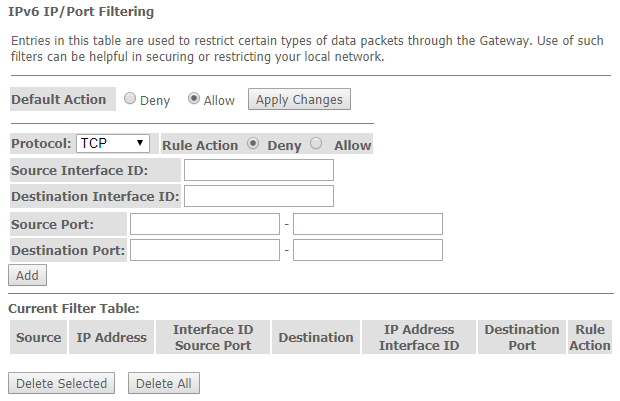
The 'IPv6 IP/ Port filtering' submenu. Packet filtering configuration
Use this page to configure the filtering of data packets transmitted through the gateway.
Advance → IPv6 → IP/Port filtering
- Default Action – default action:
- Deny – when checked, traffic pass is prohibited by default;
- Allow – when checked, traffic pass is allowed by default;
- Protocol – select protocol;
- Source Interface ID – source interface;
- Destination Interface ID – destination interface;
- Source Port – source port;
- Destination Port – destination port.
To add a filter fill the corresponding fields and click the 'Add' button. Added filters are displayed in the 'Current Filter Table'. To delete the whole table, click the 'Delete All' button; To delete one filter, select it and click the 'Delete Selected' button.
The 'Diagnostics' menu
The 'Ping' submenu. Checking the Availability of Network Devices
Use this menu to test the availability of network devices with Ping utility.
Diagnostics → Ping
To test the availability of the connected device, enter its IP address into the 'Host Address' field and click the 'Go' button.
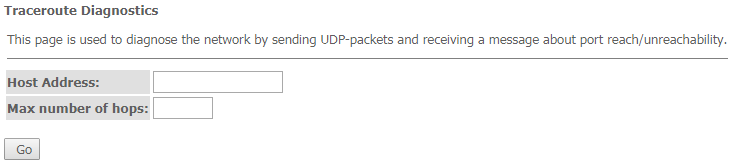
The 'Traceroute' submenu
This submenu is intended for network diagnostics by sending UDP packets and receiving a message about port availability/inaccessibility.
Diagnostics → Traceroute
The 'Admin' menu
Device management section. In this menu, you can configure passwords, time, configurations, etc.
The 'Settings' submenu. Configuration restore and reset
Admin → Settings → Backup Settings
In this section, you can copy the current settings to a file (Backup Settings) by clicking on the 'Backup Settings to File' button.
Admin → Settings → Update Settings
In this section, you can restore settings from a file that was previously saved (Update Settings) with the 'Restore' button.
Admin → Settings → Restore Default
In this section you can reset the current settings to the factory default settings (Restore Default), click the 'Reset Settings to Default' button.
The 'Commit/Reboot' submenu. Saving changes and rebooting the device
Click the 'Commit and Reboot' button to reboot the device or to save changes in system memory. The rebooting process takes a few minutes to complete.
Admin → Commit/Reboot
The 'Logout' submenu
In this section it is possible to log out by clicking on the 'Logout' button.
Admin → Logout
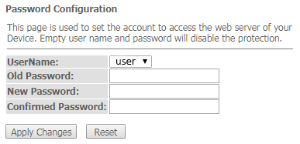
The 'Password' submenu. Access control configuration (setting passwords)
In this section you can change a password to access the device.
Admin → Password
To change the password, you must enter the existing password in the 'Old Password' field, then the new password in 'New Password' and confirm it with 'Confirmed Password'.
To confirm and save changes, click the 'Apply changes' button. Click the 'Reset' button to reset the value.
The 'Firmware upgrade' submenu. Software Update
To update firmware, it is necessary to select firmware file by using the 'Select file' button and click 'Upgrade'. To reset the value, click the 'Reset' button.
Admin → Firmware upgrade
Do not switch off or reboot the device during the update. The process may take several minutes. The device will be automatically rebooted when the update is completed.
The 'Remote Access' submenu. Remote access rules configuration
In this section you can configure remote access rules via HTTP/Telnet/ICMP protocols.
Admin → Remote Access
- Enable – enabling the rule to add;
- Service – selection of the protocol used;
- Interface – interface to which the rule applies;
- IP Address – source IP adress;
- Subnet Mask – subnet mask;
- Port – destination port.
To add a rule fill the corresponding fields and click the 'Add' button. Added rules are displayed in the 'RA Table'. To activate/deactivate the selected rule, click the 'Toggle selected' button. To delete one rule, select it with a flag in the Select column and click the 'Delete Selected' button.
The 'Time zone' submenu. System time configuration
In this section you can configure the device system time. Synchronization with accurate online time-servers is available.
Admin → Time zone
- Current time – current time;
- Time Zone Select – timezone;
- Enable Daylight Saving Time – enable daylight saving time;
- Enable SNTP Client Update – enable time synchronization via SNMP;
- WAN Interface – interface for time update;
- SNTP Server – preferred time server.
To save the changes click the 'Apply Changes' button, update the information click 'Refresh'.
The 'Statistics' menu. Traffic flow information for device ports
The 'Interface' submenu. Information about timers and errors
This section displays timers/errors for packets for each interface:
Statistics → Interface
- Interface – interface;
- Rx pkt – packets received;
- RX err – errors on receive;
- Rx drop – rejected on receive;
- Tx pkt – packets sent;
- Tx err – transmission error;
- Tx drop – rejected on transmission.
The 'PON' submenu
This section displays timers for the optical interface:
Statistics → PON
- Bytes Sent – transmitted bytes;
- Bytes Received – received bytes;
- Packets Sent – packets transmitted;
- Packets Received – packets received;
- Unicast Packet Sent – Unicast packets transmitted;
- Unicast Packet Received – Unicast packets received;
- Multicast Packets Sent – Multicast packets transmitted;
- Multicast Packets Received – Multicast packets received;
- Broadcast Packet Sent – Broadcast packets transmitted;
- Broadcast Packet Received – Broadcast packets received;
- FEC Errors – FEC errors
- Packets Dropped – packets rejected.
The list of changes
Document version | Suitable firmware version | Issue date | Revisions |
|---|---|---|---|
Version 1.2 | 1.3.2 | 11.2020 | Synchronization with Firmware version 1.3.2 |
Version 1.1 | 1.3.0 | 04.2020 | Second issue |
Version 1.0 | 1.2.1 | 01.2020 | First issue |