Wireless access point WEP-200L
User manual,
Firmware version 2.3.2 (01.2024)
IP address: http://192.168.1.10
User Name: admin
Password: password
Introduction
Annotation
Modern tendencies of telecommunication development necessitate operators to search for the most optimal technologies, allowing to meet rapidly growing needs of subscribers, while maintaining at the same time consistency of business processes, development flexibility and reducing the costs of various services. Wireless technologies are spinning up more and more, and have paced a huge way for short time from unstable low-speed communication networks of low radius to broadband access networks equitable to speed of wired networks with high criteria to the quality of provided services.
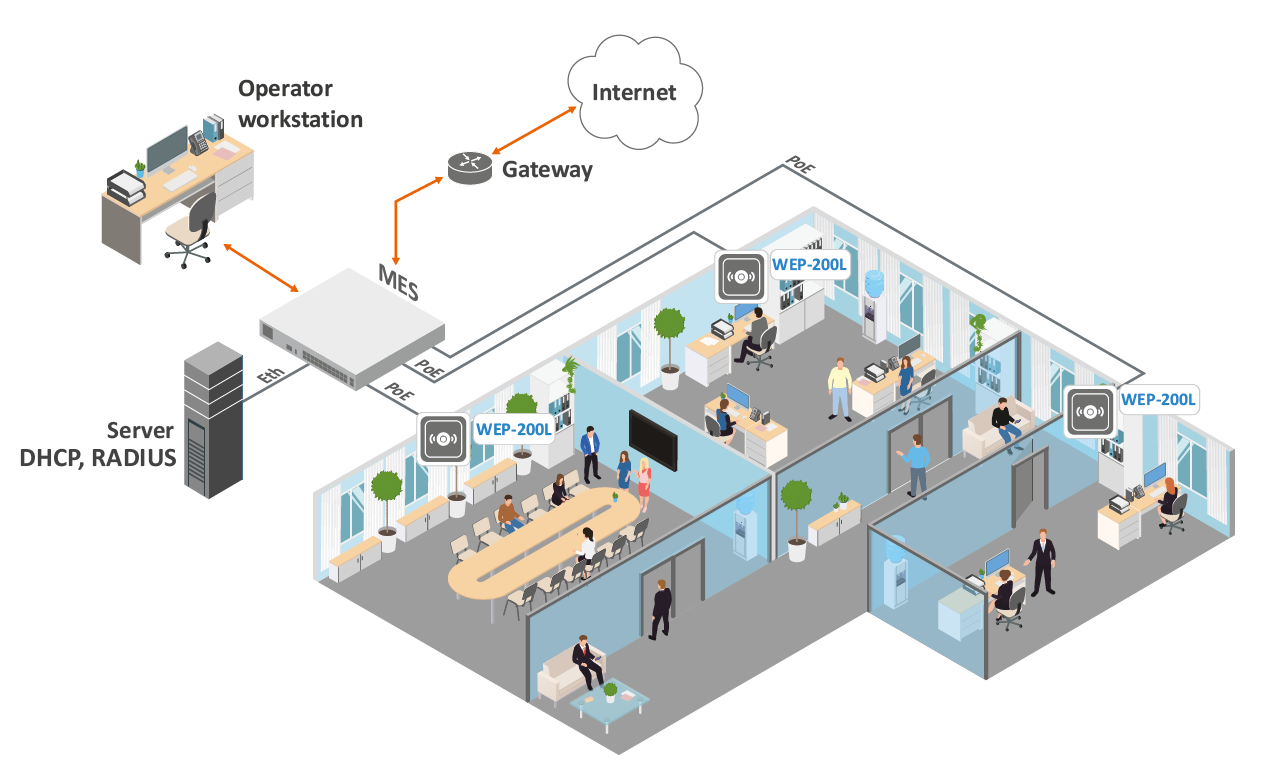
The main purpose of WEP-200L is installation inside buildings as an access point to various resources creating a seamless wireless network from several identical access points (“Roaming”), if the coverage area is large enough.
This manual specifies intended purpose, main technical parameters, design, safe operation rules, and installation and configuration recommendations for WEP-200L.
Symbols
Notes and warnings
Notes contain important information, tips or recommendations on device operation and setup.
Warnings are used to inform the user about harmful situations for the device and the user alike, which could cause malfunction or data loss.
Device description
Purpose
WEP-200L wireless access point is designed to provide the user access to high-speed and secure network.
The main purpose of the device is to create a Layer 2 wireless network at the junction with a wired network. WEP-200L connects to a wired network over 10/100/1000 Ethernet interface and using radio interfaces creates wireless high-speed access for devices that support Wi-Fi technology in the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands.
The device contains 2 radio interfaces for organizing two physical wireless networks.
WEP-200L supports modern requirements for the the quality of services and allows transmitting the most important traffic in higher priority queues than normal. Prioritization is provided by the following QoS technologies: CoS (special tags in the VLAN packet field) and ToS (tags in the IP packet field). Support for traffic shaping on each VAP allows one to fully manage access, quality of service and restrictions both for all subscribers and for everyone in particular.
The device is designed for installation in offices (government institutions, conference rooms, laboratories, hotels, etc.). Ability to create virtual hotspots with different encryption types allows one to place WEP-200L in organizations where separation of access rights is required between ordinary users and dedicated user groups.
Device specification
Interfaces:
- 1 port of Ethernet 10/100/1000BASE-T (RJ-45) with PoE support;
- Wi-Fi 2.4 GHz IEEE 802.11b/g/n;
- Wi-Fi 5 GHz IEEE 802.11a/n/ac.
Functions:
WLAN capabilities:
- Support for IEEE 802.11a/b/g/n/ac standards;
- Support for IEEE 802.11r/k/v roaming standards;
- Data aggregation, including A-MPDU (Tx/Rx) and А-MSDU (Rx);
- WMM-based priorities and packet planning;
- Wireless bridging (WDS);
- Dynamic frequency selection (DFS);
- Support for hidden SSID;
- 14 virtual access points;
- Third-party access point detection;
- Spectrum analyzer;
- Auto channel selection.
Network functions:
- Auto-negotiation of speed, duplex mode and switching between MDI and MDI-X modes;
- IPv6;
- Support for VLAN;
- Support for 802.1X authentication;
- DHCP client;
- ACL;
- NTP;
- Syslog;
- GRE;
- Transmission of subscriber traffic out of tunnels.
QoS functions:
- Priority and profile-based packet scheduling;
- Bandwidth limitation for each VAP;
- Bandwidth limitation for each client;
- WMM parameters changing.
Security:
- Centralized authorization via RADIUS server (802.1X WPA/WPA2 Enterprise);
- WPA/WPA2 data encryption;
- Support for Captive Portal.
Figure 1 shows WEP-200L application diagram.
Figure 1 — WEP-200L application diagram
The device technical parameters
Main specifications
| WAN interface parameters | |
|---|---|
| Number of ports | 1 |
| Electrical connector | RJ-45 |
| Data rate | 10/100/1000 Mbps, auto-negotiation |
| Standards | BASE-T |
| Wireless interface parameters | |
| Standards | 802.11a/b/g/n/ac |
| Frequency range | 2400–2483.5 MHz; 5150–5350 MHz, 5470–5850 MHz |
| Modulation | BPSK, QPSK, 16QAM, 64QAM, 256QAM |
| Operating channels | 802.11b/g/n: 1–13 (2402–2482 MHz) 802.11a/n/ac: 36–64 (5170–5330 MHz) 100–144 (5490–5730 MHz) 149–165 (5735–5835 MHz) |
| Data rate | 802.11a: up to 54 Mbps 802.11b: up to 11 Mbps 802.11g: up to 54 Mbps 802.11n: 2.4 GHz — up to 300 Mbps 5 GHz — up to 600 Mbps 802.11ac: up to 1733 Mbps |
| Maximum number of simultaneous sessions | 2.4 GHz: 127 5 GHz: 127 |
| Maximum output power of the transmitter | 2.4 GHz: 18 dBm 5 GHz: 20 dBm |
| Built-in antenna gain | 2.4 GHz: ~ 3 dBi 5 GHz: ~3 dBi |
| Receiver sensitivity | 2.4 GHz: up to -92 dBm 5 GHz: up to -92 dBm |
| Security | Centralized authorization via RADIUS server (802.1X WPA/WPA2 Enterprise) WPA/WPA2 data encryption Support for Captive Portal |
| Supporting MIMO 2×2 for 2.4 GHz, MIMO 4×4 for 5 GHz | |
| Control | |
| Remote control | Web interface, Telnet, SSH, CLI, SNMP, NETCONF |
| Access restriction | By password, authentication via RADIUS server |
| General parameters | |
| Flash | 128 MB SPI-NAND Flash |
| RAM | 256 MB DDR3 RAM |
| Power supply | PoE 48 V/56 V (IEEE 802.3af-2003) |
| Maximum power consumption | No more than 12.95 W |
| Operating temperature range | From +5 to +40 °C |
| Relative humidity at 25 °C | Up to 80 % |
| Dimensions (diameter × height) | 230 × 56 mm |
| Weight | 0.46 kg |
| Service life | No less than 15 years |
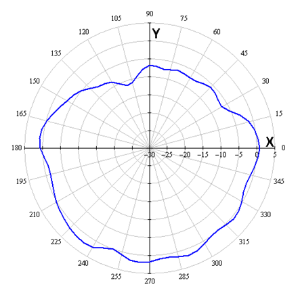
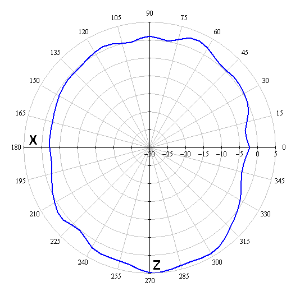
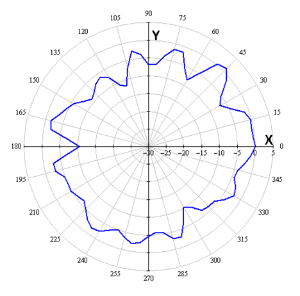
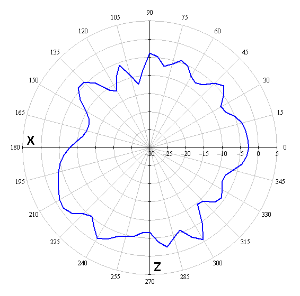
Radiation patterns
The figures below show the radiation patterns of the device.
| Measurement position | |
|---|---|
AZIMUTH (XY) | ELEVATION (XZ) |
2.4 GHz band | |
5 GHz band | |
Design
WEP-200L enclosed in a plastic case.
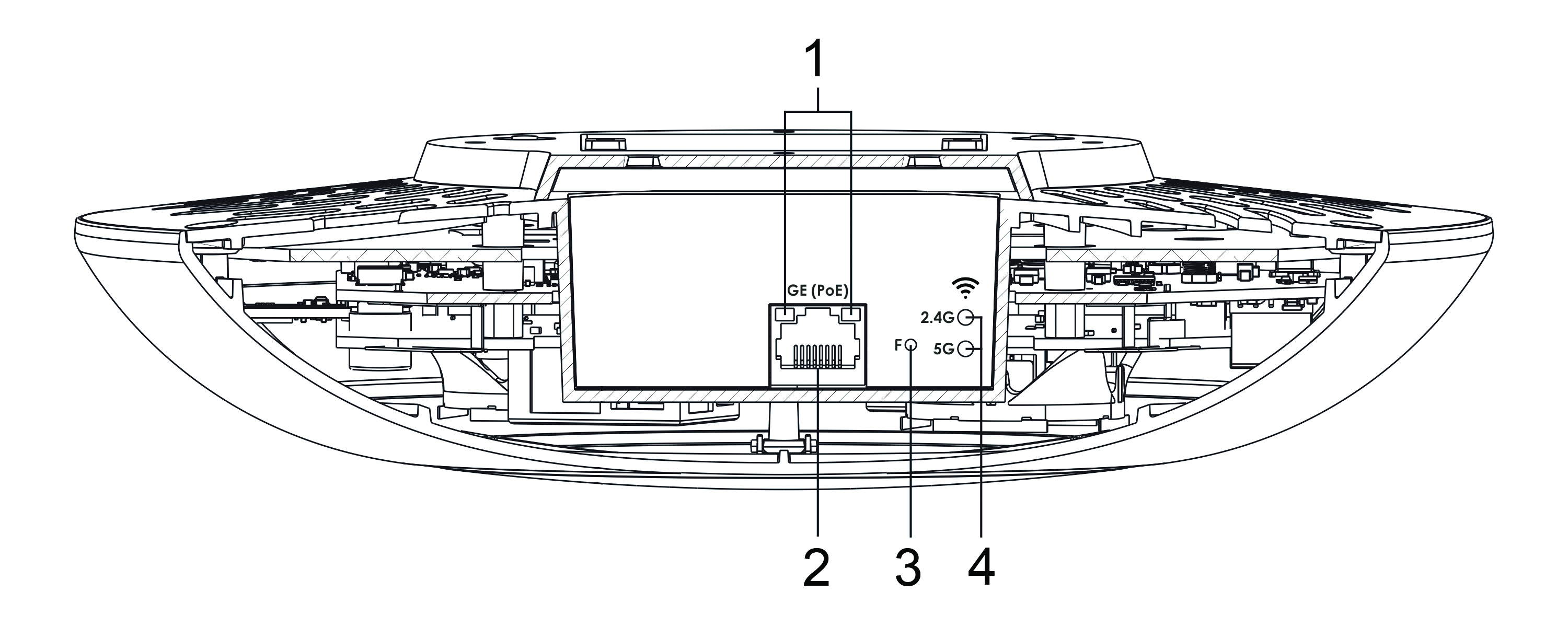
Main panel of the device
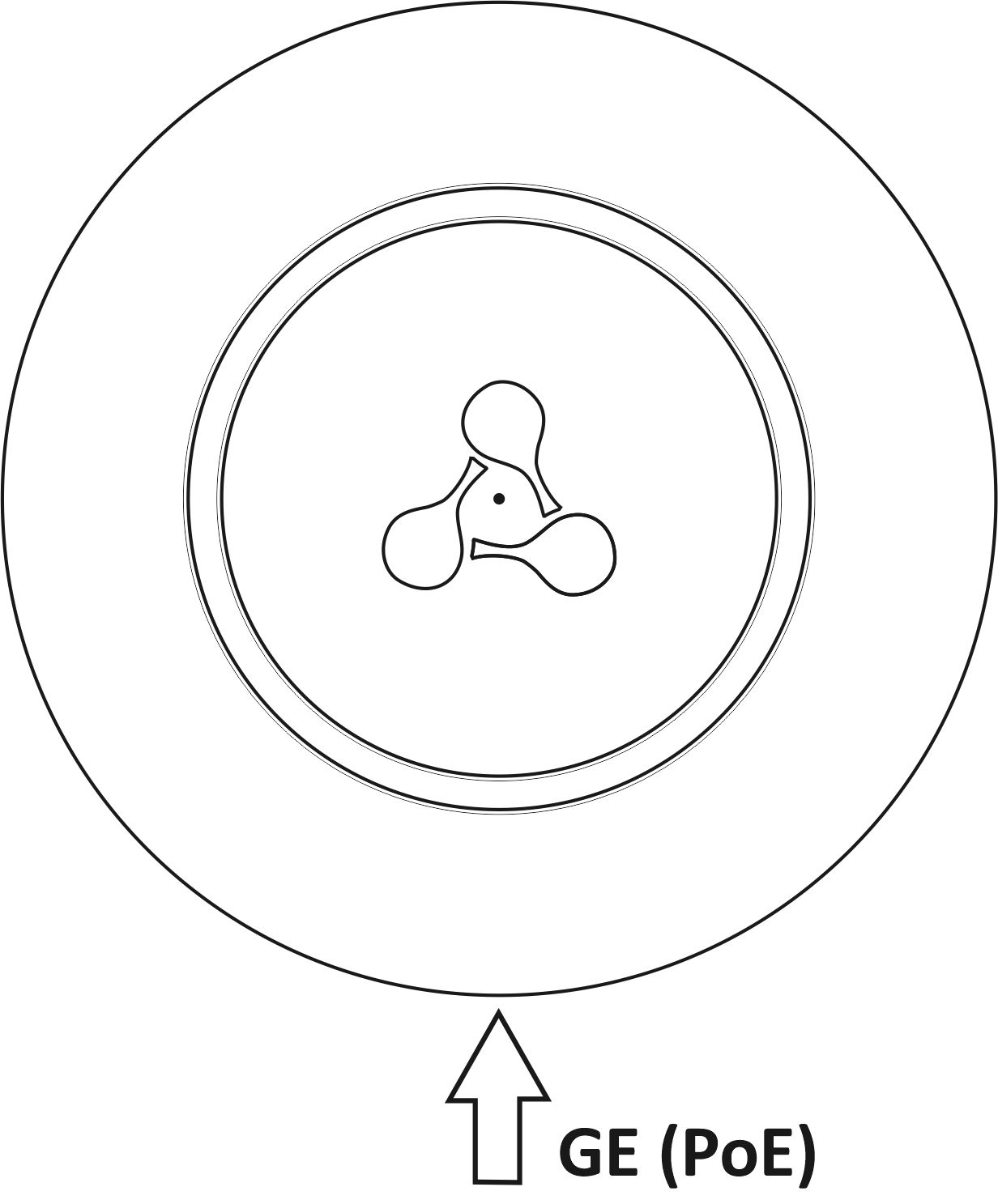
WEP-200L main panel layout is shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2 — WEP-200L main panel layout
The following indicator lights, connectors, and controls are placed on the WEP-200L main panel (see table 2).
Table 2 — Description of indicators, ports and controls
| Element | Desciption | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | LAN | GE (PoE) port status LED |
| 2 | GE (PoE) | GE port for PoE connection |
| 3 | F | Factory reset button |
| 4 | Wi-Fi | Wi-Fi module activity LEDs |
Top panel of the device
WEP-200L top panel layout is shown in Figure 3.
Figure 3 — WEP-200L top panel layout
Table 3 — Description of indicators
| Element | Desciption | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Power | Device operation status indicator |
Light indication
The current status of the device is displayed using Wi-Fi, LAN, Power LEDs. The possible indicator states are described in Table 4.
Table 4 — Light indication of device status
LED | LED status | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
Wi-Fi | Solid green | Wi-Fi network is active | |
Flashing green | Data transmission over wireless network | ||
LAN | Solid green (10, 100 Mbps)/ Solid orange (1000 Mbps) | The connection with a connected network device is established | |
| Flashing green | Packet data transmission over LAN interface | ||
Power | Solid green | The device power supply is enabled, normal operation | |
| Solid orange | The device is loaded but IP address is not received via DHCP | ||
| Soild red | The device is loading | ||
Restore the default configuration
The device can be reset to the factory configuration using the “F” button on the device. When the device is loaded, press and hold the “F” button until the “Power” indicator is flashing.
The device will be rebooted automatically. DHCP client will be launched by default. If the address is not obtained via DHCP, the device will have the factory IP address — 192.168.1.10, and the following netmask — 255.255.255.0.
Delivery package
The delivery package includes:
- WEP-200L wireless access point;
- Mounting kit;
- Operation manual on a CD (optional);
- Technical passport.
Rules and recommendations for device installation
This section defines safety rules, installation recommendations, setup procedure and the device starting procedure.
Safety rules
- Do not install the device near heat source and at places where temperature may reach values below
+5 °C or higher 40 °C. - Do not use the device in rooms with high humidity. Do not expose the device to smoke, dust, water, mechanical vibration or shock.
- Do not open the device case. There are no user serviceable parts inside.
To prevent overheating of the device components and malfunction of the device, do not block the ventilation holes with foreign objects and do not place objects on the equipment surface.
Installation recommendations
1. The recommended installation position: horizontal, on the ceiling.
2. Before installing the device and turning it on, check the device for visible mechanical defects. If defects are observed, stop the device installation, fill in the corresponding act and contact the supplier.
3. If your device has been exposed to the cold for a long period of time, let it warm up at room temperature for two hours before starting work. If your device has been exposed to high humidity for a long period of time, let it stay under normal conditions for at least 12 hours before turning it on.
4. When placing your device, in order to provide the best Wi-Fi coverage consider the following rules:
- Install the device at the center of a wireless network;
- Minimize the number of barriers (walls, ceilings, furniture, and etc.) between WEP-200L and other wireless network devices;
- Do not install the device near (about 2 m) electrical and radio devices;
- It is not recommended to use radiophone and other equipment operating at the frequency of 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz, within the range of a Wi-Fi network;
- Obstacles like glass/metal constructions, brick/concrete walls, water cans and mirrors can significantly reduce Wi-Fi action radius. It is not recommended to place the device inside a false ceiling as metal frame causes multipath signal propagation and signal attenuation.
5. When installing several access points, cell action radius must overlap with action radius of a neighboring cell at the level from -65 to -70 dBm. It is allowed to reduce the signal level to -75 dBm at cell boundaries, if it is not intended to use VoIP, video streaming and other sensitive to losses traffic in wireless network.
Calculating the number of required access points
To calculate the required number of access points, evaluate the required coverage zone. For more accurate assessment, it is necessary to make a radio examination of the room. Approximate radius of WEP-200L coverage area with a good-quality signal in case of mounting on a ceiling in typical office: 2.4 GHz — 40–50 m,
5 GHz — 20–30 m. In the absence of obstacles, the coverage radius: 2.4 GHz — up to 100 m, 5 GHz — up to
60 m. Table 5 describes rough attenuation values.
Table 5 — Attenuation values
| Material | Change of signal level, dB | |
|---|---|---|
| 2.4 GHz | 5 GHz | |
| Organic glass | -0.3 | -0.9 |
| Brick | -4.5 | -14.6 |
| Glass | -0.5 | -1.7 |
| Plaster slab | -0.5 | -0.8 |
| Wood laminated plastic | -1.6 | -1.9 |
| Plywood | -1.9 | -1.8 |
| Plaster with wirecloth | -14.8 | -13.2 |
| Breezeblock | -7 | -11 |
| Metal lattice (mesh 13 × 6 mm, metal 2 mm) | -21 | -13 |
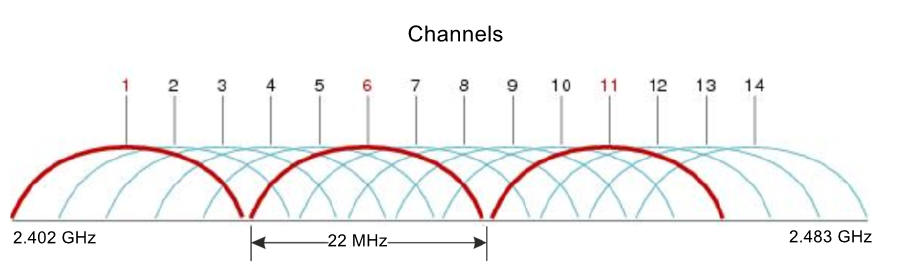
Channel selection for neighboring access points
It is recommended to set non-overlapping channels to avoid interchannel interference among neighboring access points.
Figure 4 – General diagram of frequency channel overlap in the range of 2.4 GHz
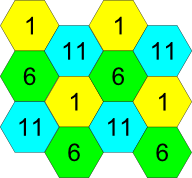
Example of channel allocation scheme among neighboring access points in frequency range of 2.4 GHz when channel width is 20 MHz, see Figure 5.
Figure 5 – Scheme of channel allocation among neighboring access points in the frequency range of 2.4 GHz when channel width is 20 MHz
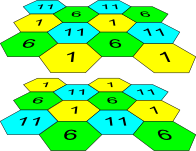
Similarly, the procedure of channel allocation is recommended to save for access point allocation between floors, see Figure 6.
Figure 6 – Scheme of channel allocation between neighboring access points that are located between floors
With a channel width of 40 MHz there are no non-overlapping channels in the 2.4 GHz band. In such cases, it is required to select channels maximally separated from each other.
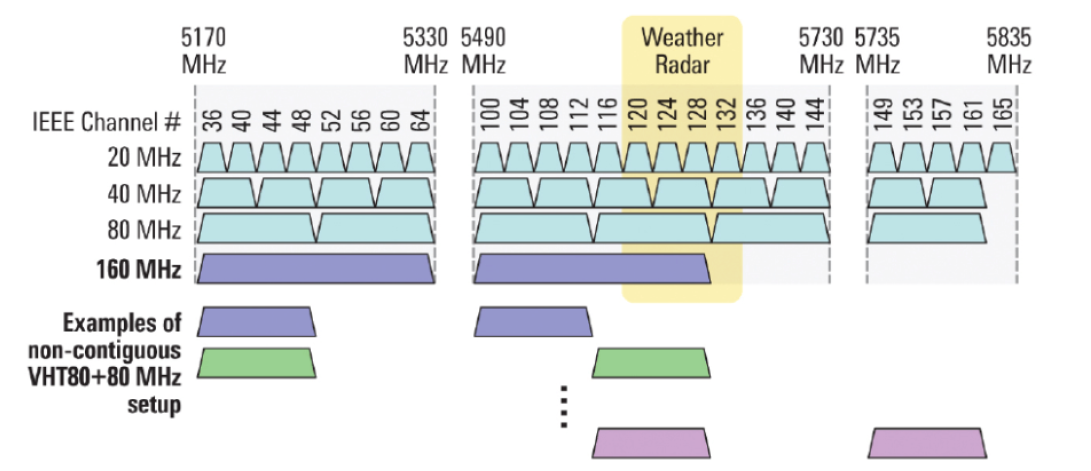
Figure 7 – Channels used in the 5 GHz band when channel width is 20, 40 or 80 MHz
WEP-200L installation
The device can be installed on the plain surface (wall or ceiling) in accordance with the safety instructions and recommendations listed above.
The device delivery package includes required mounting kit to attach the device to plain surface.
Wall mounting procedure
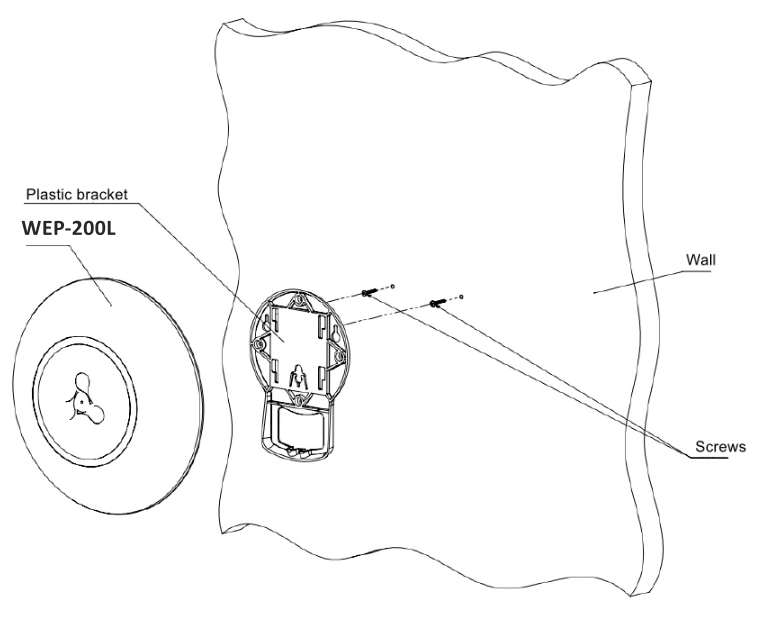
1. Fix the plastic bracket (included in the delivery package) to the wall:
Figure 8 – Attaching the bracket to a wall
- An example of placing the plastic bracket is shown in Figure 8.
- When installing the bracket, pass wires through the corresponding channels of the bracket, see Figure 8.
- Align screw holes on the bracket with the corresponding screw holes on the surface. Screw the bracket to the surface using a screwdriver.
2. Install the device.
- Connect cables to corresponding connectors of the device. Description of the connectors is given in the section Design.
- Align the device with the bracket and secure the position by pulling it down.
False ceiling mounting procedure
It is not recommended to place WEP-200L from the inside of the false ceiling, as the metal frame causes signal multipath propagation and its attenuation when passing through the lattice of the false ceiling frame.
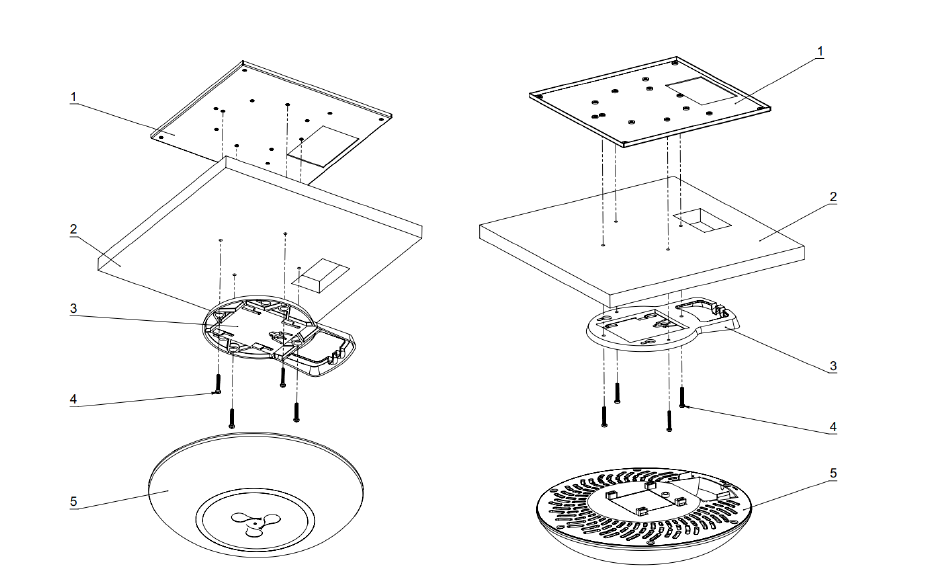
1 — metal bracket; 2 — Armstrong panel; 3 — plastic bracket; 4 — screws; 5 — device.
Figure 9 — Mounting the device on a false ceiling
1. Attach the metal and plastic brackets to the ceiling (Figure 9).
- Fasten the plastic bracket (3) on false ceiling with the metal bracket (1) in the following order: metal bracket -> Armstrong panel -> plastic bracket.
- In the Armstrong panel, make a hole with the the size of the metal bracket. Run the wires through this hole.
- Align the holes on the metal bracket, Armstrong panel and plastic bracket. Next, align the screw holes on the plastic bracket with the same holes on the metal bracket. Use a screwdriver to fix brackets with screws.
2. Install the device.
- Connect cables to corresponding connectors of the device. Description of the connectors is given in the section Design.
- Align the device with the plastic bracket and secure the position by turning the device clockwise.
Removing the device from the bracket
To remove the device from the bracket:
- Pull the device up (Figure 8).
- Remove the device.
Device management via the web interface
Getting started
In order to start the operation, you should connect to the device via WAN interface using a web browser:
1. Open a web browser, for example, Firefox, Opera, Chrome.
2. Enter the device IP address in the browser address bar.
Factory IP address: 192.168.1.10, subnet mask: 255.255.255.0. By default, the device is capable to obtain an IP address via DHCP.
When the device is successfully detected, username and password request page will be shown in the browser window:
3. Enter username into “Login” and password into “Password” field.
Factory settings: login: admin, password: password.
4. Click “Log in”. A menu for monitoring the device status will open in a browser window.
5. If necessary, select the information display language. Russian and English languages are available for web interface.
Applying configuration and discarding changes
- Applying configuration
Clicking starts the process of saving the configuration to the device flash memory and applying the new settings. All the settings come into operation without device rebooting.
The WEP-200L web interface has a visual indication of the current status of the setting applying process (Table 6).
Table 6 — Visual indication of the current status of the setting application process
| Image | State description |
|---|---|
After clicking “Apply”, the process of settings saving to device memory is launched. This is indicated by the icon in the tab name and on the "Apply" button. | |
The icon in the tab name indicates about successful saving and application of the settings. |
2. Discarding changes
.
The changes can be discarded only before clicking “Apply”. If you click “Apply”, all the changed parameters will be applied and saved to device memory. After clicking "Apply", return to the previous settings will not be possible.
Web interface basic elements
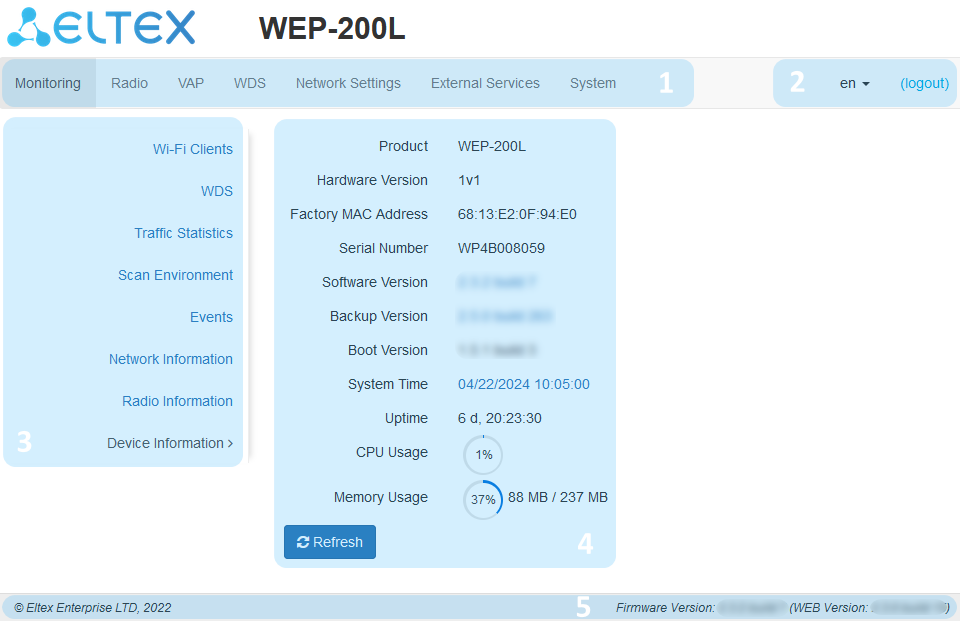
Navigation elements of the web interface are shown in the figure below.
User interface window is divided into five general areas:
- Menu tabs categorize the submenu tabs: Monitoring, Radio, VAP, WDS, Network Settings, External Services, System.
- Interface language selection and Logout button designed to end a session in the web interface under a given user.
- Submenu tabs allow one to control settings field.
- Device configuration field displays data and configuration.
- Information field displays current firmware version.
The “Monitoring” menu
In the “Monitoring” menu, the current system state can be viewed.
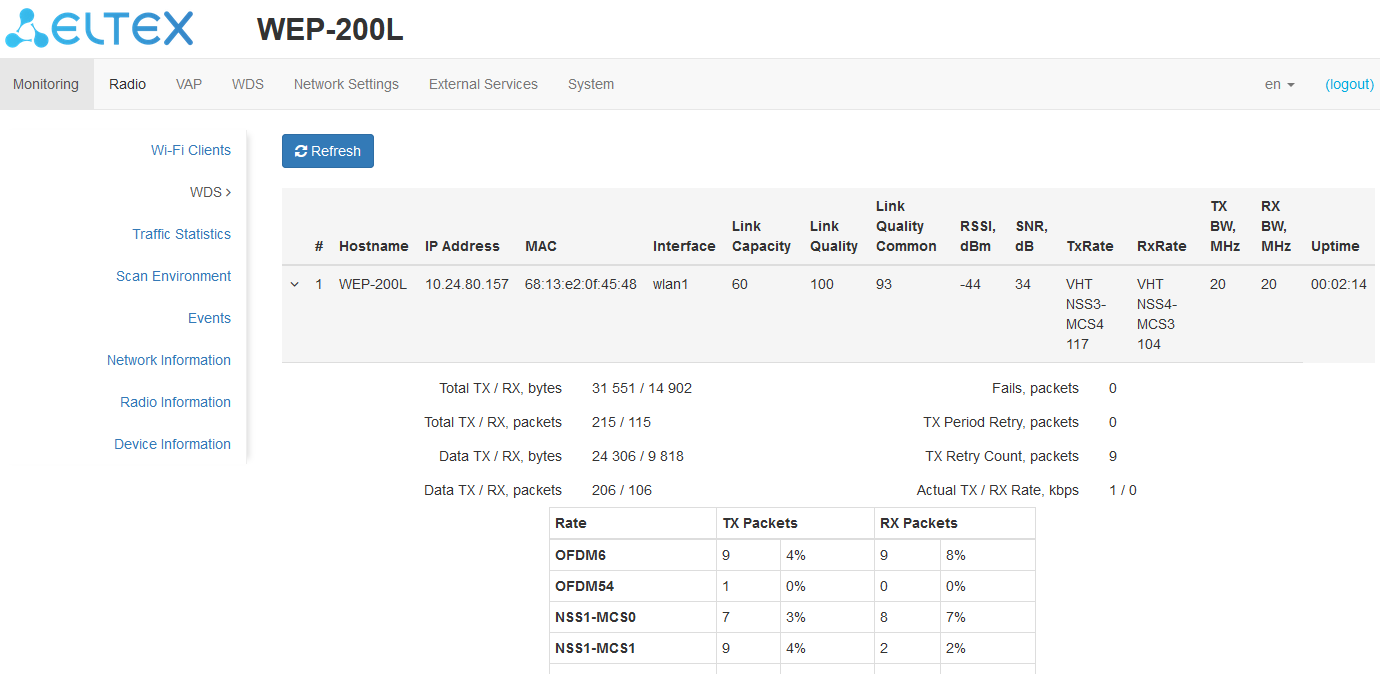
The “Wi-Fi Clients” submenu
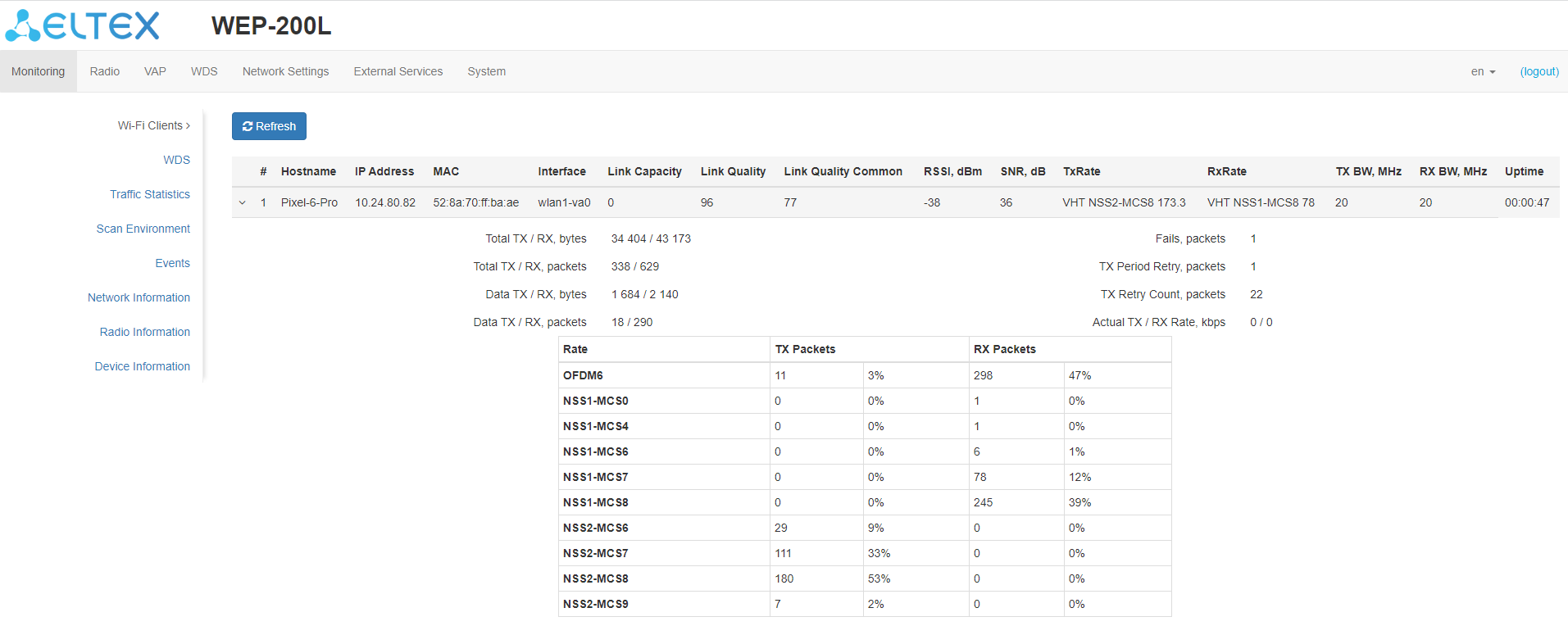
The “Wi-Fi Clients” submenu displays information about the status of connected Wi-Fi clients.
Information on connected clients is not displayed in real time. In order to update the information on the page, click “Refresh”.
- # — number of the connected device in the list;
- Hostname — network name of the device;
- IP address — IP address of the connected device;
- MAC address — MAC address of the connected device;
- Interface — WEP-200L interaction interface with the connected device;
- Link Capacity — parameter that displays how effectively the access point uses modulation to transmit. It is calculated based on the number of packets transmitted on each modulation to the client, and reduction factors. The maximum value is 100% (it means that all packets are transmitted to the client at maximum modulation for the maximum nss type supported by the client). The minimum value is 2% (in case when packets are transmitted on nss1mcs0 modulation for a client with MIMO 3x3 support). The parameter value is calculated for the last 10 seconds;
- Link Quality — parameter that displays the state of the link to the client, calculated based on the number of retransmit packets sent to the client. The maximum value is 100% (all transmitted packets were sent on the first attempt), the minimum value is 0% (no packets were successfully sent to the client). The parameter value is calculated for the last 10 seconds;
- Link Quality Common — parameter that displays the status of the link to the client, calculated based on the number of retransmit packets sent to the client. The maximum value is 100% (all transmitted packets were sent on the first attempt), the minimum value is 0% (no packets were successfully sent to the client). The parameter value is calculated for the entire time of the client connection;
- RSSI — received signal level, dBm;
- SNR — signal/noise ratio, dB;
- TxRate — channel data rate of transmission, Mbps;
- RxRate — channel data rate of reception, Mbps;
- Tx BW — transmission bandwidth, MHz;
- Rx BW — reception bandwidth, MHz;
- Uptime — Wi-Fi client connection time.
To display more detailed information on a particular client, select it from the list. A detailed description includes the following options:
- Total TX/RX, bytes — number of bytes sent/received on the connected device;
- Total TX/RX, packets — number of packets sent/received on the connected device;
- Data TX/RX, bytes — number of data bytes sent/received on the connected device;
- Data TX/RX, packets — number of data packets sent/received on the connected device;
- Fails, packets — number of packets sent with errors on the connected device;
- TX Period Retry, packets — number of retries of transmission to the connected device for the last 10 seconds;
- TX Retry Count, packets — number of retries of transmission to the connected device during the entire connection;
- Actual TX/RX Rate, Kbps — current traffic transmission rate at the moment.
The “WDS” submenu
The "WDS" submenu displays information about the status of WEP-200L access points connected via WDS.
- # — number of the connected device in the list;
- Hostname — device network name;
- IP Address — IP address of the connected device;
- MAC — MAC address of the connected device;
- Interface — interface of WEP-200L and the connected device interaction;
- Link Capacity — parameter that displays how effectively the access point uses modulation to transmit. It is calculated based on the number of packets transmitted on each modulation to the client, and reduction factors. The maximum value is 100% (it means that all packets are transmitted to the client at maximum modulation for the maximum nss type supported by the client). The minimum value is 2% (in case when packets are transmitted on nss1mcs0 modulation for a client with MIMO 3x3 support). The parameter value is calculated for the last 10 seconds;
- Link Quality — parameter that displays the state of the link to the client, calculated based on the number of retransmit packets sent to the client. Maximum value — 100% (all transmitted packets were sent on the first attempt), minimum value — 0% (no packet to the client was successfully sent). The parameter value is calculated for the last 10 seconds;
- Link Quality Common — parameter that displays the status of the link to the client, calculated based on the number of retransmit packets sent to the client. The maximum value is 100% (all transmitted packets were sent on the first attempt), the minimum value is 0% (no packets were successfully sent to the client). The parameter value is calculated for the entire time of the client connection;
- RSSI — received signal level, dBm;
- SNR — ratio signal/noise, dB;
- TxRate — channel data rate of transmission, Mbps;
- RxRate — channel data rate of reception, Mbps;
- TX BW — transmission bandwidth, MHz;
- RX BW — reception bandwidth, MHz;
- Uptime — Wi-Fi client connection time.
To display more detailed information on a particular client, select it from the list. A detailed description
includes the following options:
- Total TX/RX, bytes — number of bytes sent/received on the connected device;
- Total TX/RX, packets — number of packets sent/received on the connected device;
- Data TX/RX, bytes — number of data bytes sent/received on the connected device;
- Data TX/RX, packets — number of data packets sent/received on the connected device;
- Fails, packets — number of packets sent with errors on the connected device;
- TX Period Retry, packets — number of retries of transmission to the connected device for the last 10 seconds;
- TX Retry Count, packets — the number of retries of transmission to the connected device during the entire connection;
- Actual TX/RX Rate, Kbps — current traffic transmission rate at the moment.
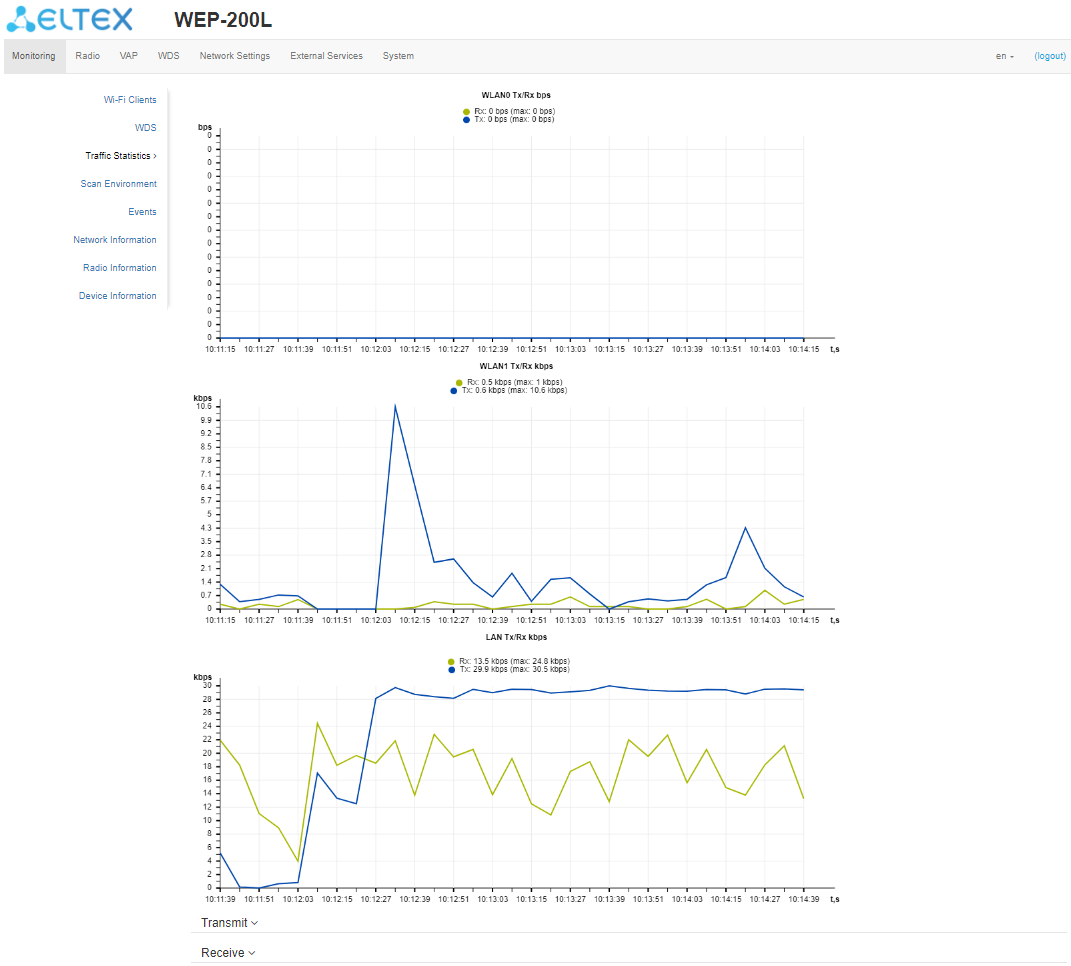
The “Traffic Statistics” submenu
The “Traffic Statistics” section displays the graphs of the transmitted/received traffic speed for the last 3 minutes, as well as statistics on the amount of transmitted/received traffic since the access point was turned on.
The LAN Tx/Rx graph shows the speed of the transmitted/received traffic via Ethernet interface of the access point for the last 3 minutes. The graph is automatically updated every 6 seconds.
The WLAN0 and WLAN1 Tx/Rx graphs show the rate of transmitted/received traffic via Radio 2.4 GHz and Radio 5 GHz interfaces for the last 3 minutes. The graph is automatically updated every 6 seconds.
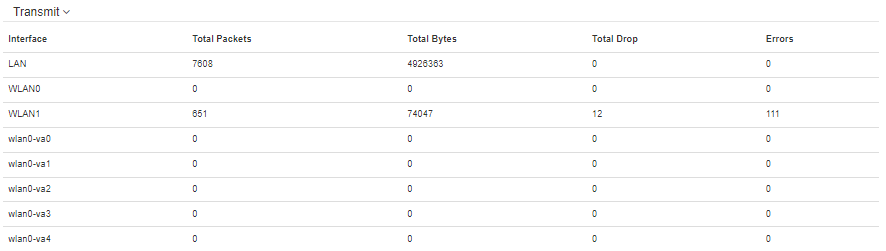
“Transmit” table description:
- Interface — name of the interface;
- Total packets — number of successfully sent packets;
- Total bytes — number of successfully sent bytes;
- Total drop — number of rejected packets;
- Errors — number of errors.
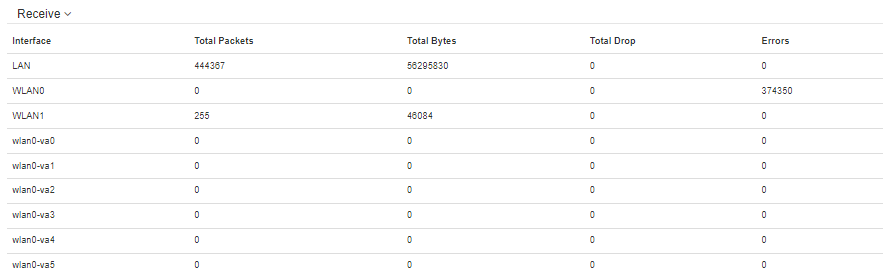
“Receive” table description:
- Interface — name of the interface;
- Total packets — number of successfully received packets;
- Total bytes — number of successfully received bytes;
- Total drop — number of rejected packets;
- Errors — number of errors.
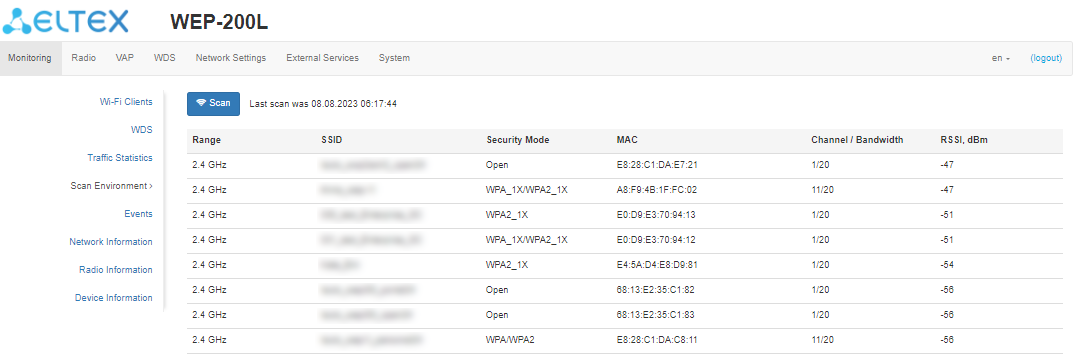
The “Scan Environment” submenu
In the “Scan Environment” submenu, scanning of the surrounding radio and detection of neighboring access points are carried out.
To start the scanning process, click the “Scan” button. After the scanning is completed, a list of detected access points and information about them will appear:
- Last scan was... — date and time of the last scanning;
- Range — specifies the range of 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz in which the access point was detected;
- SSID — SSID of the detected access point;
- Security mode — security mode of the detected access point;
- MAC — MAC address of the detected access point;
- Channel/Bandwidth — radio channel on which the detected access point operates;
- RSSI — the level with which the device receives the signal of the detected access point, dBm.
While scanning the environment, the device radio interface will be disabled, which will make it impossible to transfer data to Wi-Fi clients during scanning.
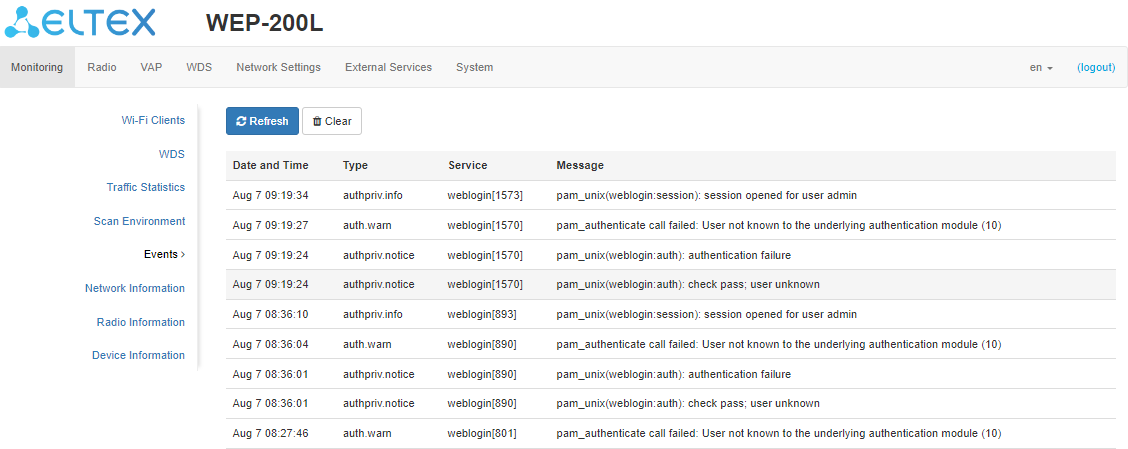
The “Events” submenu
In the “Events” submenu, it is possible to view a list of real-time informational messages which contains the following information:
- Date and Time — date and time when the event was generated;
- Type — category and severity level of the event;
- Service — name of the process that generated the message;
- Message — event description.
Table 7 — Description of event severity levels
| Level | Message severity level | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | Emergency | A critical error has occurred in the system, the system may not work properly. |
| 1 | Alert | Immediate intervention is required. |
| 2 | Critical | A critical error has occurred in the system. |
| 3 | Error | An error has occurred in the system. |
| 4 | Warning | Warning, non-emergency message. |
| 5 | Notice | System notice, non-emergency message. |
| 6 | Informational | Informational system messages. |
| 7 | Debug | Debugging messages provide the user with information to correctly configure the system. |
To receive new messages in the event log, click “Refresh“.
If necessary, all old messages can be deleted from the log by clicking “Clear”.
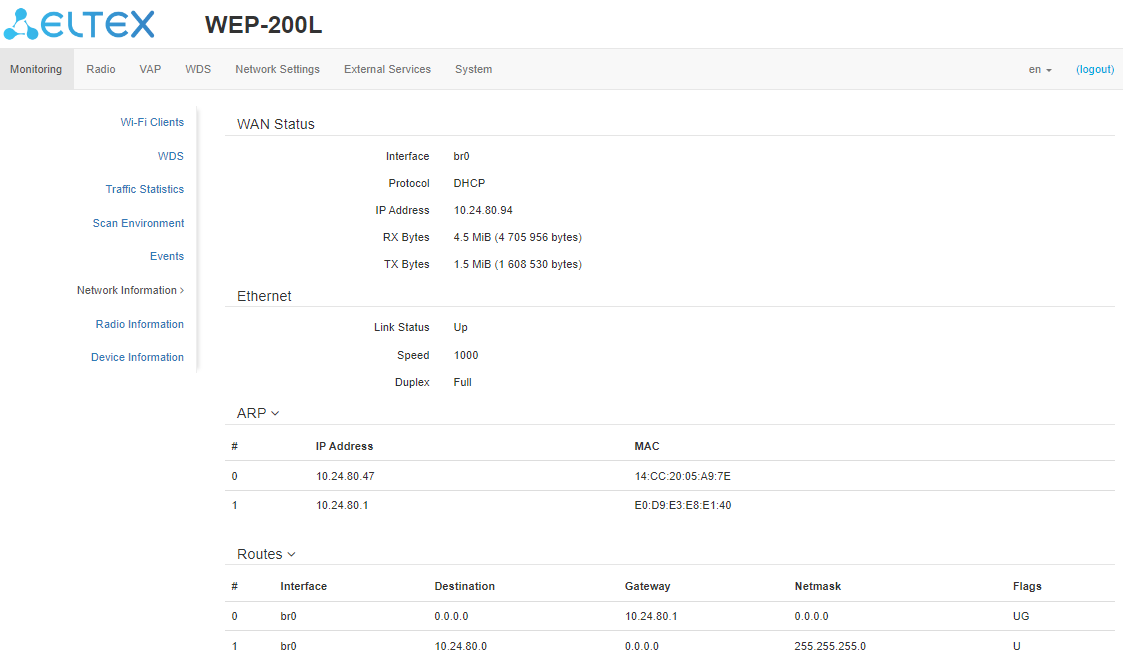
The “Network Information” submenu
In the “Network Information” submenu, general network settings of the device can be viewed.
WAN Status:
- Interface — name of the bridge interface;
- Protocol — protocol used for access to WAN;
- IP address — device IP address in external network;
- RX Bytes — number of bytes received on WAN;
- TX Bytes — number of bytes sent from WAN.
Ethernet:
- Link Status — Ethernet port status;
- Speed — Ethernet port connection speed;
- Duplex — data transfer mode:
- Full — full duplex;
- Half — half-duplex.
ARP
The ARP table contains mapping information between the IP and MAC addresses of neighboring network devices:
- IP address — device IP address;
- MAC — device MAC address.
Routes:
- Interface — name of the bridge interface;
- Destination — IP address of destination host or subnet that the route is established to;
- Gateway — IP address of the gateway through which access to the destination is carried out;
- Netmask — subnet mask;
- Flags — certain route characteristics.
The following flag values exist:
- U — means that the route is created and passable;
- H — identifies the route to the specific host;
- G — means that the route lies through the external gateway. System network interface provides routes in the network with direct connection. All other routes lie through the external gateways. G flag is used for all routes except for the routes in the direct connection networks;
- R — indicates that the route was most likely created by a dynamic routing protocol running on the local system using the reinstate parameter;
- D — indicates that the route was added as a result of receiving an ICMP Redirect Message. When the system learns the route from the ICMP Redirect message, the route will be added into the routing table in order to exclude redirection for the following packets intended for the same destination;
- M — means that the route was modified — likely by a dynamic routing protocol running on a local system with the “mod” parameter applied;
- A — points to a buffered route to which an entry in the ARP table corresponds;
- C — means that the route source is the core routing buffer;
- L — indicates that the destination of the route is one of the addresses of this computer. Such “local routes” exist in the routing buffer only;
- B — means that the route destination is a broadcasting address. Such “broadcast routes” exist in the routing buffer only;
- I — indicates that the route is connected to a ring (loopback) interface for a purpose other than to access the ring network. Such “internal routes” exist in the routing buffer only;
- ! — means that datagrams sent to this address will be rejected by the system.
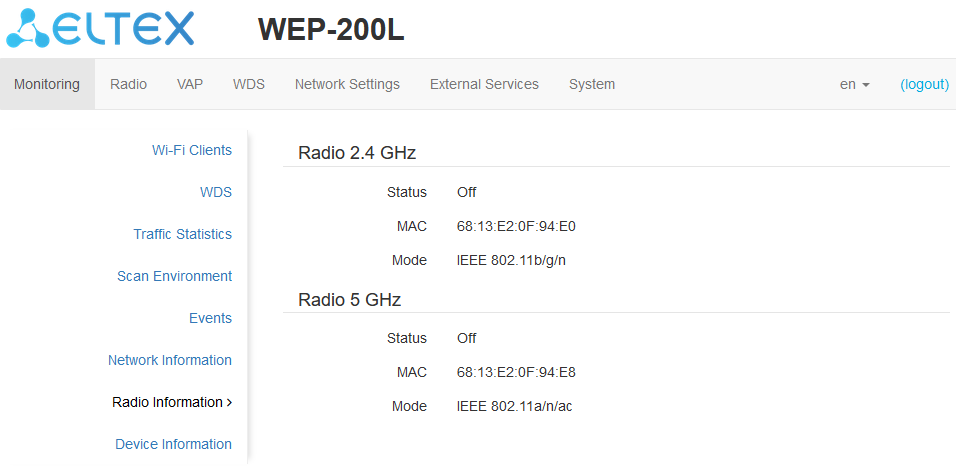
The “Radio Information” submenu
In the “Radio Information” submenu, the current status of WEP-200L radio interfaces is displayed.
The access point radio interfaces can be in two states: “On” and “Off”. The status of each radio interface is shown in the “Status” field.
The Radio status depends on whether the radio interface has enabled virtual access points (VAPs) or WDS. In case there is at least one active VAP on the radio interface, Radio will be in “On” status, otherwise — “Off”.
Depending on the Radio status, the following information is available for monitoring:
“Off”:
- Status — radio interface state;
- MAC — radio interface MAC address;
- Mode — radio interface operation mode according to IEEE 802.11 standards.
“On”:
- Status — radio interface state;
- MAC — radio interface MAC address;
- Mode — radio interface operation mode according to IEEE 802.11 standards;
- Channel — number of the wireless channel on which the radio interface is running;
- Channel bandwidth — bandwidth of the channel on which the radio interface is running.
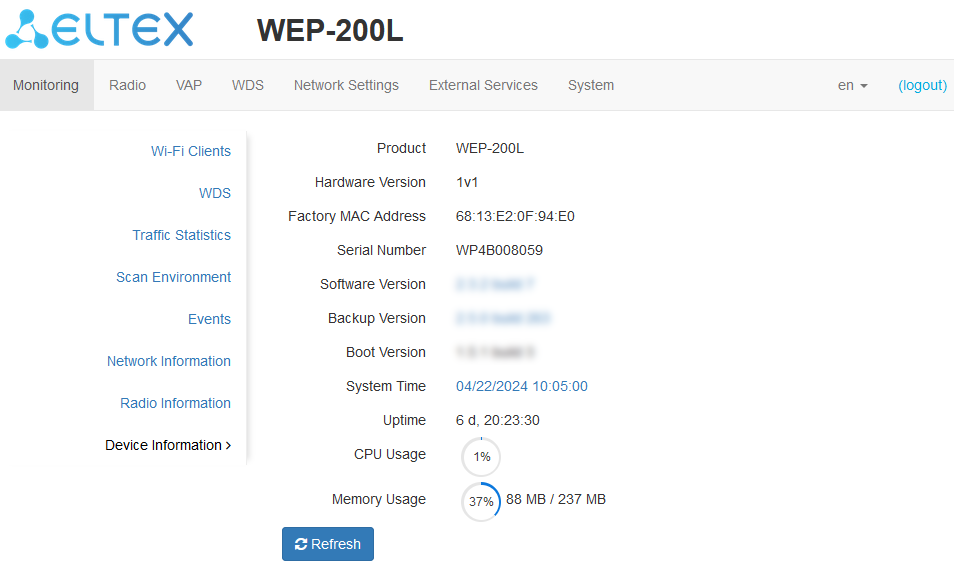
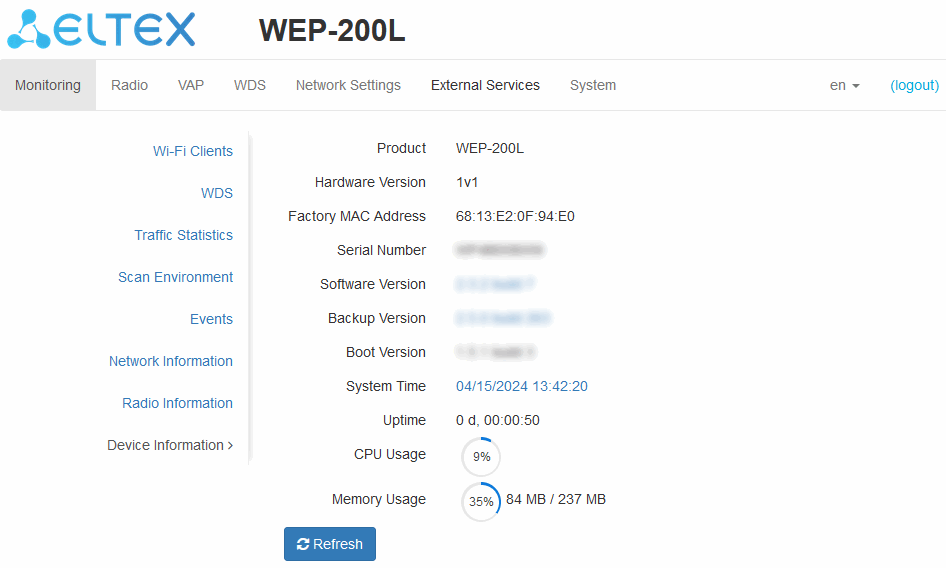
The “Device Information” submenu
The “Device Information” submenu displays WEP-200L main characteristics.
- Product — device model name;
- Hardware Version — device hardware version;
- Factory MAC Address — device WAN interface MAC address, factory set;
- Serial Number — device serial number, factory set;
- Software Version — device firmware version;
- Backup Version — previously installed firmware version;
- Boot Version — device firmware boot version;
- System Time — current time and date, set in the system;
- Uptime — operating time since the last time the device was turned on or rebooted;
- CPU Usage — average percentage of CPU load over the last 5 seconds;
- Memory Usage — percentage of device RAM usage.
The “Radio” menu
In the “Radio” menu, the wireless interface can be configured.
The “Radio 2.4 GHz” submenu
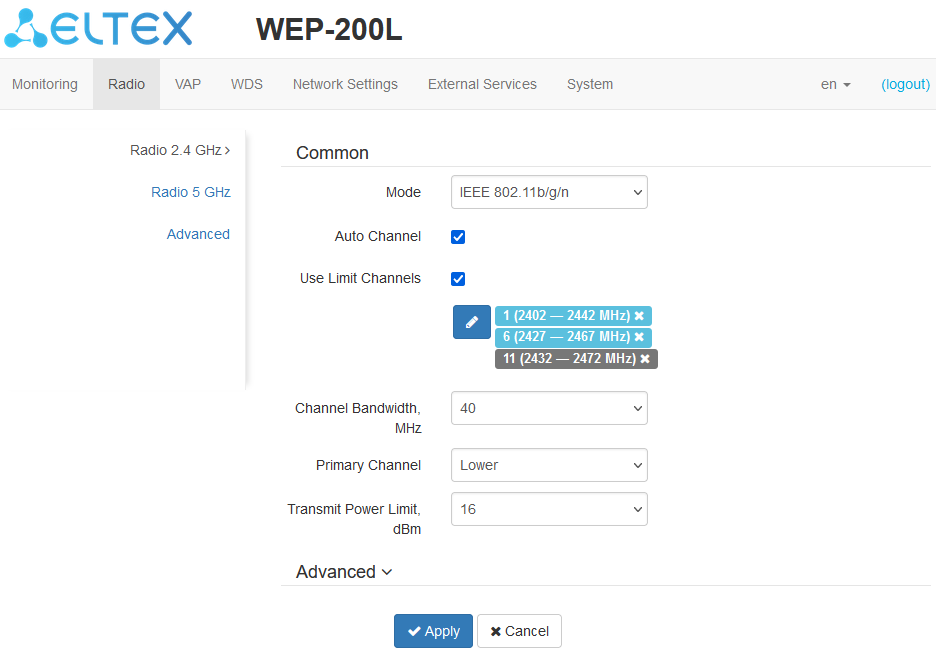
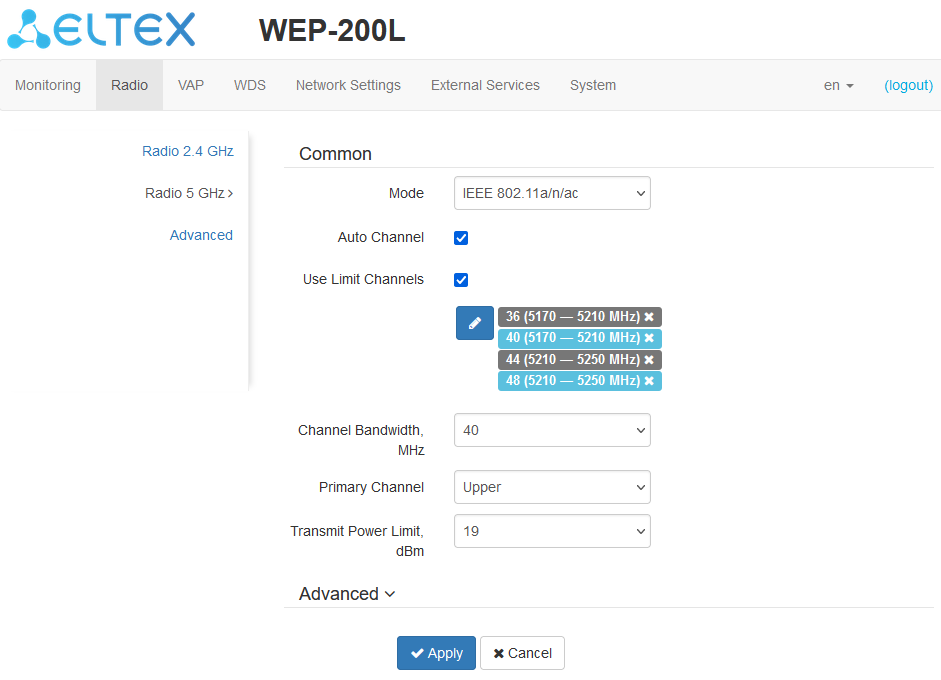
In the “Radio 2.4 GHz” submenu, the main parameters of the radio interface of the device operating in the 2.4 GHz band can be configured.
- Mode — interface operation mode according to the following standards:
- IEEE 802.11n;
- IEEE 802.11b/g;
- IEEE 802.11b/g/n.
- Auto Channel — when checked, the device will automatically select the least congested radio channel for the Wi-Fi interface. Unchecking the flag opens the access to install the static operation channel;
- Channel — select channel for data transmission;
- Use Limit Channels — when checked, the access point will use a user-defined list of channels to work in automatic channel selection mode. If the “Use Limit channels” flag is not checked or there are no channels in the list, the access point will select the operation channel from all available channels in the given band. 2.4 GHz band channels: 1–13;
- Channel Bandwidth, MHz — channel bandwidth, on which the access point operates. The parameter may take values 20 and 40 MHz;
- Primary Channel — the parameter can only be changed if the bandwidth of a statically specified channel is equal to 40 MHz. The 40 MHz channel can be considered as consisting of two 20 MHz channels, which border in the frequency range. These two 20 MHz channels are called primary and secondary channels. The primary channel is used by clients supporting 20 MHz channel bandwidth only:
- Upper — the primary channel will be the upper 20 MHz channel in the 40 MHz band;
- Lower — the primary channel will be the lower 20 MHz channel in the 40 MHz band.
- Transmit Power Limit, dBm — adjustment of the signal strength of the Wi-Fi transmitter in dBm. Accepts value from 4 to 16 dBm.
If the “Use Limit channels” list contains a channel that is not available for selection, it will be marked in grey. In order for the new configuration to be applied to an access point, only available (blue highlighted) channels must be specified in the “Use Limit channels” list.
Example. No settings have been made on the access point yet, Radio 2.4 GHz is set to 20 MHz “Channel Bandwidth” by default, and channels are specified in the “Use Limit channels” list: 1, 6, 11.
Suppose the parameter “Channel Bandwidth” should be set to 40 MHz. Upon changing this parameter from 20 MHz to 40 MHz, the following happens:
- the “Primary Channel” parameter becomes available for editing and the default value is “Lower”;
- channel 11 in the “Use Limit channels” list changes its color from blue to grey.
If to change the “Channel Bandwidth” parameter to 40 MHz and do not remove the “grey” channels from the list, then when clicking “Apply”, in the browser an error will appear — “There are errors in data. Changes were not applied”. Accordingly, the access point configuration will not be changed. This is due to the fact that channels in the “Use Limit channels” list that are highlighted in grey do not fit the definition “Primary Channel” = Lower.
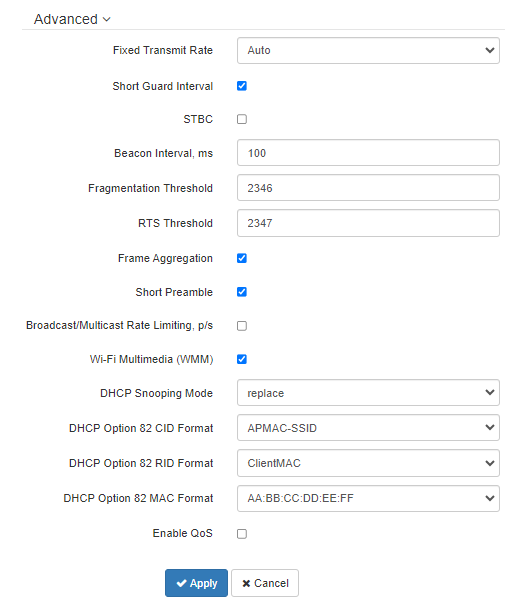
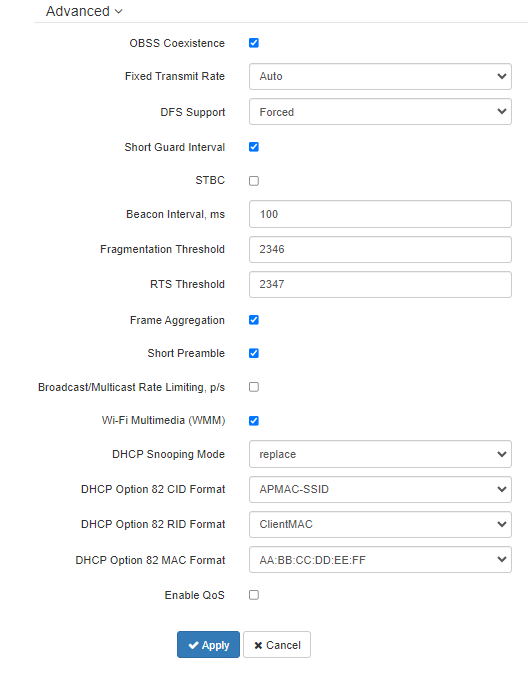
In the “Advanced” section, it is possible to configure advanced radio interface parameters of the device.
- OBSS Coexistence — automatic channel bandwidth reduction when the channel is loaded. When the flag is set, the mode is enabled;
- Fixed Transmit Rate — fixed wireless data rate, defined by IEEE 802.11b/g/n specifications;
- Short Guard Interval — support for Short Guard Interval. Access point transmits data using 400 ns guard interval (instead of 800 ns) to clients which also support Short Guard Interval;
- STBC — Space-Time Block Coding method dedicated to improve data transmission reliability. The field is available only if the selected operating mode for the radio interface includes 802.11n. When checked, the device transmits one data flow through several antennas. When unchecked, the device does not transmit the same data flow through several antennas;
- Beacon Interval, ms — beacon frames transmission period. The frames are sent to detect access points on the air. The parameter takes values from 20 to 2000 ms, by default: 100 ms;
- Fragmentation Threshold — frame fragmentation threshold, bytes. The parameter takes values 256–2346, by default: 2346;
- RTS Threshold — specifies the number of bytes over which the Request to Send will be sent. Decreasing this value may improve the performance of the access point when there are a lot of connected clients. However this reduces general throughput of wireless network. The parameter takes values from 0 to 2347, by default: 2347;
- Frame aggregation — enable support for AMPDU/AMSDU;
- Short Preamble — use of the packet short preamble;
- Broadcast/Multicast Rate Limiting, p/s — when the flag is set, transmission of broadcast / multicast traffic over the wireless network is restricted. Specify the limit for broadcast traffic in the popup window (p/s);
- Wi-Fi Multimedia (WMM) — WMM support activation (Wi-Fi Multimedia);
- DHCP Snooping Mode — selection of DHCP option 82 processing policy. Available values for selection:
- ignore — option 82 processing is disabled. Default value;
- remove — access point deletes the value of option 82;
- replace — access point substitutes or replaces the value of option 82. When selecting this value to edit, the following parameters are opened:
- DHCP Option 82 CID Format — replacement of the CID parameter value, can take values:
- APMAC-SSID — replacement of the CID parameter value to <MAC address of the access point>-<SSID name>. Default value;
- SSID — replacement of the CID parameter value to SSID name, to which the client is connected;
- custom — replacement of the CID parameter value to the value specified in the "Option 82 Unique CID";
- Option 82 Unique CID — an arbitrary string of up to 52 characters that will be passed to the CID. If the parameter value is not set, the point will change the CID to the default value — APMAC-SSID.
- DHCP Option 82 RID Format — replacement of the RID parameter value, can take the following values:
- ClientMAC — change the RID content to the MAC address of the client device. Default value;
- APMAC — change the RID content to the MAC address of the access point;
- APdomain — change the RID content to the domain in which the access point is located;
- custom — change the RID content to the value specified in the "Option 82 Unique RID";
- Option 82 Unique RID — an arbitrary string of up to 63 characters that will be passed to the RID. If the parameter value is not set, the point will change the RID to the default value — ClientMAC.
- DHCP Option 82 MAC Format — selection of octet delimiters of the MAC address, which is transmitted in CID and RID:
- AA:BB:CC:DD:EE:FF — the delimiter is a colon (:). Default value;
- AA-BB-CC-DD-EE-FF — the delimiter is a dash (-).
- DHCP Option 82 CID Format — replacement of the CID parameter value, can take values:
- Enable QoS — when the flag is set, the setting of Quality of Service functions is available.
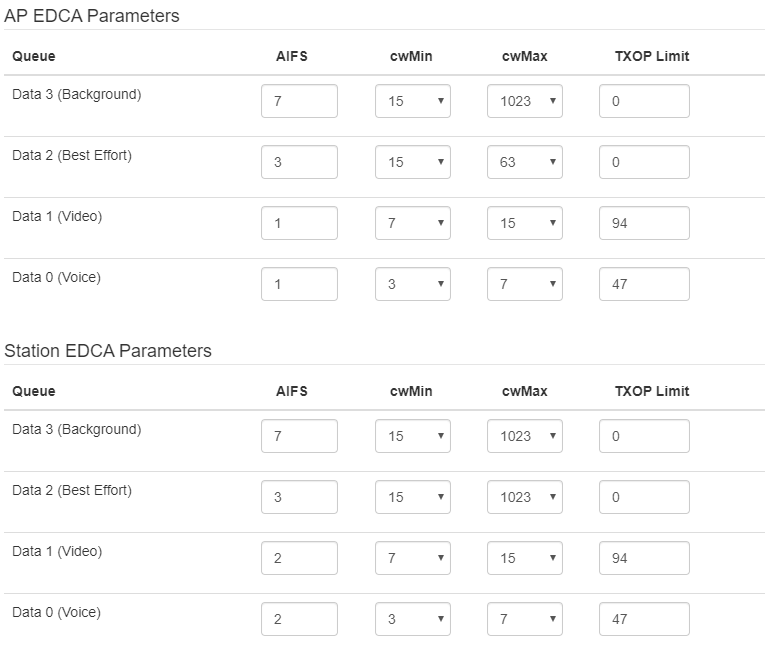
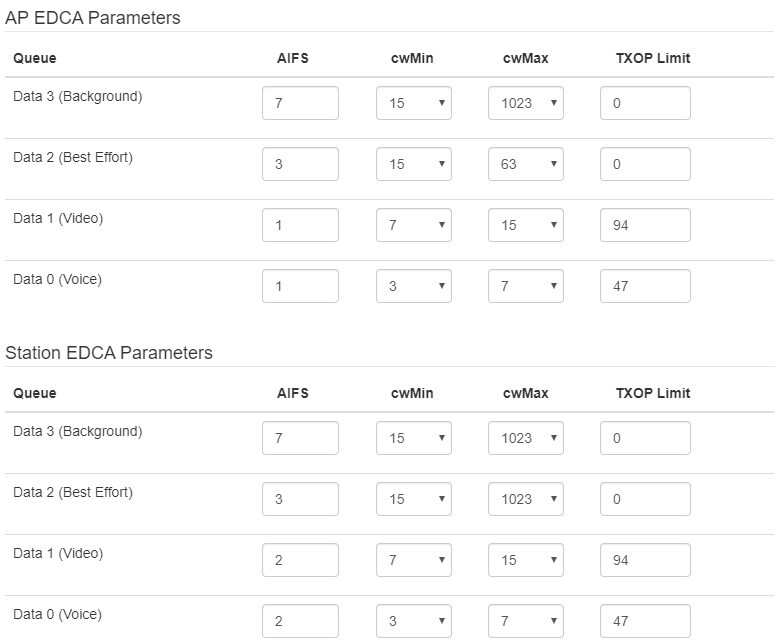
The following functions are available for quality assurance configuration:
- AP EDCA parameters — access point settings table (traffic is transmitted from the access point to the client):
- Queue — predefined queues for various kinds of traffic:
- Data 3 (Background) — low priority queue, high bandwidth (802.1p: cs1, cs2 priorities);
- Data 2 (Best Effort) — middle priority queue, middle bandwidth and delay. Most of the traditional IP data is sent to this queue (802.1p: cs0, cs3 priorities);
- Data 1 (Video) — high priority queue, minimal delay. In this queue, time-sensitive video data is automatically processed (802.1p: cs4, cs5 priorities);
- Data 0 (Voice) — high priority queue, minimal delay. In this queue, time sensitive data is automatically processed, such as: VoIP, streaming video (802.1p: cs6, cs7 priorities).
- AIFS — Arbitration Inter-Frame Spacing, defines the waiting time of data frames, measured in slots, takes values 1–255;
- cwMin — the initial timeout value before resending a frame, specified in milliseconds, takes the values 1, 3, 7, 15, 31, 63, 127, 255, 511, 1023. The value of cwMin cannot exceed the value of cwMax;
- cwMax — the maximum timeout value before resending a frame, specified in milliseconds, takes the values 1, 3, 7, 15, 31, 63, 127, 255, 511, 1023. The value of cwMax must exceed the value of cwMin;
- TXOP Limit — this parameter is used only for data transmitted from the client station to the access point. The transmission capability is the time interval, in milliseconds, when the client WME station has the rights to initiate data transmission over the wireless medium to the access point, the maximum value is 65535 milliseconds.
- Queue — predefined queues for various kinds of traffic:
- Station EDCA parameters — table of client station parameter settings (traffic is transmitted from the client station to the access point). For description of table fields, see above.
To apply a new configuration and save settings to non-volatile memory, click “Apply”. Click “Cancel” to discard the changes.
The “Radio 5 GHz” submenu
In the “Radio 5 GHz” submenu, the main parameters of the radio interface of the device operating in the 5 GHz band can be configured.
- Mode — select interface operation mode according to the following standards:
- IEEE 802.11a;
- IEEE 802.11a/n;
- IEEE 802.11a/n/ac.
- Auto Channel — when checked, the device will automatically select the least congested radio channel for the Wi-Fi interface. Removing the flag opens the access to install the static operation channel;
- Channel — select channel for data transmission;
- Use Limit Channels — when checked, the access point will use a user-defined list of channels to work in automatic channel selection mode. If the “Use Limit channels” flag is not checked or there are no channels in the list, the access point will select the operation channel from all available channels in the given band. 5 GHz band channels: 36–64, 132–144, 149–165;
- Channel Bandwidth, MHz — channel bandwidth, on which the access point operates. The parameter may take values of 20, 40 and 80 MHz;
- Primary Channel — the parameter can only be changed if the bandwidth of a statically specified channel is equal to 40 MHz. The 40 MHz channel can be considered as consisting of two 20 MHz channels, which border in the frequency range. These two 20 MHz channels are called primary and secondary channels. The primary channel is used by clients who only support 20 MHz channel bandwidth:
- Upper — the primary channel will be the upper 20 MHz channel in the 40 MHz band;
- Lower — the primary channel will be the lower 20 MHz channel in the 40 MHz band.
- Transmission Power Limit, dBm — transmitting Wi-Fi signal power adjustment, dBm. May take values between 8 and 19 dBm.
If the “Use Limit channels” list contains a channel that is not available for selection, it will be marked in grey. In order for the new configuration to be applied to an access point, only available (blue highlighted) channels must be specified in the “Use Limit channels” list.
Example. No settings have been made on the access point yet, Radio 5 GHz is set to 20 MHz “Channel Bandwidth” by default, and channels are specified in the “Use Limit channels” list: 36, 40, 44, 48.
Suppose, it is required to set “Channel Bandwidth” to 40 MHz. When you change this parameter from 20 MHz to 40 MHz, the following happens:
- the “Primary Channel” parameter becomes available for editing and the default value is “Upper”;
- channels 36 and 44 in the “Use Limit channels” list changes its color from blue to grey.
If you change the “Channel Bandwidth” parameter to 40 MHz and do not remove the “grey” channels from the list, then when you click “Apply” in the browser an error will appear — “There are errors in data. Changes were not applied”. Accordingly, the access point configuration will not be changed. This is due to the fact that channels in the “Use Limit channels” list that are highlighted in grey do not fit the definition “Primary Channel” = Upper.
In the “Advanced” section, it is possible to configure advanced radio interface parameters of the device.
- OBSS Coexistence — automatic channel bandwidth reduction when the channel is loaded. When the flag is set, the mode is enabled;
- Fixed Transmit Rate — fixed wireless data rate, defined by IEEE 802.11b/g/n specifications;
- DFS Support — dynamic frequency selection mechanism. The mechanism demands wireless devices to scan environment and avoid using channels which coincide with radiolocation system's channels at 5 GHz:
- Disabled — the mechanism is disabled. DFS channels are not available for selection;
- Enabled — the mechanism is enabled;
- Forced — the mechanism is disabled. DFS channels are available for selection.
- Short Guard Interval — support for Short Guard Interval. Access point transmits data using 400 ns guard interval (instead of 800 ns) to clients which also support Short Guard Interval;
- STBC — Space-Time Block Coding method dedicated to improve data transmission reliability. The field is available only if the selected operating mode for the radio interface includes 802.11n. When checked, the device transmits one data flow through several antennas. When unchecked, the device does not transmit the same data flow through several antennas;
- Beacon Interval, ms — beacon frames transmission period. The frames are sent to detect access points. The parameter takes values from 20 to 2000 ms, by default: 100 ms;
- Fragmentation Threshold — frame fragmentation threshold, bytes. The parameter takes values 256–2346, by default: 2346;
- RTS Threshold — specifies the number of bytes over which the Request to Send will be sent. Decreasing this value may improve the performance of the access point when there are a lot of connected clients. However this reduces general throughput of wireless network. The parameter takes values from 0 to 2347, by default: 2347;
- Frame aggregation — enables support for AMPDU/AMSDU;
- Short Preamble — use of the packet short preamble;
- Broadcast/Multicast Rate Limiting, p/s — when the flag is set, transmission of broadcast / multicast traffic over the wireless network is restricted. Specify the limit for broadcast traffic in the popup window (p/s);
- Wi-Fi Multimedia (WMM) — WMM support activation (Wi-Fi Multimedia);
- DHCP Snooping Mode — selection of DHCP option 82 processing policy. Available values for selection:
- ignore — option 82 processing is disabled. Default value;
- remove — access point deletes the value of option 82;
- replace — access point substitutes or replaces the value of option 82. When selecting this value to edit, the following parameters are opened:
- DHCP Option 82 CID Format — replacement of the CID parameter value, can take values:
- APMAC-SSID — replacement of the CID parameter value to <MAC address of the access point>-<SSID name>. Default value;
- SSID — replacement of the CID parameter value to SSID name, to which the client is connected;
- custom — replacement of the CID parameter value to the value specified in the "Option 82 Unique CID";
- Option 82 Unique CID — an arbitrary string of up to 52 characters that will be passed to the CID. If the parameter value is not set, the point will change the CID to the default value — APMAC-SSID.
- DHCP Option 82 RID Format — replacement of the RID parameter value, can take the following values:
- ClientMAC — change the RID content to the MAC address of the client device. Default value;
- APMAC — change the RID content to the MAC address of the access point;
- APdomain — change the RID content to the domain in which the access point is located;
- custom — change the RID content to the value specified in the "Option 82 Unique RID";
- Option 82 Unique RID — an arbitrary string of up to 63 characters that will be passed to the RID. If the parameter value is not set, the point will change the RID to the default value — ClientMAC.
- DHCP Option 82 MAC format — selection of octet delimiters of the MAC address, which is transmitted in CID and RID:
- AA:BB:CC:DD:EE:FF — the delimiter is a colon (:). Default value;
- AA-BB-CC-DD-EE-FF — the delimiter is a dash (-).
- DHCP Option 82 CID Format — replacement of the CID parameter value, can take values:
- Enable QoS — when the flag is set, the setting of Quality of Service functions is available.
The following functions are available for quality assurance configuration:
- AP EDCA parameters — access point settings table (traffic is transmitted from the access point to the client):
- Queue — predefined queues for various kinds of traffic:
- Data 3 (Background) — low priority queue, high bandwidth (802.1p: cs1, cs2 priorities);
- Data 2 (Best Effort) — middle priority queue, middle bandwidth and delay. Most of the traditional IP data is sent to this queue (802.1p: cs0, cs3 priorities);
- Data 1 (Video) — high priority queue, minimal delay. In this queue, time-sensitive video data is automatically processed (802.1p: cs4, cs5 priorities);
- Data 0 (Voice) — high priority queue, minimal delay. In this queue, time sensitive data is automatically processed, such as: VoIP, streaming video (802.1p: cs6, cs7 priorities).
- AIFS — Arbitration Inter-Frame Spacing, defines the waiting time of data frames, measured in slots, takes values 1–255;
- cwMin — the initial timeout value before resending a frame, specified in milliseconds, takes the values 1, 3, 7, 15, 31, 63, 127, 255, 511, 1023. The value of cwMin cannot exceed the value of cwMax;
- cwMax — the maximum timeout value before resending a frame, specified in milliseconds, takes the values 1, 3, 7, 15, 31, 63, 127, 255, 511, 1023. The value of cwMax must exceed the value of cwMin;
- TXOP Limit — this parameter is used only for data transmitted from the client station to the access point. The transmission capability is the time interval, in milliseconds, when the client WME station has the rights to initiate data transmission over the wireless medium to the access point, the maximum value is 65535 milliseconds.
- Queue — predefined queues for various kinds of traffic:
- Station EDCA parameters — table of client station parameter settings (traffic is transmitted from the client station to the access point). For description of table fields, see above.
To apply a new configuration and save settings to non-volatile memory, click “Apply”. Click “Cancel” to discard the changes.
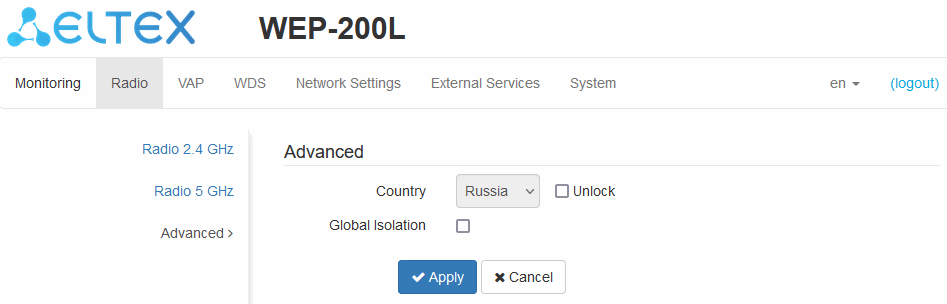
The “Advanced” submenu
In the “Advanced” submenu, it is possible to configure advanced radio interface parameters of the device.
- Country — country of access point operation. Select the “Unlock” checkbox to change a country. Depending on the selected value the channel bandwidth and transmit power limit restrictions will be applied. The list of available frequency channels depends on the selected country, which affects the automatic channel selection in the Channel = Auto mode. If the subscriber equipment is licensed for use in a different region, probably, a connection with the access point will not be established.
Local country regulations settings, including operation within legal frequency channels and output power, is the installer's responsibility.
Selecting the wrong region may result in compatibility issues with different client devices.
- Global Isolation — when checked, traffic isolation between clients of different VAPs and different radio interfaces is enabled.
To apply a new configuration and save settings to non-volatile memory, click “Apply”. Click “Cancel” to discard the changes.
The “VAP” menu
In the “VAP” menu, virtual Wi-Fi access points (VAP) can be configured.
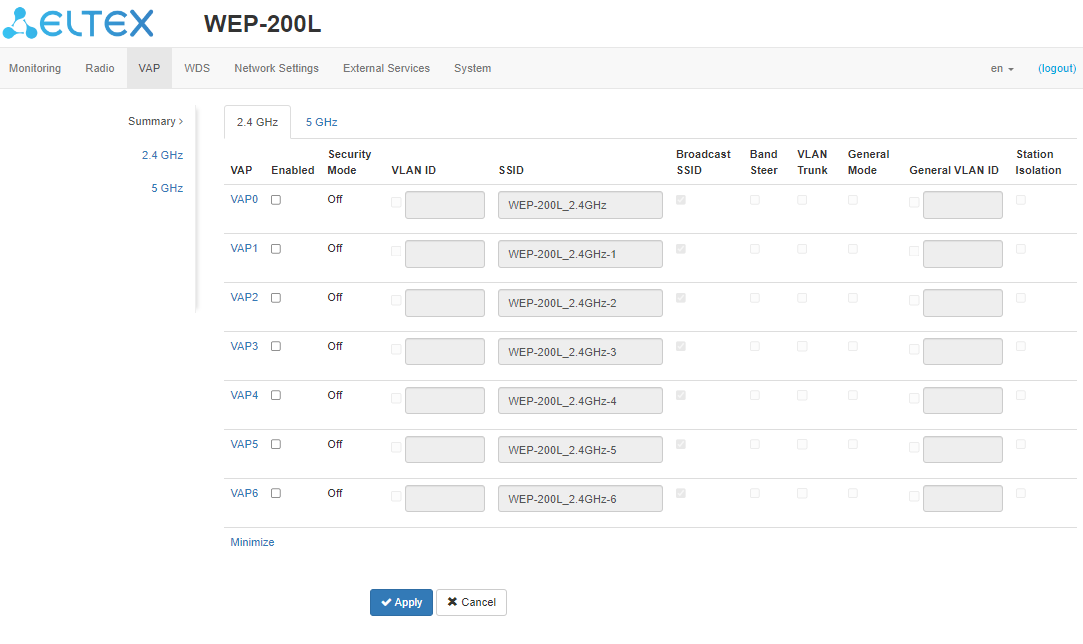
The “Summary” submenu
The “Summary” submenu displays the settings of all VAPs on Radio 2.4 GHz and Radio 5 GHz radio interfaces. The settings of each virtual access point can be viewed in sections of VAP0–VAP6.
- VAP0–VAP6 — the sequence number of the virtual access point;
- Enabled — when checked, the virtual access point is enabled, otherwise it is disabled;
- Security Mode — the type of data encryption used on the virtual access point;
- VLAN ID — VLAN number from which the tag will be removed when transmitting Wi-Fi traffic to clients connected to this VAP. When traffic flows in the opposite direction, untagged traffic from clients will be tagged with VLAN ID (when VLAN Trunk mode is disabled);
- SSID — virtual wireless network name;
- Broadcast SSID — when checked, SSID broadcasting is on, otherwise it is disabled;
- Band Steer — when the flag is set, the priority connection of the client to 5 GHz network is active. In order for this feature to work, it is required to create a VAP with the same SSID on each radio interface and activate the “Band Steer mode” on them;
- VLAN Trunk — when the flag is set, tagged traffic is transmitted to the subscriber;
- General Mode — when the flag is set, transmission of untagged traffic jointly with tagged traffic is allowed (available when Trunk VLAN mode is enabled);
- General VLAN ID — a tag will be removed from the specified VLAN ID and the traffic of this VLAN will pass to the client without a tag. When traffic passes in the opposite direction, untagged traffic will be tagged with General VLAN ID;
- Station Isolation — when checked, traffic isolation between clients in the same VAP is enabled.
To apply a new configuration and save settings to non-volatile memory, click “Apply”. Click “Cancel” to discard the changes.
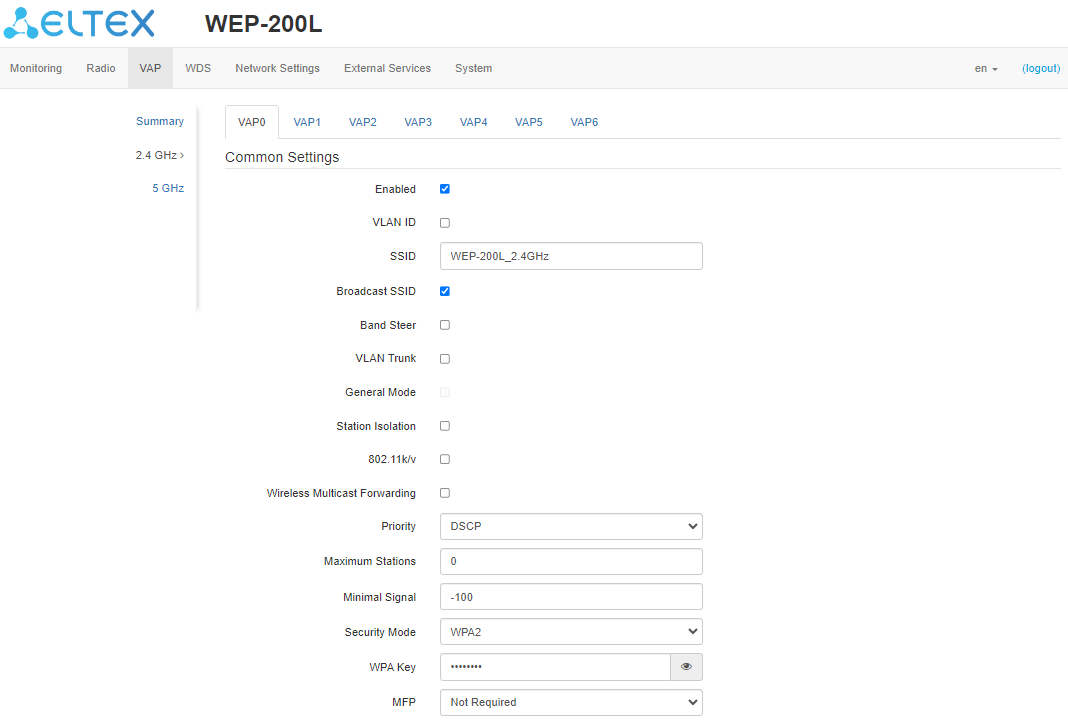
The “VAP” submenu
Common settings
- Enabled — when checked, the virtual access point is enabled, otherwise it is disabled;
- VLAN ID — VLAN number from which the tag will be removed when transmitting Wi-Fi traffic to clients connected to this VAP. When traffic flows in the opposite direction, untagged traffic from clients will be tagged with VLAN ID (when VLAN Trunk mode is disabled);
- SSID — virtual wireless network name;
- Broadcast SSID — when checked, SSID broadcasting is on, otherwise it is disabled;
- Band Steer — when the flag is set, the priority connection of the client to 5 GHz network is active. In order for this feature to work, it is required to create a VAP with the same SSID on each radio interface and activate the “Band Steer mode” on them;
- VLAN Trunk — when the flag is set, tagged traffic is transmitted to the subscriber;
- General Mode — when the flag is set, transmission of untagged traffic jointly with tagged traffic is allowed (available when Trunk VLAN mode is enabled);
- General VLAN ID — a tag will be removed from the specified VLAN ID and the traffic of this VLAN will pass to the client without a tag. When traffic passes in the opposite direction, untagged traffic will be tagged with General VLAN ID;
- Station Isolation — when checked, traffic isolation between clients in the same VAP is enabled;
- 802.11k/v — enable support for 802.11k/v standards on virtual access point;
- Wireless Multicast Forwarding — when the flag is set, traffic towards clients will be converted to Unicast before each client, if it is disabled, it will pass without modifications;
- Priority — select prioritization mode. Defines the field on the basis of which the traffic transmitted to the radio interface will be distributed in WMM queues:
- DSCP — will analyze the priority from the DSCP field of the IP packet header;
- 802.1p — will analyze the priority from the CoS (Class of Service) field of the tagged packets.
- Minimal signal — when the checkbox is selected, the function of disabling client Wi-Fi equipment when the signal level is low (Minimal Signal Level) is enabled. It is necessary to configure the following parameters:
- Minimal Signal Level, dBm — signal level in dBm below which the client equipment is disconnected from the virtual network;
- Roaming Signal Level, dBm — roaming sensitivity level in dBm, below which the client equipment switches to another access point. The parameter must be higher than the Minimal Signal Level: if the Minimal Signal Level is -75 dBm, then the Roaming Signal Level should be equal to, for example, -70 dBm;
- Minimal Signal Timeout, s — the period of time after which a decision is made to disconnect client equipment from the virtual network.
- Maximum Stations — the maximum allowable number of clients connected to the virtual network;
- MFP — management frame protection (available for WPA2 and WPA2-Enterprise selected security mode, selecting other security modes puts the MFP in the disabled state):
- Not required — management frame protection is disabled;
- Capable — protection works if the client supports MFP. Clients without MFP support can connect to this VAP;
- Required — management frame protection is enabled, clients that do not support MFP cannot connect.
- Security Mode — wireless access security mode:
- Off — do not use encryption for data transfer. The access point is available for any subscriber to connect;
- WPA, WPA2, WPA/WPA2 — encryption methods, if you select one of the methods, the following setting will be available:
- WPA Key — key/password required to connect to the virtual access point. The length of the key is from 8 to 63 characters.
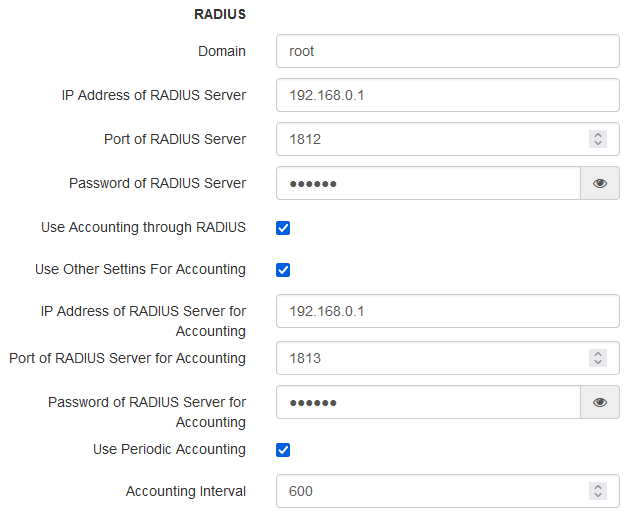
- WPA-Enterprise, WPA2-Enterprise, WPA/WPA2-Enterprise — wireless channel encryption mode, in which the client is authorized on the centralized RADIUS server. To configure this security mode, specify the parameters of the RADIUS server. Also specify a key for the RADIUS server. When selecting one of the these methods, the following setting will be available:
- Domain — user domain;
- IP Address of RADIUS Server — RADIUS server address;
- Port of RADIUS Server — port of the RADIUS server that used for authentication and authorization;
- Password of RADIUS Server — password for the RADIUS server used for authentication and authorization;
- Use Accounting through RADIUS — when checked, “Accounting” messages will be sent to the RADIUS server;
- Use Other Settings For Accounting:
- IP Address of RADIUS Server for Accounting — address of the RADIUS server, used for accounting;
- Password of RADIUS Server for Accounting — password for the RADIUS server used for accounting.
- Port of RADIUS Server for Accounting — port that will be used to collect accounts on the RADIUS server;
- Use Periodic Accounting — enable periodic sending of “Accounting” messages to the RADIUS server. The interval for sending messages can be set in the “Accounting Interval” field.
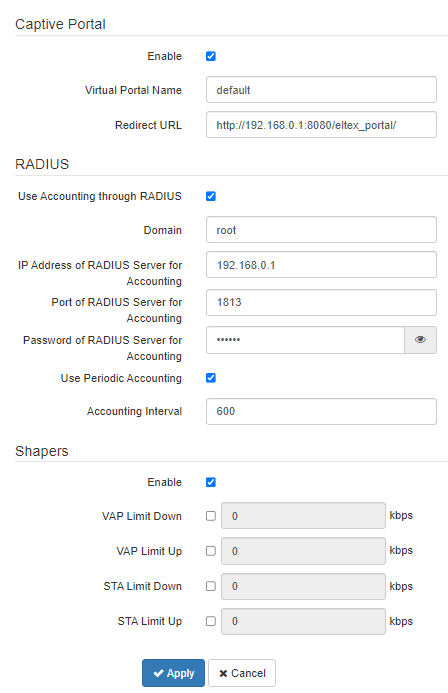
Captive Portal
When selecting one of the following security modes: Off, WPA, WPA2, WPA/WPA2, a portal authorization setting is available on the VAP.
- Enable — when checked, authorization of users in the network will be performed via the virtual portal;
- Virtual Portal Name — name of the virtual portal to which the user will be redirected when connecting to the network;
- Redirect URL — the address of the external virtual portal to which the user will be redirected when connecting to the network.
RADIUS
- Use Accounting through RADIUS — when checked, “Accounting” messages will be sent to the RADIUS server;
- Domain — user domain;
- IP Address of RADIUS Server for Accounting — address of the RADIUS server, used for accounting;
- Port of RADIUS Server for Accounting — port that will be used to collect accounts on the RADIUS server;
- Password of RADIUS Server for Accounting — password for the RADIUS server used for accounting;
- Use Periodic Accounting — enable periodic sending of “Accounting” messages to the RADIUS server. The interval for sending messages can be set in the “Accounting Interval” field.
Shapers
- Enable — activate the setting field;
- VAP Limit Down — restriction of bandwidth in the direction from the access point to the clients (in total) connected to this VAP, Kbps;
- VAP Limit Up — restriction of bandwidth in the direction from the clients (in total) connected to this VAP, to the access point, Kbps;
- STA Limit Down — restriction of bandwidth in the direction from the access point to the clients (each separately) connected to this VAP, Kbps;
- STA Limit Up — restriction of bandwidth in the direction from the clients (each separately) connected to this VAP, to the access point, Kbps.
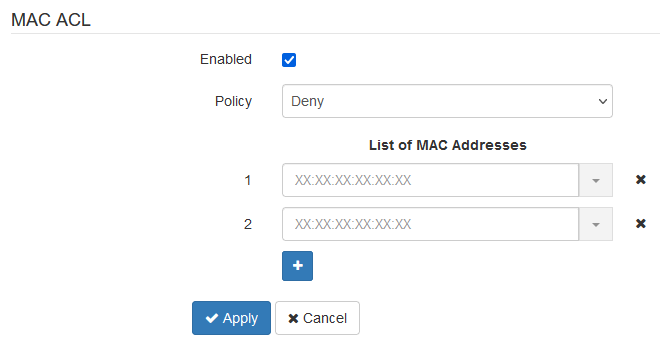
MAC ACL
This subsection configures lists of MAC addresses of clients who, depending on the selected access policy, are allowed or denied to connect to this VAP.
- Enabled — when the checkbox is selected the chosen policy is active;
- Policy — access policy. Available options:
- Deny — specified MAC addresses will be denied to connect to this VAP. The access will be allowed for everyone else;
- Allow — specified MAC addresses will be allowed to connect to this VAP. The access will be denied for everyone else.
- List of MAC Addresses — a list of MAC addresses of clients who are allowed or denied access to this VAP. Can contain up to 128 addresses.
- Policy — access policy. Available options:
To add an address to the list, click the button and enter the MAC address in the appeared field. To remove an address from the list, click the button in the corresponding line.
If there is a need to add to the list the MAC address of the client that is currently connected to the base station, click the button at the end of the line and select the desired address from the list, it will automatically be added to the field.
By default, the list displays up to 10 addresses. To see the full list if it contains more than 10 addresses, click the “Show all” button.
To apply a new configuration and save settings to non-volatile memory, click “Apply”. Click “Cancel” to discard the changes.
The “WDS” menu
The WDS menu configures wireless bridges between WEP-200L.
When configuring a WDS connection, it is necessary to select the same channel and channel width in the radio interface settings on the the devices that will be connected via WDS.
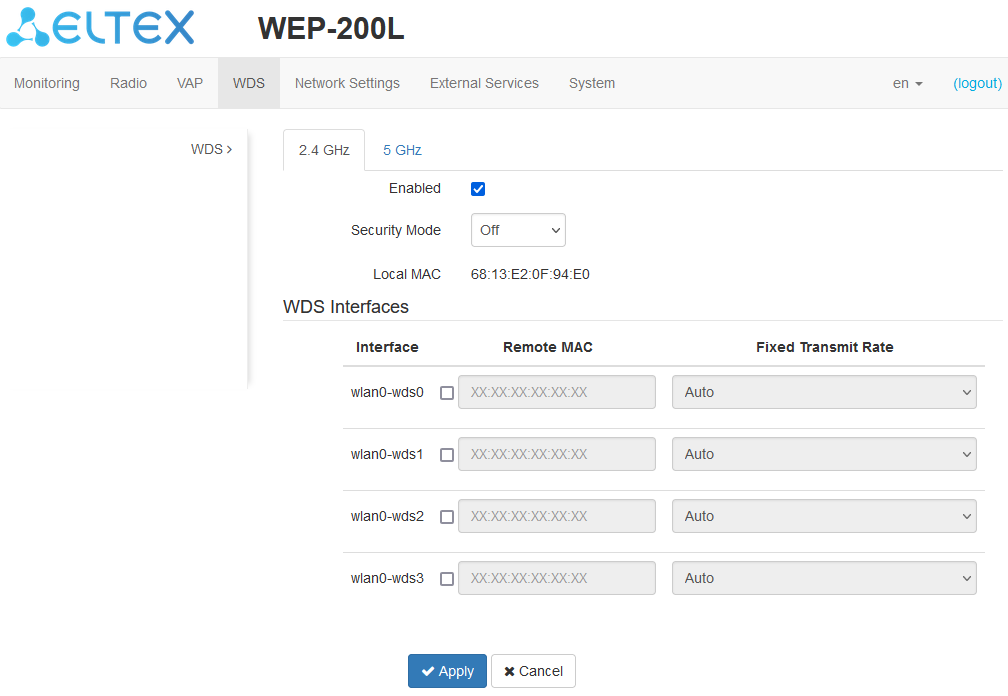
The “WDS” submenu
In the "2.4 GHz" and "5 GHz" tabs, select the radio interface of the device on which a wireless bridge should be built.
- Enabled — if the flag is selected, the wireless bridge mode is enabled, otherwise it is disabled;
- Security mode — wireless access security mode:
- Off — do not use encryption for data transfer;
- WPA2 — encryption method, when selected, the following setting will be available:
- WPA key — key/password required to connect to the remote access point. The key length is from 8 to 63 characters.
- Local MAC — MAC address of this device radio interface;
- Interface — selecting and enabling the WDS interface on which the wireless bridge will be built;
- Remote MAC — MAC address of the remote device radio interface, to which a wireless bridge is cofigured;
- Fixed Transmit Rate — fixed wireless data rate, defined by the specifications of the IEEE 802.11 standards. For each interface, select individually.
To apply a new configuration and save settings to non-volatile memory, click “Apply”. Click “Cancel” to discard the changes.
The “Network Settings” menu
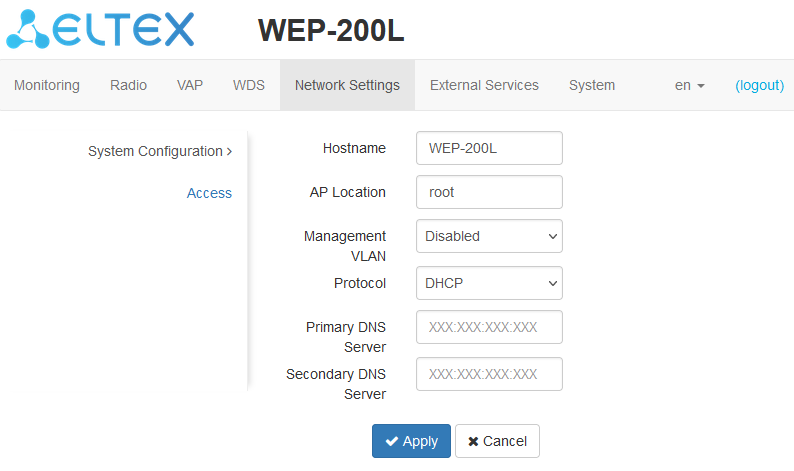
The “System Configuration” submenu
- Hostname — nertwork name of the device, specified by string from 1 to 63 characters; latin uppercase and lowercase letters, digits, hyphen “-” (hyphen can not be the last character in the name);
- AP Location — domain of the EMS management system tree host where the access point is located;
- Management VLAN:
- Disabled — Management VLAN is not used;
- Terminating — the mode in which the management VLAN is terminated at the access point (in this case, clients connected via the radio interface do not have access to this VLAN. With WDS configured on the access point, this management VLAN mode is not available for choice.);
- Forwarding — the mode in which the management VLAN is also transmitted to the radio interface (with the appropriate VAP configuration).
- VLAN ID — the VLAN ID used to access the device, takes values 1–4094;
- Protocol — select protocol for connection of the device via Ethernet interface to service provider network:
- DHCP — operation mode, when IP address, subnet mask, DNS server address, default gateway and other parameters required for operation are obtained from DHCP server automatically;
- Static — operation mode, when IP address and all the necessary parameters for WAN interface are assigned statically. If “Static” is selected, the following parameters will be available to set:
- Static IP — IP address of the device WAN interface in the provider network;
- Netmask — external subnet mask;
- Gateway — address, to which the packet is sent, if the route in routing table is not found for it.
- Primary DNS server, Secondary DNS server — IP addresses of DNS servers. If addresses of DNS servers are not automatically assigned via DHCP, set them manually.
To apply a new configuration and save settings to non-volatile memory, click “Apply”. Click “Cancel” to discard the changes.
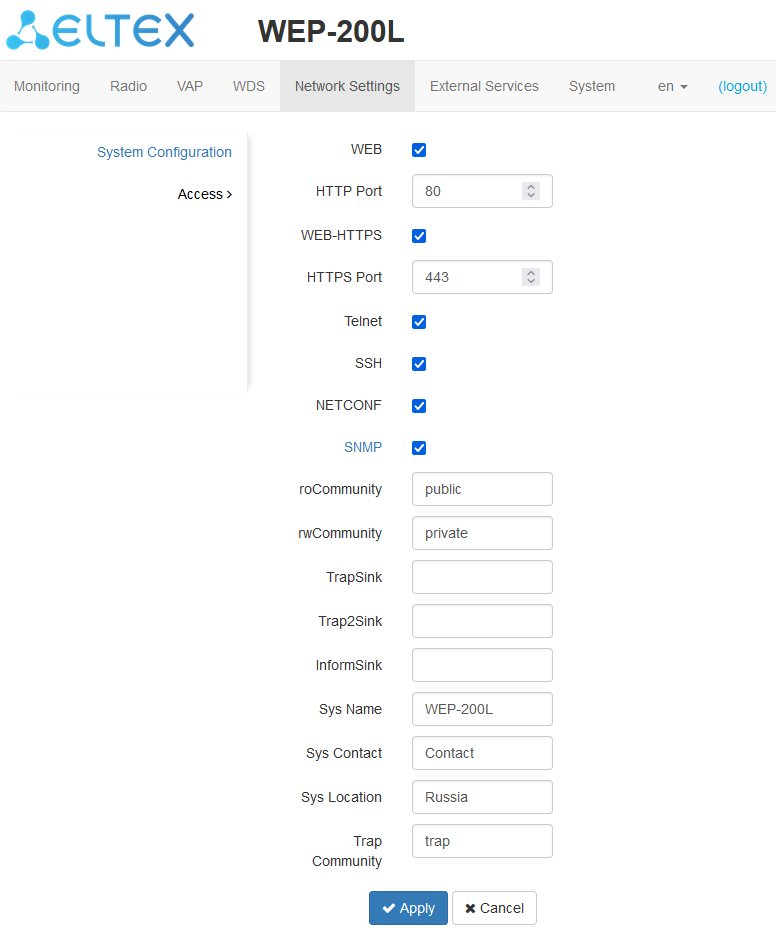
The “Access” submenu
In the “Access” submenu, the access to the device via Web interface, Telnet, SSH, NETCONF and SNMP can be configured.
- To enable access to the device via the web interface via HTTP protocol, set the flag next to “WEB”. In the window that appears, it is possible to change the HTTP port (by default: 80). The range of acceptable values of ports, in addition to the default, from 1025 to 65535 inclusive;
To enable access to the device via the web interface via HTTPS protocol, set the flag next to “WEB-HTTPS”. In the window that appears, it is possible to change the HTTPS port (by default: 443). The range of acceptable values of ports, in addition to the default, from 1025 to 65535 inclusive;
Note that the ports for the HTTP and HTTPS protocols should not have the same value.
- To enable access to the device via Telnet, check the box next to “Telnet”;
- To enable access to the device via SSH, check the box next to “SSH”;
- To enable access to the device via NETCONF, check the box next to “NETCONF”.
The WEP-200L software allows changing the device configuration, monitoring the status of the access point and its sensors, as well as managing the device using the SNMP protocol.
To change the SNMP settings, check the box next to “SNMP”, the following SNMP agent options become available:
- roCommunity — a password to read the parameters (by default: public);
- rwCommunity — a password to write parameters (by default: private);
- TrapSink — IP address or domain name of SNMPv1-trap message recipient in HOST [COMMUNITY [PORT]] format;
- Trap2Sink — IP address or domain name of SNMPv2-trap message recipient in HOST [COMMUNITY [PORT]] format;
- InformSink — IP address or domain name of Inform message recipient in HOST [COMMUNITY [PORT]] format;
- Sys Name — device name;
- Sys Contact — device vendor contact information;
- Sys Location — device location information;
- Trap community — password enclosed in traps (default value: trap).
The list of objects which are supported for reading and configuring via SNMP is given below:
- eltexLtd.1.127.1 — monitoring of access point parameters and connected client devices;
- eltexLtd.1.127.3 — access point management;
- eltexLtd.1.127.5 — access point configuring.
where eltexLtd — 1.3.6.1.4.1.35265 is Eltex Enterprise ID.
See detailed OID description on WEP/WOP-xL.
To apply a new configuration and save settings to non-volatile memory, click “Apply”. Click “Cancel” to discard the changes.
The “External Services” menu
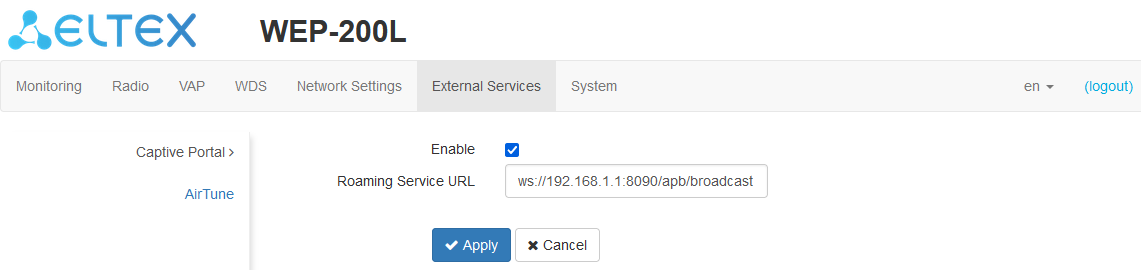
The “Captive Portal” submenu
The “Captive Portal” submenu is designed to enable and configure the APB service at the access point.
The APB service is used to provide portal roaming of clients between access points connected to the service.
- Enable — when checked, the access point will connect to the APB service, the address of which is specified in the “Roaming Service URL” field, to provide portal roaming of clients;
- Roaming Service URL — APB service address to support roaming in the portal authorization mode. Set in format: "ws://<host>:<port>/apb/broadcast".
To apply a new configuration and save settings to non-volatile memory, click “Apply”. Click “Cancel” to discard the changes.
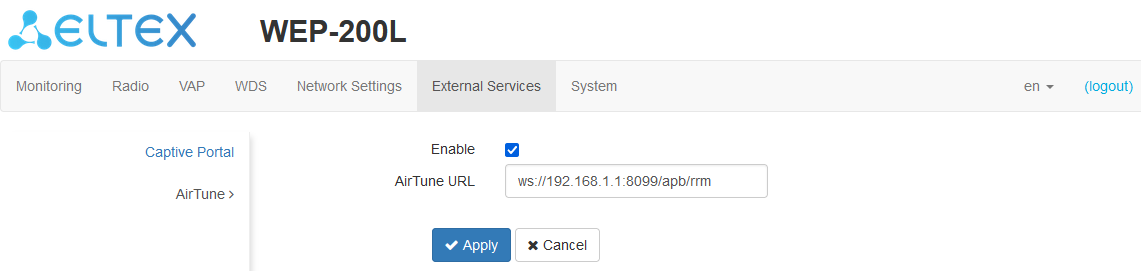
The “AirTune“ submenu
The “AirTune” submenu is designed to enable and configure the AirTune service at the access point.
The AirTune service is used to optimize Radio Resourse Management and to automatically configure seamless roaming (802.11 k/r).
- Enable — when checked, the access point will connect to the AirTune service, the address of which is specified in the “AirTune URL” field, to provide functions of Radio Resourse Management or/and roaming 802.11 k/r;
- AirTune URL — AirTune service address. Set in format: "ws://<host>:<port>/apb/rrm".
To apply a new configuration and save settings to non-volatile memory, click “Apply”. Click “Cancel” to discard the changes.
The “System” menu
In the “System” menu, the user can configure the system, time, device access via different protocols, change password, and update device firmware.
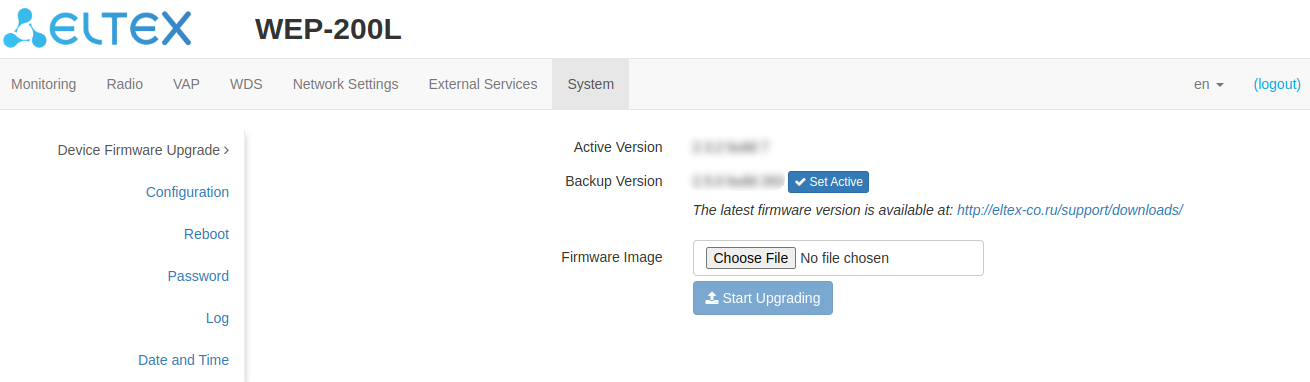
The “Device Firmware Upgrade” submenu
The “Device Firmware Upgrade” submenu is intended for upgrading the device firmware.
- Active Version — installed firmware version, which is operating at the moment;
- Backup Version — installed firmware version which can be used in case of problems with the current active firmware version;
- Set Active — a button that allows one to make a backup version of the firmware active, this will require a device reboot. The active firmware version will not be set as a backup.
Firmware upgrade
Download the firmware file from http://eltex-co.com/support/downloads/, select “Wireless“ → “Enterprise Wi-Fi Access Points“ → “WEP-200L“ and save it on your computer. After that, click “Choose File” in the Firmware Image field and specify the path to the firmware file in .tar.gz format.
To start the upgrade process, click the “Start Upgrading”. The process may take several minutes (its current status will be shown on the page). The device will be automatically rebooted when the upgrade is completed.
Do not switch off or reboot the device during a firmware upgrade.
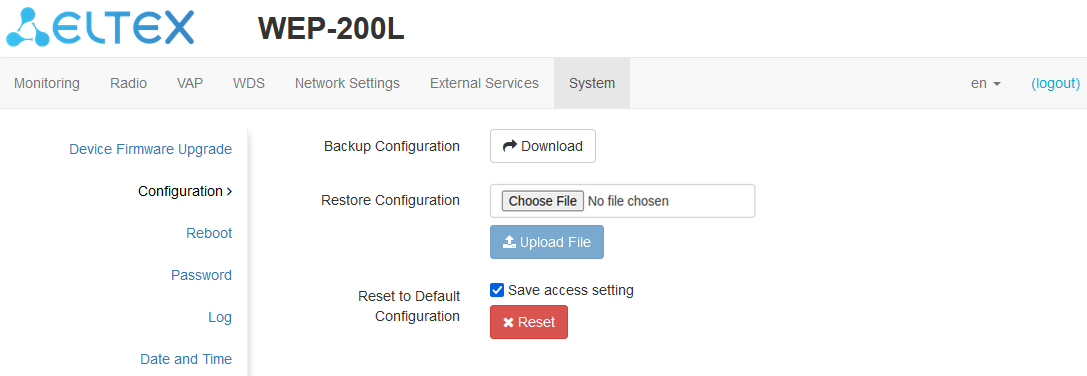
The “Configuration” submenu
In the “Configuration” submenu, the current configuration can be saved and updated.
Backup Configuration
To save current device configuration to local computer click “Download”.
Restore Configuration
To upload the configuration file saved on the local computer, use the Restore Configuration item. To update the device configuration click “Choose File”, specify a file (in .tar.gz format) and click “Upload File”. Uploaded configuration will be applied automatically and does not require device reboot.
Reset to Default Configuration
To reset all the settings to default values, click “Reset”. If the flag “Save access setting” is activated, then those settings, configurations that are responsible for access to the device (IP address settings, Telnet/SSH/SNMP/Netconf/Web access settings) will be saved.
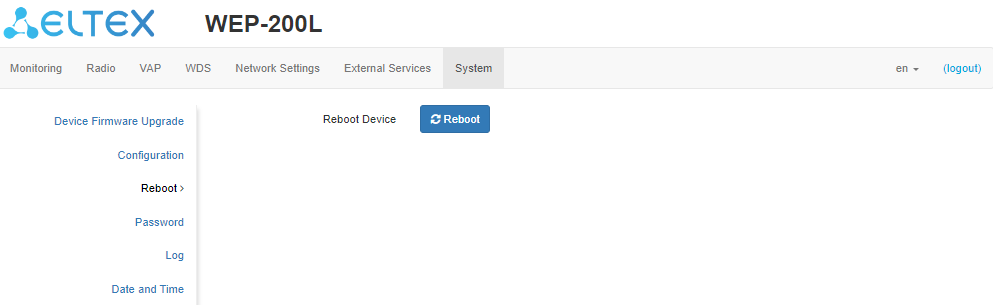
The “Reboot” submenu
To reboot the device, click “Reboot”. The device reboot process takes about 1 minute.
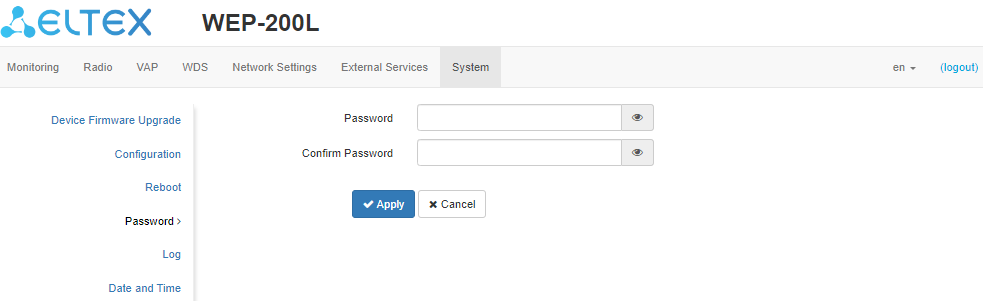
The “Password” submenu
When logging in via web interface, administrator (default password: password) has the full access to the device: read/write any settings, full device status monitoring.
To change the password, enter the new password first in the “Password” field, then in the “Confirm Password” field, and click “Apply” to save the new password.
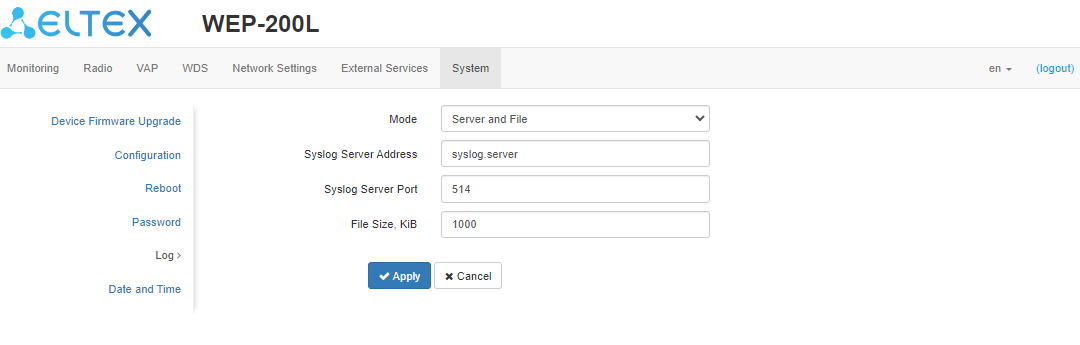
The “Log” submenu
The “Log” submenu is designed to configure the output of various kinds of debugging messages of the system in order to detect the causes of problems in the operation of the device.
- Mode — Syslog agent operation mode:
- Local File — log information is stored in a local file and is available in the device web interface on the “Monitoring/Events” tab;
- Server and File — log information is sent to a remote Syslog server and stored in a local file.
- Syslog Server Address — IP address or domain name of the Syslog server;
- Syslog Server Port — port for incoming Syslog server messages (default: 514, valid values: from 1 to 65535);
- File Size — maximum size of the log file (valid values: 1–1000 kB).
To apply a new configuration and save settings to non-volatile memory, click “Apply”. Click “Cancel” to discard the changes.
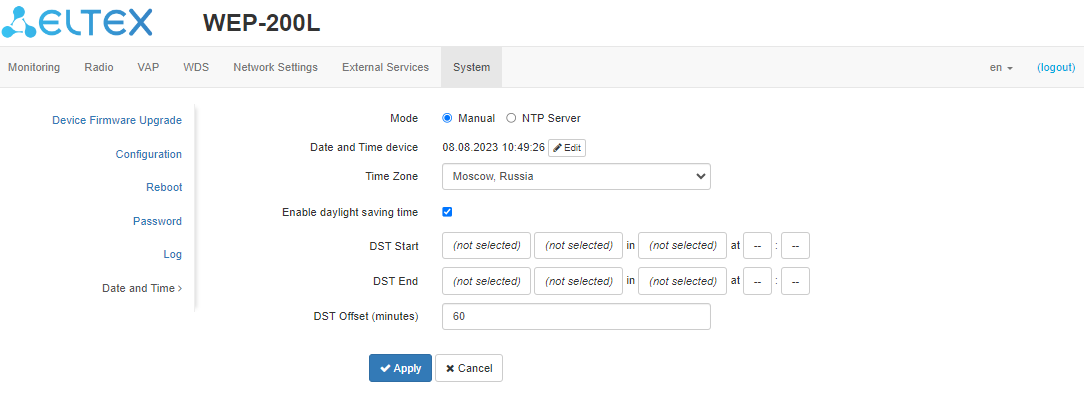
The “Date and Time” submenu
In the “Date and Time” submenu, it is possible to set the time manually or using the time synchronization protocol (NTP).
Manual
- Date and Time device — date and time on the device at the current moment. Click “Edit” to make corrections:
- Date, Time — set the current date and time or click “Set current date and time” to synchronize with the device;
- Time Zone — allows to set the timezone according to the nearest city for your region from the list;
- Enable Daylight Saving Time — when selected, automatic daylight saving change will be performed automatically within the defined time period:
- DST Start — day and time, when daylight saving time is starting;
- DST End — day and time, when daylight saving time is ending;
- DST Offset (minutes) — time period in minutes, on which time offset is performing. The parameter can take a value from 0 to 720 minutes.
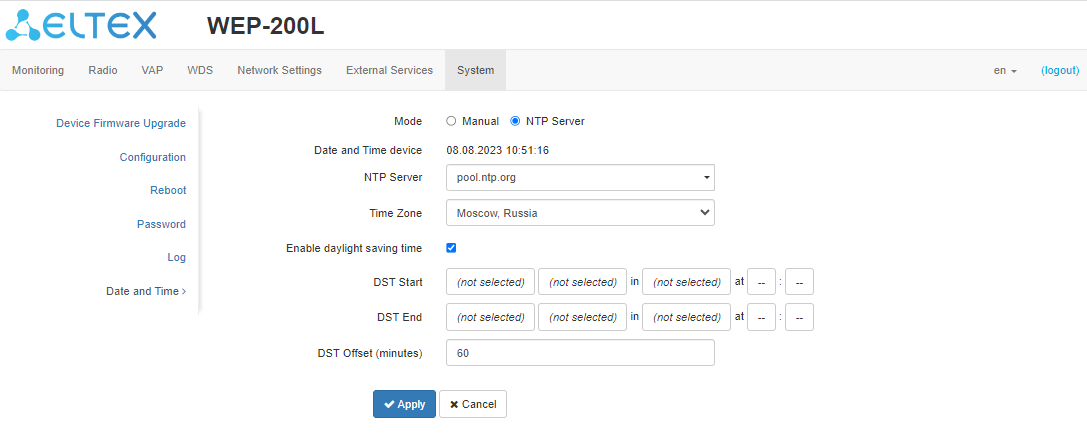
NTP server
- Date and Time device — date and time set on the device;
- NTP Server — IP address/domain name of the time synchronization server. It is possible to specify an address or select from an existing list;
- Time Zone — allows to set the time zone according to the nearest city for your region from the list;
- Daylight Saving Time Enable — when selected, automatic daylight saving change will be performed automatically within the defined time period:
- DST Start — day and time, when daylight saving time is starting;
- DST End — day and time, when daylight saving time is ending;
- DST Offset (minutes) — time period in minutes, on which time offset is performing. The parameter can take a value from 0 to 720 minutes.
To apply a new configuration and save settings to non-volatile memory, click “Apply”. Click “Cancel” to discard the changes.
Managing the device using the command line
To display the existing settings of a particular configuration section, enter the show-config command.
Press the key combination (English layout) — [Shift + ? ] to get a hint of what value this or that configuration parameter can take.
To get a list of options available for editing in this configuration section, press the Tab key.
To save the settings, enter the save command.
To go back to the previous configuration section, enter the exit command.
To go to the root partition, enter the end command.
Connection to the device
By default, WEP-200L is configured to receive the address via DHCP. If this does not happen, it is possible to connect to the device using the factory IP address.
WEP-200L factory default IP address: 192.168.1.10, subnet mask: 255.255.255.0.
Connection to the device is performed via SSH/Telnet:
ssh admin@<IP address of the device>, then enter the password
telnet <IP address of the device>, enter login and password
Network parameters configuration
WEP-200L(root):/# configure
WEP-200L(config):/# interface
WEP-200L(config):/interface# br0
WEP-200L(config):/interface/br0# common
WEP-200L(config):/interface/br0/common# static-ip X.X.X.X (where X.X.X.X is WEP-200L IP address)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/br0/common# netmask X.X.X.X (where X.X.X.X is subnet mask)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/br0/common# dns-server-1 X.X.X.X (where X.X.X.X is IP address of the dns server №1)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/br0/common# dns-server-2 X.X.X.X (where X.X.X.X is IP address of the dns server №2)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/br0/common# protocol static-ip (change operation mode from DHCP to Static-IP)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/br0/common# save (save changes)
Adding a static route
WEP-200L(config):/interface/br0/common# exit
WEP-200L(config):/interface/br0# exit
WEP-200L(config):/interface# exit
WEP-200L(config):/# route
WEP-200L(config):/route# add default (where default is route name)
WEP-200L(config):/route# default
WEP-200L(config):/route/default# destination X.X.X.X (where X.X.X.X is IP address of the network or destination node, for default route is 0.0.0.0)
WEP-200L(config):/route/default# netmask X.X.X.X (where X.X.X.X is destination network mask, for default route is 0.0.0.0)
WEP-200L(config):/route/default# gateway X.X.X.X (where X.X.X.X is gateway IP address)
WEP-200L(config):/route/default# save (save changes)
WEP-200L(root):/# configure
WEP-200L(config):/# interface
WEP-200L(config):/interface# br0
WEP-200L(config):/interface/br0# common
WEP-200L(config):/interface/br0/common# protocol dhcp
WEP-200L(config):/interface/br0/common# save (save changes)
WEP-200L(root):/# configure
WEP-200L(config):/# interface
WEP-200L(config):/interface# br0
WEP-200L(config):/interface/br0# common
WEP-200L(config):/interface/br0/common# access-rules (go to the section of access settings via IPv4 protocol)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/br0/common/access-rules# telnet false (where false is restriction of access via the TELNET protocol to the device by its IPv4 address. This setting applies only to the connection to the device via IPv4, access via IPv6 will remain if the corresponding prohibition setting has not been made in the section for IPv6. To remove the restriction, enter true)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/br0/common/access-rules# save (save changes)
Starting from software version 2.2.0, it is possible to set the MTU via DHCP (option 26).
The MTU value obtained via DHCP takes precedence over the configured setting.
The MTU size for bridge should not be larger than the smallest MTU size on the interfaces that are located in this bridge.
WEP-200L(root):/# configure
WEP-200L(config):/# interface
WEP-200L(config):/interface# br0
WEP-200L(config):/interface/br0# common
WEP-200L(config):/interface/br0/common# mtu X (where X is the MTU size in bytes. Possible values:
1–2490)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/br0/common# save (save changes)
Network parameters configuration via set-management-vlan-mode utility
Obtaining the network parameters via DHCP:
WEP-200L(root):/# set-management-vlan-mode off protocol dhcp
Static settings:
WEP-200L(root):/# set-management-vlan-mode off protocol static-ip ip-addr X.X.X.X netmask Y.Y.Y.Y gateway Z.Z.Z.Z (where X.X.X.X is static IP address, Y.Y.Y.Y is subnet mask, Z.Z.Z.Z is gateway)
Obtaining the network parameters via DHCP:
WEP-200L(root):/# set-management-vlan-mode terminating vlan-id X protocol dhcp (where X is VLAN ID used for access to the device. Acceptable values: 1–4094)
Static settings:
WEP-200L(root):/# set-management-vlan-mode terminating vlan-id X protocol static-ip ip-addr
X.X.X.X netmask Y.Y.Y.Y gateway Z.Z.Z.Z (where X is VLAN ID used for access to the device. Acceptable values: 1–4094; X.X.X.X is static IP address, Y.Y.Y.Y is subnet mask, Z.Z.Z.Z is gateway)
Obtaining the network parameters via DHCP:
WEP-200L(root):/# set-management-vlan-mode forwarding vlan-id X protocol dhcp (where X is VLAN ID used for access to the device. Acceptable values: 1–4094)
Static settings:
WEP-200L(root):/# set-management-vlan-mode forwarding vlan-id X protocol static-ip ip-addr
X.X.X.X netmask Y.Y.Y.Y gateway Z.Z.Z.Z (where X is VLAN ID used for access to the device. Acceptable values: 1–4094; X.X.X.X is static IP address, Y.Y.Y.Y is subnet mask, Z.Z.Z.Z is gateway)
WEP-200L(root):/# save (save changes)
IPv6 network parameters configuration
Access to the device via IPv6 protocol is disabled by default.
WEP-200L(root):/# configure
WEP-200L(config):/# interface
WEP-200L(config):/interface# br0
WEP-200L(config):/interface/br0# common
WEP-200L(config):/interface/br0/common# ipv6
WEP-200L(config):/interface/br0/common/ipv6# protocol dhcp (obtaining IPv6 network parameters via DHCP)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/br0/common/ipv6# enabled true (enabling access to the device via IPv6 protocol. To disable, enter false)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/br0/common/ipv6# save (save changes)
WEP-200L(root):/# configure
WEP-200L(config):/# interface
WEP-200L(config):/interface# br0
WEP-200L(config):/interface/br0# common
WEP-200L(config):/interface/br0/common# ipv6
WEP-200L(config):/interface/br0/common/ipv6# address XXXX:XXXX:XXXX:XXXX:XXXX:XXXX:XXXX:XXXX (where XXXX:XXXX:XXXX:XXXX:XXXX:XXXX:XXXX:XXXX is static IPv6 address of the WEP-200L device)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/br0/common/ipv6# address-prefix-length X (where X is static IPv6 address prefix. Takes values from 0 to 128. By default: 64)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/br0/common/ipv6# gateway XXXX:XXXX:XXXX:XXXX::/64 (IPv6 prefix is specified, for example 3211:0:0:1234::/64)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/br0/common/ipv6# dns-server-1 XXXX:XXXX:XXXX:XXXX:XXXX:XXXX:XXXX:XXXX/Y (where XXXX:XXXX:XXXX:XXXX:XXXX:XXXX:XXXX:XXXX/Y is IPv6 address of the dns server №1 with prefix)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/br0/common/ipv6# dns-server-2 XXXX:XXXX:XXXX:XXXX:XXXX:XXXX:XXXX:XXXX/Y (where XXXX:XXXX:XXXX:XXXX:XXXX:XXXX:XXXX:XXXX/Y is IPv6 address of the dns server №2 with prefix)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/br0/common/ipv6# protocol static-ip (enable use of static IPv6 networks parameters. For obtaining the IPv6 network parameters via DHCP enter dhcp)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/br0/common/ipv6# enabled true (enable access to the device via IPv6 protocol. To disable, enter false)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/br0/common/ipv6# save (save changes)
WEP-200L(root):/# configure
WEP-200L(config):/# interface
WEP-200L(config):/interface# br0
WEP-200L(config):/interface/br0# common
WEP-200L(config):/interface/br0/common# ipv6
WEP-200L(config):/interface/br0/common/ipv6# access-rules (go to the section of access settings)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/br0/common/ipv6/access-rules# telnet false (where false is restriction of access via the TELNET protocol to the device by its IPv6 address. This setting applies only to connection to the device via IPv6, access via IPv4 will remain if the corresponding prohibition setting has not been made in the section for IPv4. To remove the restriction, enter true)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/br0/common/ipv6/access-rules# save (save changes)
Similar to restricting access to the device via the TELNET protocol, you can restrict the ability to connection to the device by its IPv6 address using the following protocols: SSH, SNMP, NETCONF, web, web-HTTPS.
Virtual Wi-Fi access points (VAP) configuration
When configuring a VAP, remember that the interface names in the 2.4 GHz band start with wlan0, in the 5 GHz band with wlan1.
Table 8 — Commands for configuring security mode on VAP
| Security mode | Command to set the security mode |
|---|---|
| Without password | mode off |
| WPA | mode WPA |
| WPA2 | mode WPA2 |
| WPA/WPA2 | mode WPA_WPA2 |
| WPA-Enterprise | mode WPA_1X |
| WPA2-Enterprise | mode WPA2_1X |
| WPA/WPA2-Enterprise | mode WPA_WPA2_1X |
Below are examples of VAP configuration with different security modes for Radio 5 GHz (wlan1).
Configuration of VAP without encryption
WEP-200L(root):/# configure
WEP-200L(config):/# interface
WEP-200L(config):/interface# wlan1-va0
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0# vap
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap# ssid 'SSID_WEP-200L_open' (change SSID name)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap# ap-security
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/ap-security# mode off (encryption mode off is without password)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/ap-security# exit
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0# common
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/common# enabled true (enable VAP)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/common# save (save changes)
Configuration of VAP with WPA-Personal security mode
WEP-200L(root):/# configure
WEP-200L(config):/# interface
WEP-200L(config):/interface# wlan1-va0
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0# vap
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap# ssid 'SSID_WEP-200L_Wpa2' (change SSID name)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap# ap-security
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/ap-security# mode WPA_WPA2 (encryption mode is WPA/
WPA2)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/ap-security# key-wpa password123 (key/password
required to connect to the virtual access point. The key must be between 8 and 63 characters long)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/ap-security# exit
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap# exit
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0# common
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/common# enabled true (enable VAP)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/common# save (save changes)
Configuration of VAP with Enterprise authorization
WEP-200L(root):/# configure
WEP-200L(config):/# interface
WEP-200L(config):/interface# wlan1-va0
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0# vap
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap# ssid 'SSID_WEP-200L_enterprise' (change SSID name)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap# ap-security
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/ap-security# mode WPA_WPA2_1X (encryption mode is
WPA/WPA2-Enterprise)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/ap-security# exit
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap# radius
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/radius# domain root (where root is user domain)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/radius# auth-address X.X.X.X (where X.X.X.X is IP address
of RADIUS server)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/radius# auth-port X (where Х is port of RADIUS server used
for authentication and authorization. By default: 1812)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/radius# auth-password secret (where secret is password
for RADIUS server used for authentication and authorization)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/radius# acct-enable true (enable sending of "Accounting"
messages to the RADIUS server. By default: false)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/radius# acct-address X.X.X.X (where X.X.X.X is IP address
of RADIUS server used for accounting)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/radius# acct-password secret (where secret is password
for RADIUS server used for accounting)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/radius# acct-periodic true (enable periodic sending
of "Accounting" messages to the RADIUS server. By default: false)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/radius# acct-interval 600 (interval for sending "Accounting"
messages to the RADIUS server)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap# exit
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0# common
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/common# enabled true (enable VAP)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/common# save (save changes)
Configuration of VAP with Captive Portal
WEP-200L(root):/# configure
WEP-200L(config):/# interface
WEP-200L(config):/interface# wlan1-va0
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0# vap
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap# vlan-id X (where X is VLAN ID on VAP)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap# ap-security
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap# mode off (encryption mode off is no password)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/ap-security# exit
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/ap-security# ssid 'Portal_WEP-200L' (change SSID name)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap# captive-portal
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/captive-portal# scenarios
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/captive-portal/scenarios# scenario-redirect
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/captive-portal/scenarios/scenario-redirect# redirect-url http://<IP>:<PORT>/eltex_portal/ (specify URL of virtual portal)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/captive-portal/scenarios/scenario-redirect# index 1
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/captive-portal/scenarios/scenario-redirect# virtual-portal-name default (specify portal name. By default: default)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/captive-portal/scenarios/scenario-redirect# exit
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/captive-portal/scenarios# exit
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/captive-portal# enabled true
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/captive-portal# exit
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap# radius
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/radius# domain root (where root is user domain)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/radius# acct-enable true (enable sending of "Accounting" messages to the RADIUS server. By default: false)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/radius# acct-address X.X.X.X (where Х.Х.Х.Х is IP address of RADIUS server used for accounting)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/radius# acct-password secret (where secret is password for RADIUS server used for accounting)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/radius# acct-periodic true (enable periodic sending of "Accounting" messages to the RADIUS server. By default: false)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/radius# acct-interval 600 (interval for sending "Accounting" messages to the RADIUS server)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap# exit
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0# common
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/common# enabled true (enable VAP)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/common# save (save changes)
Advanced VAP settings
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap# vlan-id X (where X is VLAN ID number on VAP)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap# band-steer-mode true (enabling Band Steer mode. To disable, enter false)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap# vlan-trunk true (enabling VLAN trunk on VAP. To disable, enter false)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap# general-vlan-mode true (enabling General VLAN on SSID. To disable, enter false)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap# general-vlan-id X (where X is General VLAN number)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap# priority-by-dscp false (priority analysis from CoS field (Class of Service) of the tagged packets. Value by default: true. In this case, the priority from DSCP header field of the IP packet is analyzed)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap# mfp required (enable management frame protection. required — requires MFP support from client, clients without an MFP support will not be able to connect. capable — compatible with MFP, clients without an MFP support can connect. To disable, enter off)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/radius# tls-enable true (use TLS for authorization process. To disable, enter false)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap# hidden true (enabling hidden SSID. To disable, enter false)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap# station-isolation true (enable traffic isolation between clients within a single VAP. To disable, enter false)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap# sta-limit X (where X is the maximum allowable number of clients connected to the virtual network)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap# wmf-bss-enable true (enable multicast traffic replication on VAP. To disable, enter false)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap# check-signal-enable true (enabling Minimal Signal. To disable, enter false)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap# min-signal X (where X is RSSI threshold, when reached, the access point will disconnect the client from the VAP. The parameter can take values from -100 to -1)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap# check-signal-timeout X (where X is period of time in seconds after which decision is made to disconnect the client equipment from the VAP)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap# roaming-signal X (where X is RSSI threshold, when reached, the client equipment switch to another access point. The parameter can take values from -100 to -1. The roaming-signal parameter should be higher than min-signal: if min-signal = -75 dBm, roaming-signal shoul be equal, for example, -70 dBm)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap# save (save changes)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap# local-switching true (enabling subscribers traffic transmission outside of GRE tunnel. To disable, enter false. By default: disabled)
Configuring traffic shaper from the clients (each separately) connected to this VAP towards the access point:
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap# shaper-per-sta-rx
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/shaper-per-sta-rx# value X (where X is maximum speed in Kbps)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/shaper-per-sta-rx# mode kbps (enabling shaper. To disable, enter off)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/shaper-per-sta-rx# exit
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap# save (save changes)
Configuring traffic shaper from the access point towards the clients (each separately) connected to this VAP:
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap# shaper-per-sta-tx
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/shaper-per-sta-tx# value X (where X is maximum speed in Kbps)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/shaper-per-sta-tx# mode kbps (enabling shaper. To disable, enter off)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/shaper-per-sta-tx# exit
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap# save (save changes)
Configuring shaper from the clients (in total) connected to this VAP towards the access point:
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap# shaper-per-vap-rx
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/shaper-per-vap-rx# value X (where X is maximum speed in Kbps)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/shaper-per-vap-rx# mode kbps (enabling shaper. To disable, enter off)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/shaper-per-vap-rx# exit
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap# save (save changes)
Configuring shaper from the access point towards the clients (in total) connected to this VAP:
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap# shaper-per-vap-tx
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/shaper-per-vap-tx# value X (where X is maximum speed in Kbps)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/shaper-per-vap-tx# mode kbps (enabling shaper. To disable, enter off)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/shaper-per-vap-tx# exit
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap# save (save changes)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap# acl
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/acl# mac
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/acl/mac# add XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX (where
XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX is MAC address of the device, to which it is required to allow/deny access. To remove
an address from the list, use the del command)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/acl/mac# exit
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/acl# policy allow (policy selection. Possible values: allow —
allow connections only to those clients whose MAC addresses are in the list; deny — deny connections to
clients whose MAC addresses are in the list. By default: deny)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/acl# enable true (enabling MAC access control. To disable,
enter false)
If, for security reasons, it is necessary to implement protection against connections of users duplicating the MAC address of a wired device (gateway, PC, etc.), use the fdb-filtering setting, which has the following operating modes:
on-connect mode blocks all devices connection attempts via Wi-Fi if the MAC address has already been learned on the Ethernet port of the access point;
by-eth-event mode disconnects a connected client via Wi-Fi if its MAC address has been learned on the Ethernet port of the access point (the mode helps clear the old client record when roaming);
full mode combines all the previous ones, that is, it blocks the connection of a new user via Wi-Fi and disconnects the previously connected one if its MAC address matches with the device connected to the Ethernet interface.
When setting the full and on-connect modes, the roaming of Wi-Fi clients may deteriorate. So, during operation, all broadcast packets from a client reach the other access points of the network and its MAC is learned on all network access points, so when the client roaming, if its MAC address is in the Ethernet port list, reconnection may take a long time.
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap# fdb-filtering
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/fdb-filtering # enabled true (enabling function. To disable, enter false. Default: false)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/fdb-filtering #mode full (operating mode selection. Default: by-eth-event)
802.11r configuration
This type of roaming is available only for client devices supporting 802.11r.
802.11r roaming is possible only between VAPs with WPA2-Personal and WPA2-Enterprise security modes.
See instructions for configuring VAP with WPA2-Personal security mode and others in Configuration of VAP with WPA-Personal security mode section.
Each VAP on the access points should be configured individually, eg. AP1(wlan1) ↔ AP2(wlan1), AP1(wlan0) ↔ AP2(wlan0), AP1(wlan1) ↔ AP3(wlan1), etc.
Below is the example of 802.11r configuring on two access points: AP1 and AP2.
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/ft-config# enabled false
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/ft-config# r1-key-holder-id E8:28:C1:FC:D6:80 (MAC address of the VAP. Can be viewed in ifconfig command output)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/ft-config# r0-key-holder-id 12345 (unique key for this VAP)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/ft-config# mobility-domain 100 (domain should match on remote VAPs)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/ft-config# mac
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/ft-config/mac# add E4:5A:D4:E2:C4:B0 (MAC address of VAP interface of remote access point: AP2)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/ft-config/mac# E4:5A:D4:E2:C4:B0
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/ft-config/mac/E4:5A:D4:E2:C4:B0# r0-kh-id 23456 (unique key of remote VAP access point AP2: r0-key-holder-id)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/ft-config/mac/E4:5A:D4:E2:C4:B0# r1-kh-id E4:5A:D4:E2:C4:B0 (MAC address of remote VAP on AP2)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/ft-config/mac/E4:5A:D4:E2:C4:B0# r0-kh-key 0102030405060708 (random key. It shouldn't match with r1-kh-key of AP1, but it should match with r1-kh-key of remote AP2)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/ft-config/mac/E4:5A:D4:E2:C4:B0# r1-kh-key 0001020304050607 (random key. It shouldn't match with r0-kh-key of AP1, but it should match with r0-kh-key of remote AP2)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/ft-config/mac/E4:5A:D4:E2:C4:B0# exit
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/ft-config/mac# exit
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/ft-config# enabled true (enable access point operation by 802.11r protocol)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/ft-config# save (save changes)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/ft-config# enabled false
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/ft-config# r1-key-holder-id E4:5A:D4:E2:C4:B0 (MAC address of the VAP. Can be viewed in ifconfig command output)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/ft-config# r0-key-holder-id 23456 (unique key for this VAP)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/ft-config# mobility-domain 100 (domain should match on remote VAPs)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/ft-config# mac
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/ft-config/mac# add E8:28:C1:FC:D6:80 (MAC address of VAP interface of remote access point: AP1)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/ft-config/mac# E8:28:C1:FC:D6:80
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/ft-config/mac/E8:28:C1:FC:D6:80# r0-kh-id 12345 (unique key of remote VAP access point AP1: r0-key-holder-id)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/ft-config/mac/E8:28:C1:FC:D6:80# r1-kh-id E8:28:C1:FC:D6:80 (MAC address of remote VAP on AP1)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/ft-config/mac/E8:28:C1:FC:D6:80# r0-kh-key 0001020304050607 (random key. It shouldn't match with r1-kh-key of AP2, but it should match with r1-kh-key of remote AP1)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/ft-config/mac/E8:28:C1:FC:D6:80# r1-kh-key 0102030405060708 (random key. It shouldn't match with r0-kh-key of AP2, but it should match with r0-kh-key of remote AP1)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/ft-config/mac/E8:28:C1:FC:D6:80# exit
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/ft-config/mac# exit
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/ft-config# enabled true (enable access point operation by 802.11r protocol)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/ft-config# save (save changes)
802.11k configuration
802.11k protocol roaming can be organized between any networks (open/secure). If the access point is configured to work using the 802.11k protocol, then when a client connects, the access point sends the list of “friendly” access points to which a client can switch in a roaming process. The list contains information about access points' MAC addresses and channels they work with.
The use of 802.11k allows to reduce the time for finding another network when roaming, since the client does not need to scan channels on which there are no target access points available for switching.
This type of roaming is available only for client devices supporting 802.11k.
Below is the example of 802.11k configuring access point — making a list of “friendly” access points.
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/w80211kv-config# enabled false
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/w80211kv-config# mac
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/w80211kv-config/mac# add E8:28:C1:FC:D6:90 (where E8:28:C1:FC:D6:90 is MAC address of “friendly” access point)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/w80211kv-config/mac# E8:28:C1:FC:D6:90
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/w80211kv-config/mac/E8:28:C1:FC:D6:90# channel 132 (where 132 is channel on which access point with E8:28:C1:FC:D6:90 MAC address operates)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/w80211kv-config/mac/E8:28:C1:FC:D6:90# exit
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/w80211kv-config/mac# add E8:28:C1:FC:D6:70 (where E8:28:C1:FC:D6:70 is MAC address of “friendly” access point)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/w80211kv-config/mac# E8:28:C1:FC:D6:70
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/w80211kv-config/mac/E8:28:C1:FC:D6:70# channel 36 (where 36 is channel on which access point with E8:28:C1:FC:D6:70 MAC address operates)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/w80211kv-config/mac/E8:28:C1:FC:D6:70# exit
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/w80211kv-config/mac# exit
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/w80211kv-config# enabled true (enabling access point operation via 802.11k protocol)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-va0/vap/w80211kv-config# save (save changes)
Radio configuration
In the Radio section, automatic selection of the working channel is used by default. To set the channel manually or change the power, use the following commands:
WEP-200L(root):/# configure
WEP-200L(config):/# interface
WEP-200L(config):/interface# wlan0
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan0# wlan
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan0/wlan# radio
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan0/wlan/radio# channel X (where X is the number of the static channel on which the access point will operate)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan0/wlan/radio# auto-channel false (disabling Auto Channel. To enable, enter true)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan0/wlan/radio# use-limit-channels false (disabling Use Limit Channels. To enable, enter true)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan0/wlan/radio# bandwidth X (where X is channel bandwidth. Possible values: for Radio 1: 20, 40; for Radio 2: 20, 40, 80)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan0/wlan/radio# tx-power X (where X is power level, dBm. Possible values: for Radio 1: 4-16 dBm; for Radio 2: 8-19 dBm)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan0/wlan/radio# save (save changes)
Lists of available channels
Сhannels available for selection for radio 2.4 GHz :
- for 20 MHz channel width: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13.
- for 40 MHz channel width:
- if “control-sideband” = lower: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9.
- fi “control-sideband” = upper: 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13.
Сhannels available for selection for radio 5 GHz:
- for 20 MHz channel width: 36, 40, 44, 48, 52, 56, 60, 64, 132, 136, 140, 144, 149, 153, 157, 161, 165.
- for 40 MHz channel width:
- if “control-sideband” = lower: 36, 44, 52, 60, 132, 140, 149, 157.
- if “control-sideband” = upper: 40, 48, 56, 64, 136, 144, 153, 161.
- for 80 MHz channel width: 36, 40, 44, 48, 52, 56, 60, 64, 132, 136, 140, 144, 149, 153, 157, 161.
Advanced Radio settings
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan0/wlan/radio# use-limit-channels true (enabling use of limited list of channels in channel autoselection operation. To disable, enter false)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan0/wlan/radio# limit-channels '1 6 11' (where 1, 6, 11 are channels of range in which the configurable radio interface can operate)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan0/wlan/radio# control-sideband lower (parameter may take values: lower, upper. By default: for Radio 1: lower; for Radio 2: upper)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan0/wlan/radio# sgi true (enabling the use of a Short Guard Interval for data transmission of 400 ns instead of 800 ns. To disable, enter false)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan0/wlan/radio# stbc true (enabling the Space-Time Block Coding (STBC) method, aimed at improving the reliability of data transmission. To disable, enter false)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan0/wlan/radio# aggregation true (enabling aggregation on Radio: support for AMPDU/AMSDU. To disable, enter false)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan0/wlan/radio# short-preamble true (enabling the short packet preamble. To disable, enter false)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan0/wlan/radio# wmm true (enabling the support for WMM (Wi-Fi Multimedia). To disable, enter false)
Configuring is done only on Radio 5 GHz (wlan1)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1/wlan/radio# dfs X (where X is DFS mechanism operating mode. Possible values: forced: the mechanism is disabled, DFS channels are available for selection; auto: the mechanism is enabled; disabled: the mechanism is disabled, DFS channels are unavailable for selection)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan0/wlan/radio# obss-coex true (enabling automatic channel width switch mode from 40 MHz to 20 MHz with a loaded radio environment. To disable, enter false)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan0/wlan/radio# tx-broadcast-limit X (where X is restricting broadcast/multicast traffic over a wireless network, the limit for broadcast traffic is specified, packets/s)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan0/wlan/radio# qos
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan0/wlan/radio/qos# enable true (enabling the use of Quality of Service functions. To disable, enter false)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan0/wlan/radio/qos# edca-ap (configuring QoS parameters of the access point, traffic is transmitted from the access point to the client)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan0/wlan/radio/qos/edca-ap# bk (configuring QoS parameters for low-priority high-bandwidth queues (802.1p priorities: cs1, cs2))
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan0/wlan/radio/qos/edca-ap/bk# aifs X (where X is waiting time for frames of data, measured in slots. Takes the values 1–255)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan0/wlan/radio/qos/edca-ap/bk# cwmin X (X is the initial value of the time to wait before resending a frame, specified in milliseconds. Accepts values: 1, 3, 7, 15, 31, 63, 127, 255, 511, 1023. The cwMin value cannot exceed the cwMax value)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan0/wlan/radio/qos/edca-ap/bk# cwmax X (where X is maximum timeout value before resending a frame, specified in milliseconds. Accepts values: 1, 3, 7, 15, 31, 63, 127, 255, 511, 1023. The cwMax value must be greater than the cwMin value)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan0/wlan/radio/qos/edca-ap/bk# txop X (where X is the time interval in milliseconds when the WME client station has the right to initiate data transmission over the wireless medium to the access point. Max value 65535 milliseconds)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan0/wlan/radio/qos/edca-ap/bk# exit
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan0/wlan/radio/qos/edca-ap# exit
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan0/wlan/radio/qos# edca-sta (configuring QoS parameters of the client station: traffic is transmitted from the client station to the access point)
The configuration method of edca-sta is the same as that of edca-ap.
Parameters configuration for queues be, vi, vo is similar to parameters configuration for queue bk.
DHCP option 82 Configuration
DHCP option 82 is configured separately for each radio interface. This section provides examples of configuring option 82 for Radio 2.4 GHz — wlan0.
DHCP snooping operating modes:
- ignore – option 82 processing is disabled. Default value;
- replace – the access point substitutes or replaces the value of option 82;
- remove – the access point removes the value of option 82.
WEP-200L(root):/# configure
WEP-200L(config):/# interface
WEP-200L(config):/interface# wlan0 (configuring will be done for Radio 2.4 GHz. To configure option 82 on Radio 5 GHz, enter wlan1)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan0# common
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan0/common# dhcp-snooping
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan0/common/dhcp-snooping# dhcp-snooping-mode replace (selection of DHCP snooping operation in the mode of replacement or substitution of option 82)
If on the radio interface the option 82 processing policy is configured to replace, the following parameters become available for configuration:
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan0/common/dhcp-snooping# dhcp-option-82-CID-format custom (where custom is replacement of the CID content with the value specified in the dhcp-option-82-custom-CID parameter. The parameter can take values: APMAC-SSID is replacement of the CID content with <MAC address of the access point>-<SSID name>. SSID is replacement of the CID content with SSID name, to which the client is connected. By default: APMAC-SSID)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan0/common/dhcp-snooping# dhcp-option-82-RID-format custom (where custom is replacement of the RID content with the value specified in the dhcp-option-82-custom-RID parameter. The parameter can take values: ClientMAC is replacement of the RID content with MAC address of the client device. APMAC is replacement of the RID content with MAC address of the access point. APdomain is replacement of the RID content with the domain where the access point is located. By default: ClientMAC)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan0/common/dhcp-snooping# dhcp-option-82-custom- CID longstring (where longstring is value from 1 to 52 characters, which will be transmitted in CID. If the value of dhcp-option-82-custom-CID parameter is not defined, the access point will change the CID to the default value: <MAC address of the access point>-<SSID name>)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan0/common/dhcp-snooping# dhcp-option-82-custom-RID longstring (where longstring is value from 1 to 63 characters, which will be transmitted in RID. If the value of dhcp-option-82-custom-RID parameter is not defined, the access point will change the RID to the default value: MAC address of the client device)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan0/common/dhcp-snooping# dhcp-option-82-MAC-format radius (selecting octet delimiter of the MAC address which is transmitted in RID and CID. radius is a dash is used as a delimiter: AA-BB-CC-DD-EE-FF; default is a colon is used as a delimiter: AA:BB:CC:DD:EE:FF)
WDS Configuration
When configuring a WDS connection, on the devices that will be connected via WDS, it is necessary to select the same channel and channel width in the radio interface settings. More information about configuring the radio interface via the command line can be found in the Radio configuration section.
Below is the configuration of a WDS connection on the Radio 5 GHz interface (wlan1).
WEP-200L(root):/# configure
WEP-200L(config):/# interface
WEP-200L(config):/interface# wlan1-wds0 (WDS link selection. Available values for Radio 2.4 GHz:
wlan0-wds0 - wlan0-wds3; for Radio 5 GHz: wlan1-wds0 - wlan1-wds3)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-wds0# wds
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-wds0/wds# mac-addr XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX (MAC address of the remote access point radio interface, which can be found if you enter on the remote access point the monitoring radio-interface command)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-wds0/wds# exit
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-wds0# common
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-wds0/common# enabled true (enabling WDS link. To disable, enter false)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-wds0/common# exit
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1-wds0# exit
WEP-200L(config):/interface# wlan1 (when configuring WDS on Radio 2.4 GHz enter wlan0)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1# wlan
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1/wlan# wds
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1/wlan/wds# security-mode WPA2 (selection of WPA2 security mode. Available values: WPA2, off: without password)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1/wlan/wds# key-wpa password123 (key/password required for
connection to the remote access point. Key length should be between 8 and 63 characters)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1/wlan/wds# enabled true (enabling WDS. To disable, enter false)
WEP-200L(config):/interface/wlan1/wlan/wds# save
The remote access point is configured in the same way.
System settings
Device firmware update
WEP-200L(root):/# firmware upload tftp <ip address of tftp server> <Firmware file name> (example: firmware upload tftp 192.168.1.15 WEP-200L-2.3.2_build_X.tar.gz)
WEP-200L(root):/# firmware upgrade
WEP-200L(root):/# firmware upload http <URL for firmware uploading> (example: firmware upload http http://192.168.1.100:8080/files/WEP-200L-2.3.2_build_X.tar.gz)
WEP-200L(root):/# firmware upgrade
WEP-200L(root):/# firmware switch
Device configuration management
WEP-200L(root):/# manage-config upload tftp <tftp server ip address> <Configuration file name> (example: manage-config upload tftp 192.168.1.15 config.json)
WEP-200L(root):/# manage-config apply (apply configuration to the access point)
Device reboot
WEP-200L(root):/# reboot
Authentication Mode Configuration
The device has a factory account admin with password password. Delete this account recording is not possible. The password can be changed using the following commands.
WEP-200L(root):/# configure
WEP-200L(config):/# authentication
WEP-200L(config):/authentication# admin-password <New password for admin account> (from 1 up to 64 characters, including latin letters and digits)
WEP-200L(config):/authentication# save
It is possible to create additional users for local authentication as well as authentication via RADIUS.
New users should be assigned one of two roles:
admin is a user with this role will have full access to configuration and monitoring of the base station;
viewer is a user with this role will only have access to monitoring of the base station.
WEP-200L(root):/# configure
WEP-200L(config):/# authentication
WEP-200L(config):/authentication# user
WEP-200L(config):/authentication/user# add userX (where userX is the name of the new account. To delete, use the del command)
WEP-200L(config):/authentication/user# userX
WEP-200L(config):/authentication/user/userX# login userX (where userX is the name of the new account)
WEP-200L(config):/authentication/user/userX# password <Password for userX account>(from 1 up to 64 characters, including latin letters and digits)
WEP-200L(config):/authentication/user/userX# role admin (the user is given the rights to configure. Possible value viewer is only monitoring will be available to the account)
WEP-200L(config):/authentication/user/userX# save
For authentication via RADIUS server, it is necessary to configure access parameters.
WEP-200L(root):/# configure
WEP-200L(config):/# authentication
WEP-200L(config):/authentication# radius
WEP-200L(config):/authentication/radius# auth-address X.X.X.X (where X.X.X.X is IP address of the RADIUS server)
WEP-200L(config):/authentication/radius# auth-port X (where Х is RADIUS server port, used for authentication and authorization. By default: 1812)
WEP-200L(config):/authentication/radius# auth-password secret (where secret is key for the RADIUS server, used for authentication and authorization)
WEP-200L(config):/authentication/radius# exit
WEP-200L(config):/authentication# radius-auth true (enabling authentication mode via the RADIUS server. To disable, enter false)
WEP-200L(config):/authentication# save
When authentication via RADIUS server is used, be sure to create a local account that will be similar to an account on the RADIUS server.
In this case, the local account should contain a role that determines access rights (admin or viewer).
If the RADIUS server is unavailable, authentication will take place on the local account.
Setting the date and time
WEP-200L(root):/# configure
WEP-200L(config):/# date-time
WEP-200L(config):/date-time# mode ntp (enabling NTP operation mode)
WEP-200L(config):/date-time# ntp
WEP-200L(config):/date-time/ntp# server <NTP server IP address> (NTP server configuration)
WEP-200L(config):/date-time/ntp# exit
WEP-200L(config):/date-time# common
WEP-200L(config):/date-time/common# timezone 'Asia/Novosibirsk (Novosibirsk)' (timezone configuration)
WEP-200L(config):/date-time/common# save (save changes)
Advanced system settings
WEP-200L(root):/# configure
WEP-200L(config):/# system
WEP-200L(config):/system# global-station-isolation true (enabling global traffic isolation between clients of different VAPs and different radio interfaces. To disable, enter false)
WEP-200Lconfig):/system# save (save changes)
WEP-200L(root):/# configure
WEP-200L(config):/# system
WEP-200L(config):/system# hostname WEP-200L_room2 (where WEP-200L_room2 is a new device name. The parameter can accept values from 1 to 63 characters: capital and lowercase latin letters, digits, hyphen character “-” (hyphen can not be the last character in name). By default: WEP-200L)
WEP-200L(config):/system# save (save changes)
WEP-200L(root):/# configure
WEP-200L(config):/# system
WEP-200L(config):/system# ap-location ap.test.root (where ap.test.root is EMS management system device tree node domain, where access point is located. By default: root)
WEP-200L(config):/system# save (save changes)
WEP-200L(root):/# configure
WEP-200L(config):/# system
WEP-200L(config):/system# nas-id Lenina_1.Novovsibirsk.root (where Lenina_1.Novovsibirsk.root is the AP identificator. The parameter is designed for device identification on RADIUS server in case RADIUS awaits value different from MAC address. Default: AP MAC address)
WEP-200L(config):/system# save (save changes)
WEP-200L(root):/# configure
WEP-200L(config):/# lldp
WEP-200L(config):/lldp# enabled true (enabling LLDP. To disable, enter false. Default: true)
WEP-200L(config):/lldp# tx-interval 60 (changing interval of LLDP message sending. Default: 30)
WEP-200L(config):/lldp# system-name WEP-200L_reserv (where WEP-200L_reserv is new device name. Default: WEP-200L)
WEP-200L(config):/lldp# save (save changes)
APB service configuration
The APB service is used to provide portal roaming of clients between access points connected to the service.
WEP-200L(root):/# configure
WEP-200L(config):/# captive-portal
WEP-200L(config):/captive-portal# apbd
WEP-200L(config):/captive-portal/apbd# roam_service_url <APB service address> (example: roam_service_url ws://192.168.1.100:8090/apb/broadcast)
WEP-200L(config):/captive-portal/apbd# enabled true (enabling APB service. To disable, enter false)
WEP-200L(config):captive-portal/apbd# save (save changes)
Monitoring
Wi-Fi clients
WEP-200L(root):/# monitoring associated-clients
index | 0 interface | wlan1-va0 state | ASSOC SLEEP AUTH_SUCCESS hw-addr | 26:af:0a:30:ef:29 ssid | !!!DOC_test ip-addr | 169.254.68.250 authorized | true captive-portal-vap | false enterprise-vap | false rx-retry-count | 76 tx-fails | 0 tx-period-retry | 0 tx-retry-count | 0 rssi-1 | -75 rssi-2 | -75 rssi | -75 snr-1 | 17 snr | 17 snr-2 | 16 tx-rate | MCS7 SGI 72.2 rx-rate | MCS7 NO SGI 65 rx-bw | 20M rx-bw-all | 20M tx-bw | 20M mfp | false uptime | 00:00:27 multicast-groups-count | 0 wireless-mode | n perftest-capable | false link-capacity | 0 link-quality | 0 link-quality-common | 0 actual-tx-rate | 0 actual-rx-rate | 0 shaped-rx-rate | 0 actual-tx-pps | 0 actual-rx-pps | 1 shaped-rx-pps | 0 name | 0 Rate Transmitted Received ---------------------- ----------------------- ------------------------- Total Packets: 2 176 TX success: 100 Total Bytes: 173 8877 Data Packets: 0 31 Data Bytes: 0 4488 Mgmt Packets: 2 145 Mgmt Bytes: 173 127 Dropped Packets: 0 0 Dropped Bytes: 0 0 Lost Packets: 0 Rate Transmitted Received ---------------------- ----------------------- ------------------------- dsss1 2 | 100% 37 | 21% ofdm6 0 | 0% 19 | 10% ofdm24 0 | 0% 88 | 50% mcs3 0 | 0% 2 | 1% mcs4 0 | 0% 15 | 8% mcs7 0 | 0% 14 | 8% Multicast groups: none
WDS
WEP-200L(root):/# monitoring wds-entries
index | 0 interface | wlan1 state | WIFI_WDS hw-addr | cc:9d:a2:dd:00:b5 ip-addr | 100.110.0.227 hostname | WEP-200L authorized | false captive-portal-vap | false enterprise-vap | false rx-retry-count | 10304 tx-fails | 0 tx-period-retry | 38 tx-retry-count | 86 rssi-1 | -29 rssi-2 | -36 rssi-3 | -40 rssi-4 | -36 snr-1 | 38 snr-2 | 37 snr-3 | 36 snr-4 | 36 wds-interface | wlan1-wds0 tx-rate | VHT NSS2-MCS8 SGI 173.3 rx-rate | VHT NSS2-MCS8 NO SGI 156 rx-bw | 20M rx-bw-all | 20M tx-bw | 20M uptime | 00:00:16 multicast-groups-count | 0 wireless-mode | ac eltex-firmware-version | 1.5.0 build X eltex-board-type | WEP-200L perftest-capable | false snr-rssi-capable | false link-capacity | 33 link-quality | 97 link-quality-common | 97 actual-tx-rate | 281 actual-rx-rate | 12437 shaped-rx-rate | 0 actual-tx-pps | 116 actual-rx-pps | 16846 shaped-rx-pps | 0 name | 0 Rate Transmitted Received --------------------------------------------------------------------- Total Packets: | 1799 | 299260 | TX success: | 100 | | Total Bytes: | 514926 | 37828573 | Data Packets: | 1796 | 299256 | Data Bytes: | 457310 | 28251999 | Mgmt Packets: | 3 | 4 | Mgmt Bytes: | 144 | 408 | --------------------------------------------------------------------- Rate Transmitted Received --------------------------------------------------------------------- ofdm6 | 3 | 0%| 3484 | 1%| ofdm54 | 151 | 8%| 0 | 0%| nss1-mcs1 | 30 | 1%| 0 | 0%| nss1-mcs2 | 0 | 0%| 176 | 0%| nss1-mcs3 | 0 | 0%| 132 | 0%| nss1-mcs4 | 0 | 0%| 223 | 0%| nss1-mcs7 | 0 | 0%| 87 | 0%| nss2-mcs0 | 0 | 0%| 64 | 0%| nss2-mcs1 | 66 | 3%| 123 | 0%| nss2-mcs2 | 177 | 9%| 183 | 0%| nss2-mcs3 | 0 | 0%| 310 | 0%| nss2-mcs4 | 0 | 0%| 665 | 0%| nss2-mcs5 | 447 | 24%| 1318 | 0%| nss2-mcs6 | 0 | 0%| 4837 | 1%| nss2-mcs7 | 292 | 16%| 31002 | 10%| nss2-mcs8 | 633 | 35%| 256655 | 85%| ---------------------------------------------------------------------
Device information
WEP-200L(root):/# monitoring information
system-time | 12:50:37 27.09.2023 uptime | 00:04:25 software-version | 2.3.2 build X secondary-software-version | 2.3.2 build X boot-version | 2.1.0 build X memory-usage | 43 memory-free | 137 memory-used | 104 memory-total | 241 cpu-load | 9.5 cpu-average | 6.70 is-default-config | false board-type | WEP-200L hw-platform | WEP-200L factory-wan-mac | 68:13:E2:35:C3:90 factory-lan-mac | 68:13:E2:35:C3:90 factory-serial-number | WP52000345 hw-revision | 1v2 session-password-initialized | false ott-mode | false last-reboot-reason | firmware update test-changes-mode | false
Certificate information
WEP-200L(root):/# monitoring certificate
ott:
status: not present
wlc:
status: present
url: https://192.168.1.1:8044
Network information
WEP-200L(root):/# monitoring wan-status
Common information:
interface | br0
mac | cc:9d:a2:e9:14:70
rx-bytes | 456875
rx-packets | 5835
tx-bytes | 24328
tx-packets | 241
IPv4 information:
protocol | dhcp
ip-address | 100.111.66.29
netmask | 255.255.255.0
gateway | 100.111.66.1
DNS-1 | 100.111.66.15
DNS-2 | 8.8.8.8
IPv6 information:
addresses | 2002::8/128 Global
| fe80::ce9d:a2ff:fee9:1470/64 Link
dns-servers | 2002::4144
| 2002::8844
| 2222::4144
WEP-200L(root):/# monitoring ethernet
link: up speed: 1000 duplex: enabled rx-bytes: 4872597 rx-packets: 13844 tx-bytes: 2477091 tx-packets: 20923
WEP-200L(root):/# monitoring arp
# ip mac ----- -------------- ------------------- 0 192.168.1.1 02:00:48:xx:xx:xx 1 192.168.1.151 2c:fd:a1:xx:xx:xx
WEP-200L(root):/# monitoring route
Destination Gateway Mask Flags Interface --------------- -------------- ---------------- ------- ---------- 0.0.0.0 192.168.1.1 0.0.0.0 UG br0 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 U br0
WEP-200L(root):/# monitoring lldp
WEP-200L(root):/# monitoring lldp Port Device ID Port ID System Name Capabilities TTL --------- ----------------- ----------------- ----------------- ------------ ----- eth0 e0:d9:e3:eb:66:80 gi1/0/16 120
Wireless interfaces
WEP-200L(root):/# monitoring radio-interface
name | wlan0 status | on band | 2.4 GHz hwaddr | E8:28:C1:xx:xx:xx tx-power | 16 dBm noise-1 | -100 dBm noise-2 | -100 dBm channel | 11 frequency | 2462 MHz bandwidth | 20 MHz utilization | 0% thermal | 35 mode | b/g/n name | wlan1 status | on band | 5 GHz hwaddr | E8:28:C1:xx:xx:xx tx-power | 19 dBm noise-1 | -100 dBm noise-2 | -100 dBm noise-3 | -100 dBm noise-4 | -100 dBm channel | 36 frequency | 5180 MHz bandwidth | 20 MHz utilization | 0% thermal | 26 mode | a/n/ac
Event logging
WEP-200L(root):/# monitoring events
Jan 23 00:00:07 WEP-200L daemon.info syslogd[925]: started: BusyBox v1.21.1 Jan 23 00:00:09 WEP-200L daemon.info configd[955]: The AP startup configuration was loaded successfully. Jan 1 03:00:14 WEP-200L daemon.info networkd[987]: Networkd started Jan 1 03:01:17 WEP-200L daemon.info networkd[987]: DHCP-client: Interface br0 obtained lease on 192.168.1.15. Jan 23 07:17:14 WEP-200L daemon.info monitord[1055]: event: 'associated' mac: E4:0E:EE:BD:AE:6B ssid: 'WEP-200L_2.4GHz' int0
Environment scan
While scanning the environment, the device radio interface will be disabled, which will make it impossible to transfer data to Wi-Fi clients during scanning.
WEP-200L(root):/# monitoring scan-wifi
SSID Mode Security BSSID Channel RSSI, dBm Bandwidth, MHz ---------------------- ---- -------- ----------------- ------- -------- ------- !!!!Esh_test1111 AP wpa CC:9D:A2:C7:A2:E0 1 -39 20 EltexWiFi AP off E0:D9:E3:49:D5:00 1 -50 20 Eltex-WLC-Local AP wpa CC:9D:A2:FF:B2:03 6 -68 20 TEst_Ent AP wpa CC:9D:A2:C7:DF:D0 11 -75 20 sdd_wlc_enterprise AP wpa E8:28:C1:FC:D6:41 1 -77 20 WLC30_sdd1 AP wpa E8:28:C1:FC:D6:40 1 -77 20 WLC AP off E0:D9:E3:49:79:01 1 -77 20 Rostelecom AP off E8:28:C1:EC:DE:21 11 -78 20 VIP_test AP off E0:D9:E3:73:06:F2 6 -79 20 i-cisco-ent AP wpa 7C:21:0E:E2:76:C0 1 -80 20 Test_Astra_Ted AP off E4:5A:D4:E4:D3:F3 1 -80 20 Karandashev_Enterprise AP wpa E0:D9:E3:73:06:F3 6 -80 20 i-cis-MAB AP off 7C:21:0E:E2:76:C2 1 -80 20
Spectrum analyzer
The spectrum analyzer provides information on channel congestion in the 2.4 and 5 GHz bands. The result is displayed as a percentage.
While the spectrum analyzer is running, all clients are disconnected from the access point. Clients will only reconnect when the spectrum analyzer has finished its work.
The analysis time for all radio channels of two bands is approximately 5 minutes.
The spectrum analyzer operates only on those channels that are specified in the limit-channels parameter in the radio interface settings. For example, if the channels' 1 6 11 'are specified in the limit-channels on wlan0, and the channels '36 40 44 48' are specified on wlan1, then the spectrum analysis will be performed only for channels 1, 6, 11, 36, 40, 44, 48.
In order to analyze all channels of the range on which the radio interface operates, change the value of the use-limit-channels parameter in the settings of each radio interface to false. After receiving the results of the spectrum analyzer, set the use-limit-channels value back to the original value true.
For more information on configuring the radio interface through the CLI, see the Radio configuration section.
WEP-200L(root):/# monitoring spectrum-analyzer
Channel| CCA
1| 81%
2| 40%
3| 14%
4| 10%
5| 36%
6| 60%
7| 40%
8| 8%
9| 14%
10| 38%
11| 75%
12| 37%
13| 18%
36| 14%
40| 12%
44| 10%
48| 18%
52| 3%
56| 5%
60| 8%
64| 6%
132| 0%
136| 0%
140| 0%
144| 1%
149| 30%
153| 1%
157| 3%
161| 2%
165| 1%
The list of changes
| Document version | Issue date | Revisions |
|---|---|---|
| Version 1.4 | 11.2023 | Synchronization with firmware version 2.3.2 Added:
|
| Version 1.3 | 09.2023 | Synchronization with firmware version 2.2.0 Added:
|
| Version 1.2 | 04.2023 | Synchronization with firmware version 1.7.1 Changed:
|
| Version 1.1 | 03.2023 | Synchronization with firmware version 1.6.2 Added:
|
| Version 1.0 | 10.2022 | Synchronization with firmware version 1.5.1 First issue |
| Firmware version 2.3.2 | ||