Tunneling management. Firmware version 1.13.0
GRE tunnel configuration
GRE (Generic Routing Encapsulation) is a network packet tunneling protocol. Its main purpose is to encapsulate packets of the OSI model network layer into IP packets. GRE may be used for VPN establishment on 3rd level of OSI model. In ESR router implemented static unmanageable GRE tunnels, i.e. tunnels are created manually via configuration on local and remote hosts. Tunnel parameters for each side should be mutually agreeable, otherwise transferred data will not be decapsulated by the partner.
Configuration algorithm
Step | Description | Command | Keys |
|---|---|---|---|
1 | Configure L3 interface from which a GRE tunnel will be built. | ||
2 | Create a GRE tunnel and switch to its configuration mode. | esr(config)# tunnel gre <INDEX> | <INDEX> – tunnel identifier, set in the range of:
|
3 | Specify VRF instance, in which the given GRE tunnel will operate (optionally). | esr(config-gre )# ip vrf forwarding <VRF> | <VRF> – VRF name, set by the string of up to 31 characters. |
4 | Specify the description of the configured tunnel (optionally). | esr(config-gre)# description <DESCRIPTION> | <DESCRIPTION> – tunnel description, set by the string of up to 255 characters. |
5 | Set local IP address for tunnel installation. | esr(config-gre)# local address <ADDR> | <ADDR> – gateway IP address, defined as AAA.BBB.CCC.DDD where each part takes values of [0..255]. |
esr(config-gre)# local interface <IF> | <IF> – interface IP address of which is used for the tunnel installation. | ||
6 | Set remote IP address for tunnel installation. | esr(config-gre)# remote address <ADDR> | <ADDR> – gateway IP address, defined as AAA.BBB.CCC.DDD where each part takes values of [0..255]. |
7 | Specify the GRE tunnel encapsulation mode. | esr(config-gre)# mode <MODE> | <MODE> – GRE tunnel encapsulation mode:
Default value: ip |
8 | Set the IP address of a tunnel local side (only in ip mode). | esr(config-gre)# ip address <ADDR/LEN> | <ADDR/LEN> – IP address and prefix of a subnet, defined as AAA.BBB.CCC.DDD/EE where each part AAA-DDD takes values of [0..255] and EE takes values of [1..32]. You can specify up to 8 IP addresses separated by commas. For advanced IPv4 addressing features see section IP addressing configuration. |
9 | Assign the broadcast domain for encapsulation in the tunnel’s GRE packets (only in ethernet mode). | esr(config-gre)# bridge-group <BRIDGE-ID> | <BRIDGE-ID> – bridge identification number, takes values in the range of:
|
10 | Include the GRE tunnel in a security zone and configure interaction rules between zones or disable firewall (see section Firewall configuration). | esr(config-gre)# security-zone<NAME> | <NAME> – security zone name, set by the string of up to 12 characters. |
esr(config-gre)# ip firewall disable |
| ||
11 | Specify MTU size (MaximumTransmissionUnit) for the tunnel (optionally). | esr(config-gre)# mtu <MTU> | <MTU> – MTU value, takes values in the range of:
Default value: 1500. |
12 | Specify the TTL lifetime for tunnel packets (optionally). | esr(config-gre)# ttl <TTL> | <TTL> – TTL value, takes values in the range of [1..255]. Default value: Inherited from encapsulated packet. |
13 | Specify DSCP for the use in IP header of encapsulated packet (optionally). | esr(config-gre)# dscp <DSCP> | <DSCP> – DSCP code value, takes values in the range of [0..63]. Default value: inherited from encapsulated packet. |
14 | Enable key transmitting in GRE tunnel header (according to RFC 2890) and set the key value. Configured only on the both tunnel sides. | esr(config-gre)# key <KEY> | <KEY> – KEY value, takes values in the range of [1..2000000]. Default value: key is not transmitted. |
15 | Enable the calculation of the checksum and entry it to the GRE header of the packets to be sent. Also it is necessary to enable verifying of the checksum on the remote side. | esr(config-gre)# local checksum | |
16 | Enable verification of the presence and consistency of checksum values in the headers of GRE packets being received. Also it is necessary to enable calculation of the checksum on the remote side. | esr(config-gre)# remote checksum | |
17 | Enable the check for tunnel remote gateway availability (optionally) | esr(config-gre)# keepalive enable | |
18 | Change the keepalive packets timeout from the opposing party (optional) | esr(config-gre)# keepalive timeout <TIME> | <TIME> – time in seconds, takes values of [1..32767]. Default value: 10 |
19 | Change the number of attempts to check the availability of a tunnel remote gateway (optionally) | esr(config-gre)# keepalive retries <VALUE> | <VALUE> – number of attempts, takes values in the range of [1..255]. Default value: 5 |
20 | Specify the IP address for the keepalive mechanism (mandatory in ethernet mode) | esr(config-gre)# keepalive dst-address <ADDR> | <ADDR> – IP address to check GRE tunnel capability. |
21 | Change the time interval during which the statistics on the tunnel load is averaged (optional). | esr(config-gre)# load-average <TIME> | <TIME> – interval in seconds, takes values of [5..150]. Default value: 5 |
22 | Enable sending snmp-trap about tunnel enabling/disabling. | esr(config-gre)# snmp init-trap | |
23 | Enable the mechanism of IP addresses iterative query using DHCP on the specified interfaces when the GRE tunnel is disconnected via keepalive (optionally) | esr(config-gre)# keepalive dhcp dependent-interface <IF> | <IF> – physical/logical interface on which IP address obtaining via DHCP is enabled. |
24 | Specify the time interval between GRE tunnel disabling and IP address iterative query on the interface/interfaces specified by the keepalive dhcp dependent-interface command (optionally) | esr(config-gre)# keepalive dhcp link-timeout <SEC> | <SEC> – time interval between GRE tunnel disabling and IP address requery via DHCP on the interfaces |
25 | Override the MSS (Maximum segment size) field in incoming TCP packets (optional). | esr(config-gre)# ip tcp adjust-mss <MSS> | <MSS> – MSS value, takes values in the range of [500..1460]. Default value: 1460 |
26 | Enable recording of the current tunnel usage statistics (optional). | esr(config-gre)# history statistics | |
27 | Enable the tunnel. | esr(config-gre)# enable | |
It is also possible to configure the GRE tunnel:
| |||
IP-GRE tunnel configuration example
Objective:
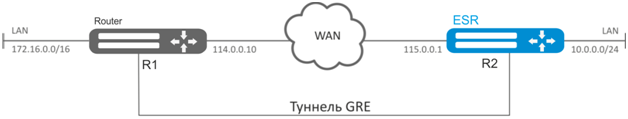
Establish L3-VPN for company offices using IP network with GRE protocol for traffic tunneling.
- IP address 115.0.0.1 is used as a local gateway for the tunnel;
- IP address 114.0.0.10 is used as a remote gateway for the tunnel;
- IP address of the tunnel at the local side is 25.0.0.1/24.
Solution:
Pre-configure interfaces on the routers for connection with WAN, enable GRE packets reception from a security zone where WAN connected interfaces operate.
Create GRE 10 tunnel:
esr(config)# tunnel gre 10Specify local and remote gateways (IP addresses of WAN border interfaces):
esr(config-gre)# local address 115.0.0.1
esr(config-gre)# remote address 114.0.0.10Specify tunnel IP address 25.0.0.1/24:
esr(config-gre)# ip address 25.0.0.1/24Also, the tunnel should belong to the security zone in order to create rules that allow traffic to pass through the firewall. To define the tunnel inherence to a zone, use the following command:
esr(config-gre)# security-zone untrustedEnable tunnel:
esr(config-gre)# enable
esr(config-gre)# exitCreate route to the partner's local area network on the router. Specify previously created GRE tunnel as a destination interface.
esr(config)# ip route 172.16.0.0/16 tunnel gre 10 When settings are applied, traffic will be encapsulated into the tunnel and sent to the partner regardless of their GRE tunnel existence and settings validity.
Alternatively, you may specify the following parameters for GRE tunnel:
Enable GRE header checksum calculation and inclusion into a packet with encapsulated packet for outbound traffic:
esr(config-gre)# local checksumCODEEnable check for GRE checksum presence and validity for inbound traffic:
esr(config-gre)# remote checksumCODESpecify a unique identifier:
esr(config-gre)# key 15808CODESpecify DSCP, MTU, TTL values:
esr(config-gre)# dscp 44 esr(config-gre)# mtu 1426 esr(config-gre)# ttl 18CODEEnable and configure keepalive mechanism:
esr(config-gre)# keepalive enable esr(config-gre)# keepalive timeout <TIME> esr(config-gre)# keepalive retries <VALUE>CODE
To view the tunnel status, use the following command:
esr# show tunnels status gre 10To view sent and received packet counters, use the following command:
esr# show tunnels counters gre 10To view the tunnel configuration, use the following command:
esr# show tunnels configuration gre 10IPv4-over-IPv4 tunnel configuration is performed in the same manner.
During tunnel creation, you should enable GRE protocol (47) in the firewall.
DMVPN configuration
DMVPN (Dynamic Multipoint Virtual Private Network) — technology for creating virtual private networks, with the ability to dynamically create tunnels between hosts. The advantage of this solution is its high scalability and ease of setup when connecting branches to the head office. DMVPN is used in the Hub-and-Spoke topology, and allows the construction of direct VPN Spoke-to-Spoke tunnels in addition to the usual Spoke-to-Hub tunnels. This means that branches can communicate with each other directly, without the need for traffic to pass through the Hub.
To establish such a connection, clients (NHC) over an encrypted IPsec tunnel send their internal (tunnel) address and external (NBMA) address to the NHRP server (NHS). When a client wants to connect to another NHC, it sends a request to the server to find out its external address. Having received a response from the server, the client can now independently establish a connection to the remote branch.
Configuration algorithm
Step | Description | Command | Keys |
|---|---|---|---|
1 | Check the availability of 'external' IP addresses located on physical interfaces. |
| |
2 | Prepare IPsec tunnels for use with dynamic GRE tunnels. |
| See section Policy-based IPsec VPN configuration. |
2 | Create a GRE tunnel and switch to its configuration mode. | esr(config)# tunnel gre <INDEX> | <INDEX> – tunnel identifier. |
3 | Switch the GRE tunnel to multipoint mode. | esr(config-gre )# multipoint | |
4 | Set an open password for NHRP packets (optional). | esr(config-gre)# ip nhrp authentication <WORD> | <WORD> – unencrypted password, set by the string of [1..8] characters, may include [0-9a-fA-F] characters. |
5 | Specify the time during which a record about this client will exist on the NHS (optional). | esr(config-gre)# ip nhrp holding-time <TIME> | <TIME> – the time in seconds during which a record about this client will exist on the server takes the values [1..65535]. Default value: 7200 |
6 | Set the 'logic (tunnel)' address of the NHRP server. | esr(config-gre)# ip nhrp nhs <ADDR> [ no-registration ] | <ADDR/LEN> – address, defined as AAA.BBB.CCC.DDD/EE where each part AAA-DDD takes values of [0..255] and EE takes values of [1..32];
|
7 | Match the 'internal' tunnel address with the 'external' NBMA address. | esr(config-gre)# ip nhrp map <ADDR> <ADDR> | <ADDR> – IP address, defined as AAA.BBB.CCC.DDD where each part takes values of [0..255]. |
8 | Define the destination of multicast traffic. | esr(config-gre)# ip nhrp multicast { dynamic | nhs | <ADDR> } |
<ADDR> – send to specifically configured server, defined as AAA.BBB.CCC.DDD where each part takes values of [0..255]. |
9 | Enable the ability to send NHRP Traffic Indication packets. Running on the NHS (optionally). | esr(config-gre)# ip nhrp redirect | |
10 | Enable the ability to create shortest routes. Running on the NHC (optionally). | esr(config-gre)# ip nhrp shortcut | |
11 | Map IPsec-VPN to the mGRE tunnel (optionally). | esr(config-gre)# ip nhrp ipsec <WORD> { static | dynamic } | <WORD> – VPN name, set by the string of up to 31 characters.
|
12 | Enable NHRP. | esr(config-gre)# ip nhrp enable | |
13 | Organize IP connectivity using the dynamic routing protocol. | ||
Other settings are the same as for the static GRE-tunnel (see section GRE-tunnel configuration) | |||
Configuration example 1
Objective:
Organize DMVPN between company offices using mGRE tunnels, NHRP (Next Hop Resolution Protocol), Dynamic Routing Protocol (BGP), Ipsec. In our example, we will have a HUB router and two branches. The HUB is the DMVPN server (NHS), and the branches are DMVPN clients (NHC).
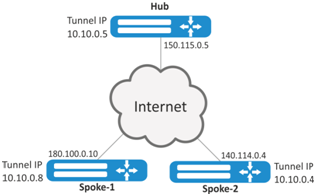
External IP addres of Hub — 150.115.0.5;
External IP address of Spoke-1 — 180.100.0.10;
External IP address of Spoke-2 — 140.114.0.4.
IPsec VPN parameters:
IKE:
- Diffie-Hellman group: 2;
- encryption algorithm: AES128;
- authentication algorithm: SHA1.
IPSEC:
- encryption algorithm: AES128;
- authentication algorithm: SHA1.
Solution:
Hub configuration
Create GRE tunnel:esr# configure esr(config)# tunnel gre 5CODESpecify the IP address of the interface bordering the ISP:
esr(config-gre)# local address 150.115.0.5CODESpecify MTU value:
esr(config-gre)# mtu 1416CODESpecify ttl value:
esr(config-gre)# ttl 16CODESpecify IP address of GRE tunnel:
esr(config-gre)# ip address 10.10.0.5/24CODESwitch the GRE tunnel into multipoint mode to be able to connect to multiple points:
esr(config-gre)# multipointCODEProceed to NHRP configuration. Configure multicast to dynamically learnt addresses:
esr(config-gre)# ip nhrp multicast dynamicCODEConfigure the dynamic routing protocol for the Hub. In our example, this will be BGP:
esr(config)# router bgp 65005 esr(config-bgp)# address-family ipv4 esr(config-bgp-af)# neighbor 10.10.0.8 esr(config-bgp-neighbor)# remote-as 65008 esr(config-bgp-neighbor)# enable esr(config-bgp-neighbor)# exit esr(config-bgp-af)# neighbor 10.10.0.4 esr(config-bgp-neighbor)# remote-as 65004 esr(config-bgp-neighbor)# enable esr(config-bgp-neighbor)# exit esr(config-bgp-af)# enableCODEConfigure IPsec for the Hub:
esr(config)# security ike proposal IKEPROP esr(config-ike-proposal)# encryption algorithm aes128 esr(config-ike-proposal)# dh-group 2 esr(config-ike-proposal)# exitCODEesr(config)# security ike policy IKEPOLICY esr(config-ike-policy)# pre-shared-key ascii-text encrypted 8CB5107EA7005AFF esr(config-ike-policy)# proposal IKEPROP esr(config-ike-policy)# exitCODEesr(config)# security ike gateway IKEGW esr(config-ike-gw)# ike-policy IKEPOLICY esr(config-ike-gw)# local address 150.115.0.5 esr(config-ike-gw)# local network 150.115.0.5/32 protocol gre esr(config-ike-gw)# remote address any esr(config-ike-gw)# remote network any esr(config-ike-gw)# mode policy-based esr(config-ike-gw)# exitCODEesr(config)# security ipsec proposal IPSECPROP esr(config-ipsec-proposal)# encryption algorithm aes128 esr(config-ipsec-proposal)# exitCODEesr(config)# security ipsec policy IPSECPOLICY esr(config-ipsec-policy)# proposal IPSECPROP esr(config-ipsec-policy)# exitCODEesr(config)# security ipsec vpn IPSECVPN esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# mode ike esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# ike establish-tunnel route esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# ike gateway IKEGW esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# ike ipsec-policy IPSECPOLICY esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# enableCODEMap IPsec to the GRE tunnel so that clients can establish an encrypted connection:
esr(config-gre)# ip nhrp ipsec IPSECVPN dynamicCODEEnable NHRP and the tunnel:
esr(config-gre)# ip nhrp enable esr(config-gre)# enableCODE- Spoke configuration
Perform the standard DMVPN configuration on the tunnel:
esr# configure esr(config-gre)# tunnel gre 8 esr(config-gre)# mtu 1416 esr(config-gre)# ttl 16 esr(config-gre)# multipoint esr(config-gre)# local address 180.100.0.10 esr(config-gre)# ip address 10.10.0.8/24CODESpecify the time while the client record will be stored on the server:
esr(config-gre)# ip nhrp holding-time 300CODESpecify the tunnel address of NHS:
esr(config-gre)# ip nhrp nhs 10.10.0.5/24CODESpecify the tunnel address – real:
esr(config-gre)# ip nhrp map 10.10.0.5 150.115.0.5CODEConfigure the multicast to the NHRP server:
esr(config)# ip nhrp multicast nhsCODEConfigure the BGP for spoke:
esr(config)# router bgp 65008 esr(config-bgp)# address-family ipv4 esr(config-bgp-af)# neighbor 10.10.0.5 esr(config-bgp-neighbor)# remote-as 65005 esr(config-bgp-neighbor)# enable esr(config-bgp-neighbor)# exit esr(config-bgp-af)# enableCODEConfigure IPsec. When creating the IKE protocol gateway for NHS, specify particular destination addresses. When creating an IKE gateway for NHC – the destination address will be any:
esr(config)# security ike proposal IKEPROP esr(config-ike-proposal)# encryption algorithm aes128 esr(config-ike-proposal)# dh-group 2 esr(config-ike-proposal)# exitCODEesr(config)# security ike policy IKEPOLICY esr(config-ike-policy)# pre-shared-key ascii-text encrypted 8CB5107EA7005AFF esr(config-ike-policy)# proposal IKEPROP esr(config-ike-policy)# exitCODEesr(config)# security ike gateway IKEGW_HUB esr(config-ike-gw)# ike-policy IKEPOLICY esr(config-ike-gw)# local address 180.100.0.10 esr(config-ike-gw)# local network 180.100.0.10/32 protocol gre esr(config-ike-gw)# remote address 150.115.0.5 esr(config-ike-gw)# remote network 150.115.0.5/32 protocol gre esr(config-ike-gw)# mode policy-based esr(config-ike-gw)# exitCODEesr(config)# security ike gateway IKEGW_SPOKE esr(config-ike-gw)# ike-policy IKEPOLICY esr(config-ike-gw)# local address 180.100.0.10 esr(config-ike-gw)# local network 180.100.0.10/32 protocol gre esr(config-ike-gw)# remote address any esr(config-ike-gw)# remote network any esr(config-ike-gw)# mode policy-based esr(config-ike-gw)# exitCODEesr(config)# security ipsec proposal IPSECPROP esr(config-ipsec-proposal)# encryption algorithm aes128 esr(config-ipsec-proposal)# exitCODEesr(config)# security ipsec policy IPSECPOLICY esr(config-ipsec-policy)# proposal IPSECPROP esr(config-ipsec-policy)# exitCODEesr(config)# security ipsec vpn IPSECVPN_HUB esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# mode ike esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# ike establish-tunnel route esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# ike gateway IKEGW_HUB esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# ike ipsec-policy IPSECPOLICY esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# enableCODEesr(config)# security ipsec vpn IPSECVPN_SPOKE esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# mode ike esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# ike establish-tunnel route esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# ike gateway IKEGW_SPOKE esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# ike ipsec-policy IPSECPOLICY esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# enableCODEMap IPsec to the GRE tunnel, in order to be able to establish an encrypted connection with the server and with other network clients:
esr(config-gre)# ip nhrp ipsec IPSECVPN_HUB static esr(config-gre)# ip nhrp ipsec IPSECVPN_SPOKE dynamicCODEEnable NHRP and the tunnel:
esr(config-gre)# ip nhrp enable esr(config-gre)# enableCODETo view the NHRP records status, use the following command:
esr# show ip nhrpCODEYou can clear NHRP records with the command:
esr# clear ip nhrpCODE
Configuration example 2
Objective:
Organize DMVPN between company offices with corresponding subnets LAN1 and LAN2, using mGRE tunnels, NHRP (Next Hop Resolution Protocol), Dynamic Routing Protocol (OSPF), IPsec. In our example, we will have a HUB router and two branches. The HUB is the DMVPN server (NHS), and the branches are DMVPN clients (NHC).
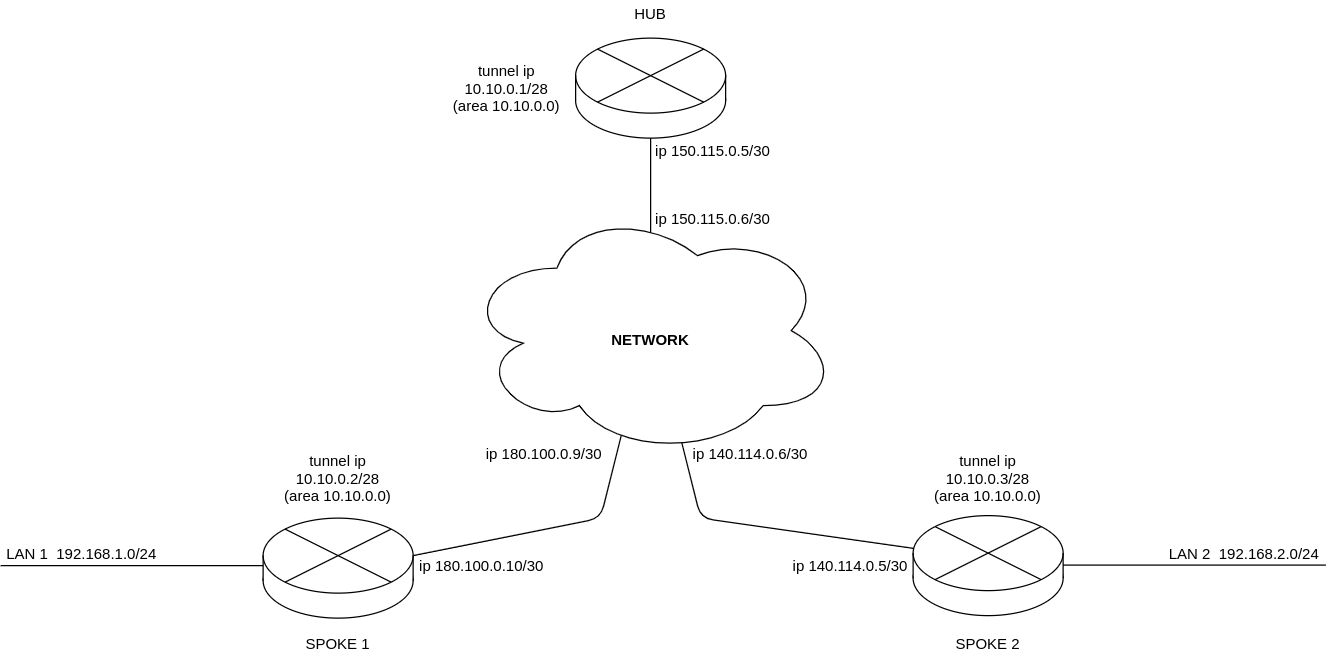
When using the DMVPN scheme, the hub must be a DR router. Thus, the routes of local subnets spoke 1 and spoke 2 will be relayed through the hub.
External IP addres of Hub — 150.115.0.5;
External IP address of Spoke-1 — 180.100.0.10;
External IP address of Spoke-2 — 140.114.0.4.
IPsec VPN parameters:
IKE:
- Diffie-Hellman group: 2;
- encryption algorithm: AES128;
- authentication algorithm: MD5.
IPSEC:
- Diffie-Hellman group: 2;
- encryption algorithm: AES128;
- authentication algorithm: MD5.
Solution:
Hub configuration
Preliminary, configure the OSPF protocol.esr(config)# router ospf log-adjacency-changes esr(config)# router ospf 1 esr(config-ospf)# router-id 77.77.77.77 esr(config-ospf)# area 10.10.0.0 esr(config-ospf-area)# enable esr(config-ospf-area)# exit esr(config-ospf)# enable esr(config-ospf)# exitCODEConfigure the interface and identify its inherence to a security zone.
esr(config)# interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1 esr(config-if-gi)# security-zone untrusted esr(config-if-gi)# ip address 150.115.0.5/30 esr(config-if-gi)# exitCODEConfigure the GRE tunnel, define the security zone membership, configure OSPF on the GRE tunnel, configure NHRP and enable the tunnel and NHRP with the enable command. To make the hub DR, you must set the maximum priority.
esr(config)# tunnel gre 1 esr(config-gre)# ttl 16 esr(config-gre)# mtu 1416 esr(config-gre)# multipoint esr(config-gre)# security-zone untrusted esr(config-gre)# local address 150.115.0.5 esr(config-gre)# ip address 10.10.0.1/28 esr(config-gre)# ip ospf instance 1 esr(config-gre)# ip ospf area 10.10.0.0 esr(config-gre)# ip ospf priority 255 esr(config-gre)# ip ospf esr(config-gre)# ip nhrp multicast dynamic esr(config-gre)# ip nhrp enable esr(config-gre)# enable esr(config-gre)# exitCODECreate static routes for the subnets of the spoke interfaces 180.100.0.8/30 and 140.114.0.4/30.
esr(config)# ip route 180.100.0.8/30 150.115.0.6 esr(config)# ip route 140.114.0.4/30 150.115.0.6CODEConfigure IPsec for the Hub.
esr(config)# security ike proposal ike_prop1 esr(config-ike-proposal)# authentication algorithm md5 esr(config-ike-proposal)# encryption algorithm aes128 esr(config-ike-proposal)# dh-group 2 esr(config-ike-proposal)# exitCODEesr(config)# security ike policy ike_pol1 esr(config-ike-policy)# pre-shared-key ascii-text password esr(config-ike-policy)# proposal ike_prop1 esr(config-ike-policy)# exitCODEesr(config)# security ike gateway ike_spoke esr(config-ike-gw)# ike-policy ike_pol1 esr(config-ike-gw)# local address 150.115.0.5 esr(config-ike-gw)# local network 150.115.0.5/32 protocol gre esr(config-ike-gw)# remote address any esr(config-ike-gw)# remote network any esr(config-ike-gw)# mode policy-based esr(config-ike-gw)# exitCODEesr(config)# security ipsec proposal ipsec_prop1 esr(config-ipsec-proposal)# authentication algorithm md5 esr(config-ipsec-proposal)# encryption algorithm aes128 esr(config-ipsec-proposal)# pfs dh-group 2 esr(config-ipsec-proposal)# exitCODEesr(config)# security ipsec policy ipsec_pol1 esr(config-ipsec-policy)# proposal ipsec_prop1 esr(config-ipsec-policy)# exitCODEesr(config)# security ipsec vpn ipsec_spoke esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# mode ike esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# ike establish-tunnel route esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# ike gateway ike_spoke esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# ike ipsec-policy ipsec_pol1 esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# enable esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# exitCODEMap IPsec to the GRE tunnel so that clients can establish an encrypted connection.
esr(config)# tunnel gre 1 esr(config-gre)# ip nhrp ipsec ipsec_spoke dynamic esr(config-gre)# exitCODEspoke1 configuration
Preliminary configure the OSPF protocol with the advertising of the subnet LAN1.esr(config)# router ospf log-adjacency-changes esr(config)# router ospf 1 esr(config-ospf)# router-id 1.1.1.1 esr(config-ospf)# area 10.10.0.0 esr(config-ospf-area)# network 192.168.1.0/24 esr(config-ospf-area)# enable esr(config-ospf-area)# exit esr(config-ospf)# enable esr(config-ospf)# exitCODEConfigure the interface and identify its inherence to a security zone.
esr(config)# interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1 esr(config-if-gi)# security-zone untrusted esr(config-if-gi)# ip address 180.100.0.10/30 esr(config-if-gi)# exitCODEConfigure the GRE tunnel, define the security zone membership, configure OSPF on the GRE tunnel, configure NHRP and enable the tunnel and NHRP with the enable command. To make the hub DR, you must set the minimum priority on spoke.
esr(config)# tunnel gre 1 esr(config-gre)# ttl 16 esr(config-gre)# mtu 1416 esr(config-gre)# multipoint esr(config-gre)# ip firewall disable esr(config-gre)# local address 180.100.0.10 esr(config-gre)# ip address 10.10.0.2/28 esr(config-gre)# ip ospf instance 1 esr(config-gre)# ip ospf area 10.10.0.0 esr(config-gre)# ip ospf priority 0 esr(config-gre)# ip ospf esr(config-gre)# ip nhrp holding-time 300 esr(config-gre)# ip nhrp map 10.10.0.1 150.115.0.5 esr(config-gre)# ip nhrp nhs 10.10.0.1/28 esr(config-gre)# ip nhrp multicast nhs esr(config-gre)# ip nhrp enable esr(config-gre)# enable esr(config-gre)# exitCODECreate static routes for the subnets of the spoke interfaces 180.100.0.8/30 and 140.114.0.4/30.
esr(config)# ip route 150.115.0.4/30 180.100.0.9 esr(config)# ip route 140.114.0.4/30 180.100.0.9CODEConfigure IPsec for the Hub.
esr(config)# security ike proposal ike_prop1 esr(config-ike-proposal)# authentication algorithm md5 esr(config-ike-proposal)# encryption algorithm aes128 esr(config-ike-proposal)# dh-group 2 esr(config-ike-proposal)# exitCODEesr(config)# security ike policy ike_pol1 esr(config-ike-policy)# pre-shared-key ascii-text password esr(config-ike-policy)# proposal ike_prop1 esr(config-ike-policy)# exitCODEesr(config)# security ike gateway ike_spoke esr(config-ike-gw)# ike-policy ike_pol1 esr(config-ike-gw)# local address 180.100.0.10 esr(config-ike-gw)# local network 180.100.0.10/32 protocol gre esr(config-ike-gw)# remote address any esr(config-ike-gw)# remote network any esr(config-ike-gw)# mode policy-based esr(config-ike-gw)# exit esr(config)# security ike gateway ike_hub esr(config-ike-gw)# ike-policy ike_pol1 esr(config-ike-gw)# local address 180.100.0.10 esr(config-ike-gw)# local network 180.100.0.10/32 protocol gre esr(config-ike-gw)# remote address 150.115.0.5 esr(config-ike-gw)# remote network 150.115.0.5/32 protocol gre esr(config-ike-gw)# mode policy-based esr(config-ike-gw)# exitCODEesr(config)# security ipsec proposal ipsec_prop1 esr(config-ipsec-proposal)# authentication algorithm md5 esr(config-ipsec-proposal)# encryption algorithm aes128 esr(config-ipsec-proposal)# pfs dh-group 2 esr(config-ipsec-proposal)# exitCODEesr(config)# security ipsec policy ipsec_pol1 esr(config-ipsec-policy)# proposal ipsec_prop1 esr(config-ipsec-policy)# exitCODEesr(config)# security ipsec vpn ipsec_spoke esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# mode ike esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# ike establish-tunnel route esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# ike gateway ike_spoke esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# ike ipsec-policy ipsec_pol1 esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# enable esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# exit esr(config)# security ipsec vpn ipsec_hub esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# mode ike esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# ike establish-tunnel route esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# ike gateway ike_hub esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# ike ipsec-policy ipsec_pol1 esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# enable esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# exitCODEMap IPsec to the GRE tunnel, in order to be able to establish an encrypted connection with the server and with other network clients.
esr(config)# tunnel gre 1 esr(config-gre)# ip nhrp ipsec ipsec_hub static esr(config-gre)# ip nhrp ipsec ipsec_spoke dynamic esr(config-gre)# exitCODETo view the NHRP records status, use the following command.
esr# show ip nhrpCODEAdditionally, in the security zone-pair untrusted self, the protocols for the GRE over IPSec tunnel must be allowed.
esr(config)# security zone-pair untrusted self esr(config-zone-pair)# rule 10 esr(config-zone-pair-rule)# action permit esr(config-zone-pair-rule)# match protocol gre esr(config-zone-pair-rule)# enable esr(config-zone-pair-rule)# exit esr(config-zone-pair)# rule 11 esr(config-zone-pair-rule)# action permit esr(config-zone-pair-rule)# match protocol esp esr(config-zone-pair-rule)# enable esr(config-zone-pair-rule)# exit esr(config-zone-pair)# rule 12 esr(config-zone-pair-rule)# action permit esr(config-zone-pair-rule)# match protocol ah esr(config-zone-pair-rule)# enable esr(config-zone-pair-rule)# exit esr(config-zone-pair)# exitCODE
L2TPv3 tunnel configuration
L2TPv3 (Layer 2 Tunnelling Protocol Version 3) is a protocol used for tunneling of 2nd level OSI model packets between two IP nodes. IP or UDP is used as an encapsulation protocol. L2TPv3 may be used as an alternative to MPLS P2P L2VPN (VLL) for L2 VPN establishment. In ESR router implemented static unmanageable L2TPv3 tunnels, i.e. tunnels are created manually via configuration on local and remote hosts. Tunnel parameters for each side should be mutually agreeable, otherwise transferred data will not be decapsulated by the partner.
Configuration algorithm
Step | Description | Command | Keys |
1 | Configure L3 interface from which a L2TPv3 tunnel will be built. |
| |
2 | Create a L2TPv3 tunnel and switch to its configuration mode. | esr(config)# tunnel l2tpv3 <INDEX> | <INDEX> – tunnel identifier, set in the range of:
|
3 | Specify the description of the configured tunnel (optionally). | esr(config-l2tpv3)# description <DESCRIPTION> | <DESCRIPTION> – tunnel description, set by the string of up to 255 characters. |
4 | Set local IP address for tunnel installation. | esr(config-l2tpv3)# local address <ADDR> | <ADDR> – gateway IP address, defined as AAA.BBB.CCC.DDD where each part takes values of [0..255]. |
5 | Set remote IP address for tunnel installation. | esr(config-l2tpv3)# remote address <ADDR> | <ADDR> – gateway IP address, defined as AAA.BBB.CCC.DDD where each part takes values of [0..255]. |
6 | Select encapsulation method for L2TPv3 tunnel. | esr(config-l2tpv3)# protocol <TYPE> | <TYPE> – encapsulation type, possible values:
|
7 | Set local session identifier. | esr(config-l2tpv3)# local session-id <SESSION-ID> | <SESSION-ID> – session identifier, takes values in the range of [1..200000]. |
8 | Set remote session identifier. | esr(config-l2tpv3)# remote session-id <SESSION-ID> | <SESSION-ID> – session identifier, takes values in the range of [1..200000]. |
9 | Define local UDP port (if UDP was selected as encapsulation method). | esr(config-l2tpv3)# local port <UDP> | <UDP> – UDP port number in the range of [1..65535]. |
10 | Define remote UDP port (if UDP was selected as encapsulation method). | esr(config-l2tpv3)# remote port <UDP> | <UDP> – UDP port number in the range of [1..65535]. |
11 | Assign the broadcast domain for encapsulation in the tunnel’s L2TPV3 packets. | esr(config-l2tpv3)# bridge-group <BRIDGE-ID> | <BRIDGE-ID> – bridge identification number, takes values in the range of:
|
12 | Enable the tunnel. | esr(config-l2tpv3)# enable | |
13 | Specify MTU size (MaximumTransmissionUnit) for the tunnels (optionally). | esr(config-l2tpv3)# mtu <MTU> | <MTU> – MTU value, takes values in the range of:
Default value: 1500. |
14 | Define the local cookie value to check the conformance of data being transmitted and session (optionally). | esr(config-l2tpv3)# local cookie <COOKIE> | <COOKIE> – COOKIE value, the parameter takes values of 8 or 16 characters in hexadecimal form. |
15 | Define the remote cookie value to check the conformance of data being transmitted and session (optionally). | esr(config-l2tpv3)# remote cookie <COOKIE> | <COOKIE> – COOKIE value, the parameter takes values of 8 or 16 characters in hexadecimal form. |
16 | Specify the time interval during which the statistics on the tunnel load is averaged (optionally). | esr(config-l2tpv3)# load-average <TIME> | <TIME> – interval in seconds, takes values of [5..150]. Default value: 5. |
17 | Enable recording of the current tunnel usage statistics (optional). | esr(config-subif)# history statistics | |
It is also possible to configure the L2TPv3 tunnel:
| |||
L2TPv3 tunnel configuration example
Objective:
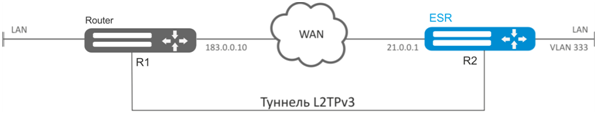
Establish L2 VPN for company offices using IP network with L2TPv3 protocol for traffic tunneling.
- UDP is used as an encapsulation protocol, port number at the local side and port number at the partner's side is 519;
- IP address 21.0.0.1 is used as a local gateway for the tunnel;
- IP address 183.0.0.10 is used as a remote gateway for the tunnel;
- Tunnel identifier at the local side equals 2, at the partner's side - 3;
- Tunnel identifier inside the tunnel equals 100, at the partner's side - 200;
- Forward traffic into the tunnel from the bridge with identifier 333.
Solution:
Create L2TPv3 333 tunnel:
esr# configure
esr(config)# tunnel l2tpv3 333Specify local and remote gateways (IP addresses of WAN border interfaces):
esr(config-l2tpv3)# local address 21.0.0.1
esr(config-l2tpv3)# remote address 183.0.0.10Specify the type of encapsulating protocol and UDP port numbers:
esr(config-l2tpv3)# protocol udp
esr(config-l2tpv3)# local port 519
esr(config-l2tpv3)# remote port 519Specify identifiers for session inside the tunnel for local and remote sides:
esr(config-l2tpv3)# local session-id 100
esr(config-l2tpv3)# remote session-id 200Define the inherence of L2TPv3 tunnel to a bridge that should be mapped to remote office network (for bridge configuration, see Section Configuration example of bridge for VLAN and L2TPv3 tunnel):
esr(config-l2tpv3)# bridge-group 333Enable previously created tunnel and exit:
esr(config-l2tpv3)# enable
esr(config-l2tpv3)# exitCreate sub-interface for switching of traffic coming from the tunnel into LAN with VLAN id 333:
esr(config)# interface gi 1/0/2.333Define the inherence of sub-interface to a bridge that should be mapped to LAN (for bridge configuration, see Section Configuration of PPP via E1):
esr(config-subif)# bridge-group 333
esr(config-subif)# exitWhen settings are applied, traffic will be encapsulated into the tunnel and sent to the partner regardless of their L2TPv3 tunnel existence and settings validity.
Tunnel settings for the remote office should mirror local ones. IP address 183.0.0.10 should be used as a local gateway. IP address 21.0.0.1 should be used as a remote gateway for the tunnel. Encapsulation protocol port number at the local side should be 520, at the partner's side – 519. Session identifier inside the tunnel should be equal to 200, at the partner's side – 100. Also, the tunnel should belong to a bridge that should be connected with the partner's network.
To view the tunnel status, use the following command:
esr# show tunnels status l2tpv3 333To view sent and received packet counters, use the following command:
esr# show tunnels counters l2tpv3 333To view the tunnel configuration, use the following command:
esr# show tunnels configuration l2tpv3 333In addition to tunnel creation, you should enable UDP inbound traffic in the firewall with source port 519 and destination port 519.
IPsec VPN configuration
IPsec is a set of protocols that enable security features for data transferred via IP protocol. This set of protocols allows for identity validation (authentication), IP packet integrity check and encryption, and also includes protocols for secure key exchange over the Internet.
Route-based IPsec VPN configuration algorithm
Step | Description | Command | Keys |
|---|---|---|---|
1 | Create a VTI tunnel and switch to its configuration mode. | esr(config)# tunnel vti <TUN> | <TUN> – device tunnel name. |
2 | Specify the local IP address of the VTI tunnel. | esr(config-vti)#local address <ADDR> | <ADDR> – IP address of a local gateway. |
3 | Specify the remote IP address of the VTI tunnel. | esr(config-vti)#remote address <ADDR> | <ADDR> – IP address of a remote gateway. |
4 | Specify the IP address of the VTI tunnel local side. | esr(config-vti)# ip address <ADDR/LEN> | <ADDR/LEN> – IP address and prefix of a subnet, defined as AAA.BBB.CCC.DDD/EE where each part AAA-DDD takes values of [0..255] and EE takes values of [1..32]. |
5 | Include the VTI tunnel in a security zone and configure interaction rules between zones or disable firewall for VTI tunnel. | esr(config-vti)# security-zone<NAME> | <NAME> – security zone name, set by the string of up to 12 characters. |
esr(config-vti)# ip firewall disable | |||
6 | Enable the tunnel. | esr(config-vti)#enable | |
7 | Create an IKE profile and switch to its configuration mode. | esr(config)# security ike proposal <NAME> | <NAME> – IKE protocol name, set by the string of up to 31 characters. |
8 | Specify the description of the configured IKE profile (optionally). | esr(config-ike-proposal)# description<DESCRIPTION> | <DESCRIPTION> – tunnel description, set by the string of up to 255 characters. |
9 | Specify IKE authentication algorithm (optionally). | esr(config-ike-proposal)# authentication algorithm <ALGORITHM> | <ALGORITHM> – authentication algorithm, takes values of: md5, sha1, sha2-256, sha2‑384, sha2-512. Default value: sha1 |
10 | Specify IKE encryption algorithm (optionally). | esr(config-ike-proposal)# encryption algorithm <ALGORITHM> | <ALGORITHM> – encryption protocol, takes the following values: des, 3des, blowfish128, blowfish192, blowfish256, aes128, aes192, aes256, aes128ctr, aes192ctr, aes256ctr, camellia128, camellia192, camellia256. Default value: 3des |
11 | Define Diffie-Hellman group number (optionally). | esr(config-ike-proposal)# dh-group <DH-GROUP> | <DH-GROUP> – Diffie-Hellman group number, takes values of [1, 2, 5, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18]. Default value: 1 |
12 | Specify IKE authentication mode (optionally) | esr(config-ike-proposal)# authentication method <METHOD> | <METHOD> – key authentication method. May take the following values:
Default value: pre-shared-key |
13 | Create an IKE policy and switch to its configuration mode. | esr(config)# security ike policy <NAME> | <NAME> – IKE policy name, set by the string of up to 31 characters. |
14 | Specify the lifetime of IKE protocol connection (optionally). | esr(config-ike-proposal)# lifetime seconds <SEC> | <SEC> – time interval, takes values of [4..86400] seconds. Default value: 3600 |
15 | Bind IKE profile to IKE policy. | esr(config-ike-policy)# proposal <NAME> | <NAME> – IKE protocol name, set by the string of up to 31 characters. |
16 | Specify authentication key (mandatory if pre-shared-key is selected as authentication mode) | esr(config-ike-policy)# pre-shared-key ascii-text<TEXT> | <TEXT> – string [1..64] ASCII characters. |
17 | Create an IKE gateway and switch to its configuration mode. | esr(config)# security ike gateway <NAME> | <NAME> – IKE protocol gateway name, set by the string of up to 31 characters. |
18 | Bind IKE policy to IKE gateway. | esr(config-ike-gw)# ike-policy <NAME> | <NAME> – IKE protocol policy name, set by the string of up to 31 characters. |
19 | Specify IKE version (optionally). | esr(config-ike-gw)# version <VERSION> | <version> – IKE protocol version: v1-only or v2-only. Default value: v1-only |
20 | Set the route-based mode. | esr(config-ike-gw)# mode route-based | |
21 | Specify the action for DPD (optionally). | esr(config-ike-gw)# dead-peer-detection action <MODE> | <MODE> – DPD operation mode:
Default value: none |
22 | Specify the interval between sending messages via DPD mechanism (optionally). | esr(config-ike-gw)# dead-peer-detection interval <SEC> | <SEC> – interval between sending messages via DPD mechanism, takes values of [1..180] seconds. Default value: 2 |
23 | Specify the time period of response to DPD mechanism messages (optionally). | esr(config-ike-gw)# dead-peer-detection timeout <SEC> | <SEC> – time interval of response to DPD mechanism messages, takes values of [1..180] seconds. Default value: 30 seconds |
24 | Bind VTI tunnel to IKE gateway. | esr(config-ike-gw)# bind-interface vti <VTI> | <VTI> – VTI ID. |
25 | Create IPsec profile. | esr(config)# security ipsec proposal <NAME> | <NAME> – IPsec protocol profile name, set by the string of up to 31 characters. |
26 | Specify IPsec authentication algorithm (optionally) | esr(config-ipsec-proposal)# authentication algorithm <ALGORITHM> | <ALGORITHM> – authentication algorithm, takes values of: md5, sha1, sha2-256, sha2‑384, sha2-512. Default value: sha1 |
27 | Specify IPsec encryption algorithm (optionally) | esr(config-ipsec-proposal)# encryption algorithm <ALGORITHM> | <ALGORITHM> – encryption protocol, takes the following values: des, 3des, blowfish128, blowfish192, blowfish256, aes128, aes192, aes256, aes128ctr, aes192ctr, aes256ctr, camellia128, camellia192, camellia256. Default value: 3des |
28 | Specify encapsulation protocol for IPsec (optionally). | esr(config-ipsec-proposal)# protocol <PROTOCOL> | <PROTOCOL> – encapsulation protocol, takes the following values: Default value: esp |
29 | Create an IPsec policy and switch to its configuration mode. | esr(config)# security ipsec policy <NAME> | <NAME> – IPsec policy name, set by the string of up to 31 characters. |
30 | Bind IPsec profile to IPsec policy. | esr(config-ipsec-policy)# proposal <NAME> | <NAME> – IPsec protocol profile name, set by the string of up to 31 characters. |
31 | Specify the lifetime of IPsec tunnel (optionally). | esr(config-ipsec- policy)# lifetime { seconds <SEC> | | <SEC> – IPsec tunnel lifetime after which the re-approval is carried out. Takes values in the range of [1140..86400] seconds. <PACKETS> – number of packets after transmitting of which the IPsec tunnel re-approval is carried out. Takes values in the range of [4..86400]. <KB> – traffic amount after transmitting of which the IPsec tunnel re-approval is carried out. Takes values in the range of [4..86400] seconds. Default value: 28800 seconds |
32 | Create IPsec VPN policy and switch to its configuration mode. | esr(config)# security ipsec vpn <NAME> | <NAME> – VPN name, set by the string of up to 31 characters. |
33 | Define the matching mode of data required for VPN enabling. | esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# mode <MODE> | <MODE> – VPN operation mode. |
34 | Bind IPsec policy to IPsec VPN. | esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# ike ipsec-policy <NAME> | <NAME> – IPsec policy name, set by the string of up to 31 characters. |
35 | Set the DSCP value for the use in IP headers of IKE outgoing packets (optionally). | esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# ike dscp <DSCP> | <DSCP> – DSCP code value, takes values in the range of [0..63]. Default value: 63 |
36 | Set VPN activation mode. | esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# ike establish-tunnel <MODE> | <MODE> – VPN activation mode:
|
37 | Bind IKE gateway to IPsec VPN. | esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# ike gateway <NAME> | <NAME> – IKE gateway name, set by the string of up to 31 characters. |
38 | Set the time interval value in seconds after which the connection is closed, if no packet has been received or sent via SA (optionally). | esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# ike idle-time <TIME> | <TIME> – interval in seconds, takes values of [4..86400]. |
39 | Disable key re-approval before the IKE connection is lost due to the timeout, the number of transmitted packets or bytes (optionally). | esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# ike rekey disable | |
40 | Configure the start of IKE connection keys re-approval before the expiration of the lifetime (optionally). | esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# ike rekey margin { seconds <SEC> | | <SEC> – time interval in seconds remaining before the connection release (set by the lifetimeseconds command, see 22.2.13). Takes values in the range of [4..86400]. <PACKETS> – number of packets remaining before the connection release (set by the lifetimepackets command). Takes values in the range of [4..86400]. <KB> – traffic volume in kilobytes remaining before the connection release (set by the lifetimekilobytes command). Takes values in the range of [4..86400]. Default value:
|
41 | Set the level of margin seconds, margin packets, margin kilobytes values random spread (optionally). | esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# ike rekey randomization <VALUE> | <VALUE> – maximum ratio of values spread, takes values of [1..100]. Default value: 100% |
42 | Specify the description for IPsec-VPN (optionally). | esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# description <DESCRIPTION> | <DESCRIPTION> – profile description, set by the string of up to 255 characters. |
43 | Enable IPsec VPN. | esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# enable |
Route-based IPsec VPN configuration example
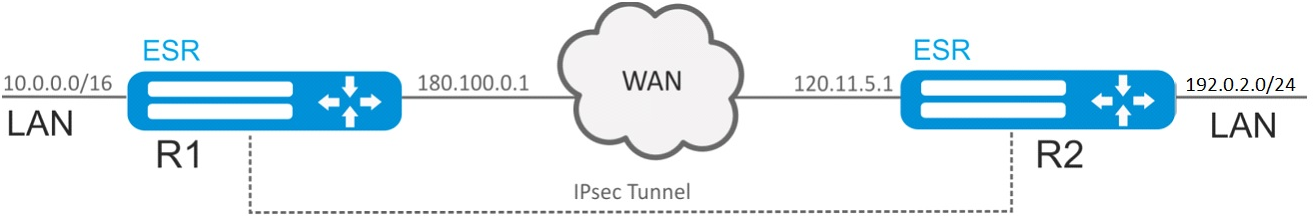
Objective:
Configure IPsec tunnel between R1 and R2.
- R1 IP address: 120.11.5.1;
- R2 IP address: 180.100.0.1;
IKE:
- Diffie-Hellman group: 2;
- encryption algorithm: AES 128 bit;
- authentication algorithm: MD5.
IP sec:
- encryption algorithm: AES 128 bit;
- authentication algorithm: MD5.
Solution:
R1 configuration
Configure external network interface and identify its inherence to a security zone:esr# configure esr(config)# interface gi 1/0/1 esr(config-if-gi)# ip address 180.100.0.1/24 esr(config-if-gi)# security-zone untrusted esr(config-if-gi)# exitCODECreate VTI tunnel. Traffic will be routed via VTI into IPsec tunnel. Specify IP addresses of WAN border interfaces as local and remote gateways:
esr(config)# tunnel vti 1 esr(config-vti)# local address 180.100.0.1 esr(config-vti)# remote address 120.11.5.1 esr(config-vti)# enable esr(config-vti)# exitCODETo configure security zones rules, you should create ISAKMP port profile:
esr(config)# object-group service ISAKMP esr(config-object-group-service)# port-range 500 esr(config-object-group-service)# exitCODECreate a static route to the remote LAN. For each subnet located beyond the IPsec tunnel, specify a route via VTI tunnel:
esr(config)# ip route 192.0.2.0/24 tunnel vti 1CODECreate IKE protocol profile. Select Diffie-Hellman group 2, AES 128 bit encryption algorithm and MD5 authentication algorithm in the profile. The given security parameters are used for IKE connection protection:
esr(config)# security ike proposal ike_prop1 esr(config-ike-proposal)# dh-group 2 esr(config-ike-proposal)# authentication algorithm md5 esr(config-ike-proposal)# encryption algorithm aes128 esr(config-ike-proposal)# exitCODECreate IKE protocol policy. For the policy, specify the list of IKE protocol profiles that may be used for node and authentication key negotiation:
esr(config)# security ike policy ike_pol1 esr(config-ike-policy)# pre-shared-key hexadecimal 123FFF esr(config-ike-policy)# proposal ike_prop1 esr(config-ike-policy)# exitCODECreate IKE protocol gateway. For this profile, specify VTI tunnel, policy, protocol version and mode of traffic redirection into the tunnel.
esr(config)# security ike gateway ike_gw1 esr(config-ike-gw)# ike-policy ike_pol1 esr(config-ike-gw)# mode route-based esr(config-ike-gw)# bind-interface vti 1 esr(config-ike-gw)# version v2-only esr(config-ike-gw)# exitCODECreate security parameters profile for IPsec tunnel. For the profile, select Diffie-Hellman group 2, AES 128 bit encryption algorithm and MD5 authentication algorithm. Use the following parameters to secure IPsec tunnel:
esr(config)# security ipsec proposal ipsec_prop1 esr(config-ipsec-proposal)# authentication algorithm md5 esr(config-ipsec-proposal)# encryption algorithm aes128 esr(config-ipsec-proposal)# exitCODECreate a policy for IPsec tunnel. For the policy, specify the list of IPsec tunnel profiles that may be used for node negotiation:
esr(config)# security ipsec policy ipsec_pol1 esr(config-ipsec-policy)# proposal ipsec_prop1 esr(config-ipsec-policy)# exitCODECreate IPsec VPN. For VPN, specify IKE protocol gateway, IPsec tunnel policy, key exchange mode and connection establishment method. When all parameters are entered, enable tunnel using the enable command.
esr(config)# security ipsec vpn ipsec1 esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# mode ike esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# ike establish-tunnel route esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# ike gateway ike_gw1 esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# ike ipsec-policy ipsec_pol1 esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# enable esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# exit esr(config)# exitCODE- R2 configuration
Configure external network interface and identify its inherence to a security zone:
esr# configure esr(config)# interface gi 1/0/1 esr(config-if)# ip address 120.11.5.1/24 esr(config-if)# security-zone untrusted esr(config-if)# exitCODECreate VTI tunnel. Traffic will be routed via VTI into IPsec tunnel. Specify IP addresses of WAN border interfaces as local and remote gateways:
esr(config)# tunnel vti 1 esr(config-vti)# remote address 180.100.0.1 esr(config-vti)# local address 120.11.5.1 esr(config-vti)# enable esr(config-vti)# exitCODETo configure security zones rules, you should create ISAKMP port profile:
esr(config)# object-group service ISAKMP esr(config-object-group-service)# port-range 500 esr(config-object-group-service)# exitCODECreate a static route to the remote LAN. For each subnet located beyond the IPsec tunnel, specify a route via VTI tunnel:
esr(config)# ip route 10.0.0.0/16 tunnel vti 1CODECreate IKE protocol profile. Select Diffie-Hellman group 2, AES 128 bit encryption algorithm and MD5 authentication algorithm in the profile. The given security parameters are used for IKE connection protection:
esr(config)# security ike proposal ike_prop1 esr(config-ike-proposal)# dh-group 2 esr(config-ike-proposal)# authentication algorithm md5 esr(config-ike-proposal)# encryption algorithm aes128 esr(config-ike-proposal)# exit esr(config)#CODECreate IKE protocol policy. For the policy, specify the list of IKE protocol profiles that may be used for node and authentication key negotiation:
esr(config)# security ike policy ike_pol1 esr(config-ike-policy)# pre-shared-key hexadecimal 123FFF esr(config-ike-policy)# proposal ike_prop1 esr(config-ike-policy)# exitCODECreate IKE protocol gateway. For this profile, specify VTI tunnel, policy, protocol version and mode of traffic redirection into the tunnel.
esr(config)# security ike gateway ike_gw1 esr(config-ike-gw)# ike-policy ike_pol1 esr(config-ike-gw)# mode route-based esr(config-ike-gw)# bind-interface vti 1 esr(config-ike-gw)# version v2-only esr(config-ike-gw)# exitCODECreate security parameters profile for IPsec tunnel. For the profile, select Diffie-Hellman group 2, AES 128 bit encryption algorithm and MD5 authentication algorithm. Use the following parameters to secure IPsec tunnel:
esr(config)# security ipsec proposal ipsec_prop1 esr(config-ipsec-proposal)# authentication algorithm md5 esr(config-ipsec-proposal)# encryption algorithm aes128 esr(config-ipsec-proposal)# exitCODECreate a policy for IPsec tunnel. For the policy, specify the list of IPsec tunnel profiles that may be used for node negotiation:
esr(config)# security ipsec policy ipsec_pol1 esr(config-ipsec-policy)# proposal ipsec_prop1 esr(config-ipsec-policy)# exitCODECreate IPsec VPN. For VPN, specify IKE protocol gateway, IPsec tunnel policy, key exchange mode and connection establishment method. When all parameters are entered, enable tunnel using the enable command.
esr(config)# security ipsec vpn ipsec1 esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# mode ike esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# ike establish-tunnel route esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# ike gateway ike_gw1 esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# ike ipsec-policy ipsec_pol1 esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# enable esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# exit esr(config)# exitCODETo view the tunnel status, use the following command:
esr# show security ipsec vpn status ipsec1CODETo view the tunnel configuration, use the following command:
esr# show security ipsec vpn configuration ipsec1CODE
In the firewall, you should enable ESP and ISAKMP protocol (UDP port 500).
Policy-based IPsec VPN configuration algorithm
Step | Description | Command | Keys |
|---|---|---|---|
1 | Create an IKE instance and switch to its configuration mode. | esr(config)# security ike proposal <NAME> | <NAME> – IKE protocol name, set by the string of up to 31 characters. |
2 | Specify the description of the configured tunnel (optionally). | esr(config-ike-proposal)# description<DESCRIPTION> | <DESCRIPTION> – tunnel description, set by the string of up to 255 characters. |
3 | Specify IKE authentication algorithm. | esr(config-ike-proposal)# authentication algorithm <ALGORITHM> | <ALGORITHM> – authentication algorithm, takes values of: md5, sha1, sha2-256, sha2‑384, sha2-512. |
4 | Specify IKE encryption algorithm. | esr(config-ike-proposal)# encryption algorithm <ALGORITHM> | <ALGORITHM> – encryption protocol, takes the following values: des, 3des, blowfish128, blowfish192, blowfish256, aes128, aes192, aes256, aes128ctr, aes192ctr, aes256ctr, camellia128, camellia192, camellia256. |
5 | Define Diffie-Hellman group number. | esr(config-ike-proposal)# dh-group <DH-GROUP> | <DH-GROUP> – Diffie-Hellman group number, takes values of [1, 2, 5, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18]. |
6 | Specify the authentication mode. | esr(config-ike-proposal)# authentication method <METHOD> | <METHOD> – key authentication method. May take the following values:
|
7 | Create an IKE profile policy and switch to its configuration mode. | esr(config)# security ike policy <NAME> | <NAME> – IKE policy name, set by the string of up to 31 characters. |
8 | Specify the lifetime of IKE protocol connection (optionally). | esr(config-ike-proposal)# lifetime seconds <SEC> | <SEC> – time interval, takes values of [4..86400] seconds. |
9 | Bind the policy to profile. | esr(config-ike-policy)# proposal <NAME> | <NAME> – IKE protocol name, set by the string of up to 31 characters. |
10 | Specify authentication key. | esr(config-ike-policy)#pre-shared-key ascii-text<TEXT> | <TEXT> – string [1..64] ASCII characters. |
11 | Create an IKE gateway and switch to its configuration mode. | esr(config)# security ike gateway <NAME> | <NAME> – IKE protocol gateway name, set by the string of up to 31 characters. |
12 | Bind IKE policy. | esr(config-ike-gw)# ike-policy <NAME> | <NAME> – IKE protocol policy name, set by the string of up to 31 characters. |
13 | Specify IKE version (optionally). | esr(config-ike-gw)# version <VERSION> | <version> – IKE protocol version: v1-only or v2-only. |
14 | Set the mode of traffic redirection into the tunnel. | esr(config-ike-gw)#mode<MODE> | <MODE> – mode of traffic redirection into the tunnel, takes the following values:
|
15 | Specify the action for DPD (optionally). | esr(config-ike-gw)# dead-peer-detection action <MODE> | <MODE> – DPD operation mode:
|
16 | Specify the interval between sending messages via DPD mechanism (optionally). | esr(config-ike-gw)#dead-peer-detection interval <SEC> | <SEC> – interval between sending messages via DPD mechanism, takes values of [1..180] seconds. |
17 | Specify the time period of response to DPD mechanism messages (optionally). | esr(config-ike-gw)# dead-peer-detection timeout <SEC> | <SEC> – time interval of response to DPD mechanism messages, takes values of [1..180] seconds. |
18 | Specify IKE version (optionally). | esr(config-ike-gw)# version <VERSION> | <version> – IKE protocol version: v1-only or v2-only. |
19 | Set sender’s IP subnets. | esr(config-ike-gw)# local network <ADDR/LEN> | <ADDR/LEN> – subnet IP address and mask of a sender. The parameter is defined as AAA.BBB.CCC.DDD/EE where each part AAA-DDD takes values of [0..255] and EE takes values of [1..32]. <TYPE> – protocol type, takes the following values: esp, icmp, ah, eigrp, ospf, igmp, ipip, tcp, pim, udp, vrrp, rdp, l2tp, gre; <ID> – IP identification number, takes values of [0x00-0xFF]; <PORT> – TCP/UDP port, takes values of [1..65535]. |
20 | Specify the IP address of IPsec tunnel local gateway. | esr(config-ike-gw)#local address <ADDR> | <ADDR> – IP address of a local gateway. |
21 | Specify the IP address of IPsec tunnel remote gateway. | esr(config-ike-gw)#remote address <ADDR> | <ADDR> – IP address of a remote gateway. |
22 | Set recipient’s subnet IP address as well as IP and port. | esr(config-ike-gw)# remote network <ADDR/LEN> | <ADDR/LEN> – subnet IP address and mask of a sender. The parameter is defined as AAA.BBB.CCC.DDD/EE where each part AAA-DDD takes values of [0..255] and EE takes values of [1..32]. <TYPE> – protocol type, takes the following values: esp, icmp, ah, eigrp, ospf, igmp, ipip, tcp, pim, udp, vrrp, rdp, l2tp, gre; <ID> – IP identification number, takes values of [0x00-0xFF]; <PORT> – TCP/UDP port, takes values of [1..65535]. |
23 | Create IPsec profile. | esr(config)# security ipsec proposal <NAME> | <NAME> – IPsec protocol profile name, set by the string of up to 31 characters. |
24 | Specify IPsec authentication algorithm. | esr(config-ipsec-proposal)# authentication algorithm <ALGORITHM> | <ALGORITHM> – authentication algorithm, takes values of: md5, sha1, sha2-256, sha2‑384, sha2-512. |
26 | Specify IPsec encryption algorithm. | esr(config-ipsec-proposal)# encryption algorithm <ALGORITHM> | <ALGORITHM> – encryption protocol, takes the following values: des, 3des, blowfish128, blowfish192, blowfish256, aes128, aes192, aes256, aes128ctr, aes192ctr, aes256ctr, camellia128, camellia192, camellia256. |
26 | Specify protocol (optionally). | esr(config-ipsec-proposal)#protocol <PROTOCOL> | <PROTOCOL> – encapsulation protocol, takes the following values: |
27 | Create an IPsec profile policy and switch to its configuration mode. | esr(config)# security ipsec policy <NAME> | <NAME> – IPsec policy name, set by the string of up to 31 characters. |
28 | Bind the policy to profile. | esr(config-ipsec-policy)# proposal <NAME> | <NAME> – IPsec protocol profile name, set by the string of up to 31 characters. |
29 | Specify the lifetime of IPsec tunnel (optionally). | esr(config-ipsec-policy)# lifetime { seconds <SEC> | | <SEC> – IPsec tunnel lifetime after which the re-approval is carried out. Takes values in the range of [1140..86400] seconds. <PACKETS> – number of packets after transmitting of which the IPsec tunnel re-approval is carried out. Takes values in the range of [4..86400]. <KB> – traffic amount after transmitting of which the IPsec tunnel re-approval is carried out. Takes values in the range of [4..86400] seconds. |
30 | Create IPsec VPN policy and switch to its configuration mode. | esr(config)# security ipsecvpn <NAME> | <NAME> – VPN name, set by the string of up to 31 characters. |
31 | Define the matching mode of data required for VPN enabling. | esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# mode <MODE> | <MODE> – VPN operation mode. |
32 | Bind IPsec policy to VPN. | esr(config-ipsec-vpn)#ike ipsec-policy <NAME> | <NAME> – IPsec policy name, set by the string of up to 31 characters. |
33 | Set the DSCP value for the use in IP headers of IKE outgoing packets (optionally). | esr(config-ipsec-vpn)#ike dscp <DSCP> | <DSCP> – DSCP code value, takes values in the range of [0..63]. |
34 | Set VPN activation mode. | esr(config-ipsec-vpn)#ike establish-tunnel <MODE> | <MODE> – VPN activation mode:
|
35 | Bind IKE gateway to VPN. | esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# ike gateway <NAME> | <NAME> – IKE gateway name, set by the string of up to 31 characters. |
36 | Set the time interval value in seconds after which the connection is closed, if no packet has been received or sent via SA (optionally). | esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# ike idle-time <TIME> | <TIME> – interval in seconds, takes values of [4..86400]. |
37 | Disable key re-approval before the IKE connection is lost due to the timeout, the number of transmitted packets or bytes (optionally). | esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# ike rekey disable | |
38 | Configure the start of IKE connection keys re-approval before the expiration of the lifetime (optionally). | esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# ike rekey margin { seconds <SEC> | | <SEC> – time interval in seconds remaining before the connection release (set by the lifetimeseconds command). Takes values in the range of [4..86400]. <PACKETS> – number of packets remaining before the connection release (set by the lifetimepackets command). Takes values in the range of [4..86400]. <KB> – traffic volume in kilobytes remaining before the connection release (set by the lifetimekilobytes command). Takes values in the range of [4..86400]. |
39 | Set the level of margin seconds, margin packets, margin kilobytes values random spread (optionally). | esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# ike rekey randomization <VALUE> | <VALUE> – maximum ratio of values spread, takes values of [1..100]. |
40 | Describe VPN (optionally). | esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# description <DESCRIPTION> | <DESCRIPTION> – profile description, set by the string of up to 255 characters. |
41 | Enable IPsec VPN. | esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# enable |
Policy-based IPsec VPN configuration example
Objective:
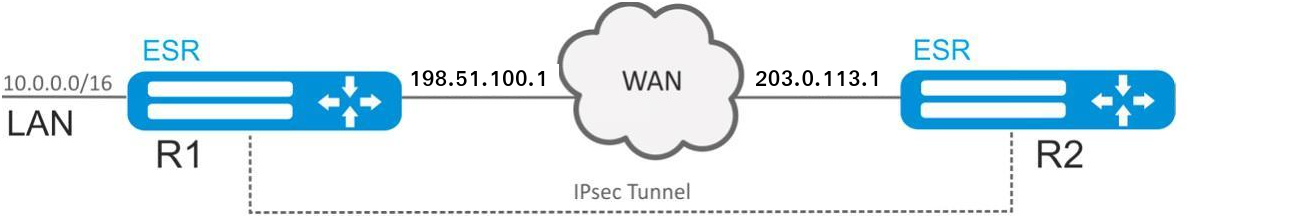
Configure IPsec tunnel between R1 and R2.
R1 IP address – 198.51.100.1;
R2 IP address – 203.0.113.1;
IKE:
- Diffie-Hellman group: 2;
- encryption algorithm: AES 128 bit;
- authentication algorithm: MD5.
IPSEC:
- encryption algorithm: AES 128 bit;
- authentication algorithm: MD5.
Solution:
- R1 configuration
Configure external network interface and identify its inherence to a security zone:
esr# configure esr(config)# interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1 esr(config-if-gi)# ip address 198.51.100.1/24 esr(config-if-gi)# security-zone untrusted esr(config-if-gi)# exitCODETo configure security zones rules, you should create ISAKMP port profile:
esr(config)# object-group service ISAKMP esr(config-object-group-service)# port-range 500 esr(config-object-group-service)# exitCODECreate IKE protocol profile. Select Diffie-Hellman group 2, AES 128 bit encryption algorithm and MD5 authentication algorithm in the profile. The given security parameters are used for IKE connection protection:
esr(config)# security ike proposal ike_prop1 esr(config-ike-proposal)# dh-group 2 esr(config-ike-proposal)# authentication algorithm md5 esr(config-ike-proposal)# encryption algorithm aes128 esr(config-ike-proposal)# exitCODECreate IKE protocol policy. For the policy, specify the list of IKE protocol profiles that may be used for node and authentication key negotiation:
esr(config)# security ike policy ike_pol1 esr(config-ike-policy)# pre-shared-key hexadecimal 123FFF esr(config-ike-policy)# proposal ike_prop1 esr(config-ike-policy)# exitCODECreate IKE protocol gateway. For this profile, specify VTI tunnel, policy, protocol version and mode of traffic redirection into the tunnel.
esr(config)# security ike gateway ike_gw1 esr(config-ike-gw)# ike-policy ike_pol1 esr(config-ike-gw)# local address 198.51.100.1 esr(config-ike-gw)# local network 10.0.0.0/16 esr(config-ike-gw)# remote address 203.0.113.1 esr(config-ike-gw)# remote network 192.0.2.0/24 esr(config-ike-gw)# mode policy-based esr(config-ike-gw)# exitCODECreate security parameters profile for IPsec tunnel. For the profile, select Diffie-Hellman group 2, AES 128 bit encryption algorithm and MD5 authentication algorithm. Use the following parameters to secure IPsec tunnel:
esr(config)# security ipsec proposal ipsec_prop1 esr(config-ipsec-proposal)# authentication algorithm md5 esr(config-ipsec-proposal)# encryption algorithm aes128 esr(config-ipsec-proposal)# exitCODECreate a policy for IPsec tunnel. For the policy, specify the list of IPsec tunnel profiles that may be used for node negotiation:
esr(config)# security ipsec policy ipsec_pol1 esr(config-ipsec-policy)# proposal ipsec_prop1 esr(config-ipsec-policy)# exitCODECreate IPsec VPN. For VPN, specify IKE protocol gateway, IPsec tunnel policy, key exchange mode and connection establishment method. When all parameters are entered, enable tunnel using the enable command.
esr(config)# security ipsec vpn ipsec1 esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# mode ike esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# ike establish-tunnel immediate esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# ike gateway ike_gw1 esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# ike ipsec-policy ipsec_pol1 esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# enable esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# exit esr(config)# exitCODE - R2 configuration
Configure external network interface and identify its inherence to a security zone:
esr# configure esr(config)# interface gi 1/0/1 esr(config-if)# ip address 203.0.113.1/24 esr(config-if)# security-zone untrusted esr(config-if)# exitCODETo configure security zones rules, you should create ISAKMP port profile:
esr(config)# object-group service ISAKMP esr(config-addr-set)# port-range 500 esr(config-addr-set)# exitCODECreate IKE protocol profile. Select Diffie-Hellman group 2, AES 128 bit encryption algorithm and MD5 authentication algorithm in the profile. The given security parameters are used for IKE connection protection:
esr(config)# security ike proposal ike_prop1 esr(config-ike-proposal)# dh-group 2 esr(config-ike-proposal)# authentication algorithm md5 esr(config-ike-proposal)# encryption algorithm aes128 esr(config-ike-proposal)# exit esr(config)#CODECreate IKE protocol policy. For the policy, specify the list of IKE protocol profiles that may be used for node and authentication key negotiation:
esr(config)# security ike policy ike_pol1 esr(config-ike-policy)# pre-shared-key hexadecimal 123FFF esr(config-ike-policy)# proposal ike_prop1 esr(config-ike-policy)# exitCODECreate IKE protocol gateway. For this profile, specify VTI tunnel, policy, protocol version and mode of traffic redirection into the tunnel.
esr(config)# security ike gateway ike_gw1 esr(config-ike-gw)# ike-policy ike_pol1 esr(config-ike-gw)# remote address 198.51.100.1 esr(config-ike-gw)# remote network 10.0.0.0/16 esr(config-ike-gw)# local address 203.0.113.1 esr(config-ike-gw)# local network 192.0.2.0/24 esr(config-ike-gw)# mode policy-based esr(config-ike-gw)# exitCODECreate security parameters profile for IPsec tunnel. For the profile, select Diffie-Hellman group 2, AES 128 bit encryption algorithm and MD5 authentication algorithm. Use the following parameters to secure IPsec tunnel:
esr(config)# security ipsec proposal ipsec_prop1 esr(config-ipsec-proposal)# authentication algorithm md5 esr(config-ipsec-proposal)# encryption algorithm aes128 esr(config-ipsec-proposal)# exitCODECreate a policy for IPsec tunnel. For the policy, specify the list of IPsec tunnel profiles that may be used for node negotiation:
esr(config)# security ipsec policy ipsec_pol1 esr(config-ipsec-policy)# proposal ipsec_prop1 esr(config-ipsec-policy)# exitCODECreate IPsec VPN. For VPN, specify IKE protocol gateway, IPsec tunnel policy, key exchange mode and connection establishment method. When all parameters are entered, enable tunnel using the enable command.
esr(config)# security ipsec vpn ipsec1 esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# mode ike esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# ike establish-tunnel immediate esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# ike gateway ike_gw1 esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# ike ipsec-policy ipsec_pol1 esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# enable esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# exit esr(config)# exitCODETo view the tunnel status, use the following command:
esr# show security ipsec vpn status ipsec1CODETo view the tunnel configuration, use the following command:
esr# show security ipsec vpn configuration ipsec1CODE
In the firewall, you should enable ESP and ISAKMP protocol (UDP port 500).
Remote Access IPsec VPN configuration algorithm
Remote Access IPsec VPN – scenario for organizing temporary VPN connections in which the IPsec VPN server is waiting for incoming connections, and clients make temporary connections to the server to gain access to network resources.
An additional feature of RA IPsec VPN is the ability to use the second IPsec authentication factor – Extended Authentication (XAUTH), where the second authentication factor is the login-password pair for the IPsec VPN client.
Step | Description | Command | Keys |
|---|---|---|---|
1 | Create an IKE instance and switch to its configuration mode. | esr(config)# security ike proposal <NAME> | <NAME> – IKE protocol name, set by the string of up to 31 characters. |
2 | Specify the description of the configured tunnel (optionally). | esr(config-ike-proposal)# description <DESCRIPTION> | <DESCRIPTION> – tunnel description, set by the string of up to 255 characters. |
3 | Specify IKE authentication algorithm (optionally). | esr(config-ike-proposal)# authentication algorithm <ALGORITHM> | <ALGORITHM> – authentication algorithm, takes values of: md5, sha1, sha2-256, sha2‑384, sha2-512. |
4 | Specify the IP address of the VTI tunnel local side (optional). | esr(config-vti)# ip address <ADDR/LEN> | <ADDR/LEN> – IP address and prefix of a subnet, defined as AAA.BBB.CCC.DDD/EE where each part AAA-DDD takes values of [0..255] and EE takes values of [1..31]. |
5 | Define Diffie-Hellman group number (optionally). | esr(config-ike-proposal)# dh-group <DH-GROUP> | <DH-GROUP> – Diffie-Hellman group number, takes values of [1, 2, 5, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18]. Default value: 1 |
6 | Create an IKE profile policy and switch to its configuration mode. | esr(config)# security ike policy <NAME> | <NAME> – IKE policy name, set by the string of up to 31 characters. |
7 | Specify the authentication mode. | esr(config-ike- policy)# authentication method <METHOD> | <METHOD> – key authentication method. May take the following values:
|
8 | Set the client mode (only for client). | esr(config-ike- policy)# authentication mode client | |
9 | Specify the lifetime of IKE protocol connection (optionally). | esr(config-ike- policy)# lifetime seconds <SEC> | <SEC> – time interval, takes values of [4..86400] seconds. Default value: 3600 |
10 | Bind the policy to profile. | esr(config-ike-policy)# proposal <NAME> | <NAME> – IKE protocol name, set by the string of up to 31 characters. |
11 | Specify authentication key. | esr(config-ike-policy)#pre-shared-key ascii-text <TEXT> | <TEXT> – string [1..64] ASCII characters. |
12 | Create an access profile. | esr(config)# access profile <NAME> | <NAME> – access profile name, set by the string of up to 31 characters. |
13 | Create user name. | esr(config-access-profile)# user <LOGIN> | <LOGIN> – login for client, set by the string of up to 31 characters. |
14 | Specify a password for a user | esr(config-profile)# password ascii-text <TEXT> | <TEXT> – string [8..32] ASCII characters. |
15 | Create a destination address pool (only for server). | esr(config)# address-assignment pool <NAME> | <NAME> – destination addresses pool name, set by the string of up to 31 characters. |
16 | Set the subnet from which IP clients will be issued (only for server). | esr(config-pool)# ip prefix <ADDR/LEN> | <ADDR/LEN> – address and prefix of the subnet. |
17 | Create an IKE gateway and switch to its configuration mode. | esr(config)# security ike gateway <NAME> | <NAME> – IKE protocol gateway name, set by the string of up to 31 characters. |
18 | Bind IKE policy. | esr(config-ike-gw)# ike-policy <NAME> | <NAME> – IKE protocol policy name, set by the string of up to 31 characters. |
19 | Set the mode of traffic redirection into the tunnel. | esr(config-ike-gw)# mode <MODE> | <MODE> – mode of traffic redirection into the tunnel, takes the following values:
|
20 | Specify the action for DPD (optionally). | esr(config-ike-gw)# dead-peer-detection action <MODE> | <MODE> – DPD operation mode:
Default value: none |
21 | Specify the interval between sending messages via DPD mechanism (optionally). | esr(config-ike-gw)#dead-peer-detection interval <SEC> | <SEC> – interval between sending messages via DPD mechanism, takes values of [1..180] seconds. Default value: 2 |
22 | Specify the time period of response to DPD mechanism messages (optionally). | esr(config-ike-gw)# dead-peer-detection timeout <SEC> | <SEC> – time interval of response to DPD mechanism messages, takes values of [1..180] seconds. Default value: 30 |
23 | Specify IKE version (optionally). | esr(config-ike-gw)# version <VERSION> | <version> – IKE protocol version: v1-only or v2-only. Default value: v1-only |
24 | Set the IP subnet of the source (only for server). | esr(config-ike-gw)# local network <ADDR/LEN> | <ADDR/LEN> – subnet IP address and mask of a sender. The parameter is defined as AAA.BBB.CCC.DDD/EE where each part AAA-DDD takes values of [0..255] and EE takes values of [1..32]. <TYPE> – protocol type, takes the following values: esp, icmp, ah, eigrp, ospf, igmp, ipip, tcp, pim, udp, vrrp, rdp, l2tp, gre; <ID> – IP identification number, takes values of [0x00-0xFF]; <PORT> – TCP/UDP port, takes values of [1..65535]. |
25 | Specify the IP address of IPsec tunnel local gateway. | esr(config-ike-gw)#local address <ADDR> | <ADDR> – IP address of a local gateway. |
26 | Specify the IP address of IPsec tunnel remote gateway. | esr(config-ike-gw)#remote address [any | <ADDR/LEN> | Any – set as a remote address – any client address in the server configuration; <ADDR/LEN> – IP address and subnet mask of the server, in client configuration. |
27 | Set the pool for dynamic allocation of IP addresses to clients (only for server). | esr(config-ike-gw)# remote network dynamic pool <NAME> | <NAME> – destination addresses pool name, set by the string of up to 31 characters. |
28 | Set the dynamic establishment mode of the remote subnet (only for client). | esr(config-ike-gw)# remote network dynamic client | |
29 | Set access profile for XAUTH parameters (only for server). | esr(config-ike-gw)# xauth access-profile <NAME> | <NAME> – access profile name, set by the string of up to 31 characters. |
30 | Set access profile and login for XAUTH parameters (only for client). | esr(config-ike-gw)# xauth access-profile <NAME> client <LOGIN> | <NAME> – access profile name, set by the string of up to 31 characters; <LOGIN> – login for client, set by the string of up to 31 characters. |
31 | Define a dedicated IP termination interface for building IPsec VPN (only for client). | esr(config-ike-gw)# assign-interface loopback <INDEX> | <INDEX> – interface index, takes values of [1..65535]. |
32 | Create IPsec profile. | esr(config)# security ipsec proposal <NAME> | <NAME> – IPsec protocol profile name, set by the string of up to 31 characters. |
33 | Specify IPsec authentication algorithm (optionally). | esr(config-ipsec-proposal)# authentication algorithm <ALGORITHM> | <ALGORITHM> – authentication algorithm, takes values of: md5, sha1, sha2-256, sha2‑384, sha2-512. Default value: sha1 |
34 | Specify IPsec encryption algorithm (optionally). | esr(config-ipsec-proposal)# encryption algorithm <ALGORITHM> | <ALGORITHM> – encryption protocol, takes the following values: des, 3des, blowfish128, blowfish192, blowfish256, aes128, aes192, aes256, aes128ctr, aes192ctr, aes256ctr, camellia128, camellia192, camellia256. Default value: 3des |
35 | Specify protocol (optionally). | esr(config-ipsec-proposal)#protocol <PROTOCOL> | <PROTOCOL> – encapsulation protocol, takes the following values:
Default value: esp |
36 | Configuration config-ipsec-proposal | esr(config)# security ipsec policy <NAME> | <NAME> – IPsec policy name, set by the string of up to 31 characters. |
37 | Bind the policy to profile. | esr(config-ipsec-policy)# proposal <NAME> | <NAME> – IPsec protocol profile name, set by the string of up to 31 characters. |
38 | Specify the lifetime of IPsec tunnel (optionally). | esr(config-ipsec-policy)# lifetime { seconds <SEC> | | <SEC> – IPsec tunnel lifetime after which the re-approval is carried out. Takes values in the range of [1140..86400] seconds. Default value: 540 <PACKETS> – number of packets after transmitting of which the IPsec tunnel re-approval is carried out. Takes values in the range of [4..86400]. Default value: disabled. <KB> – traffic amount after transmitting of which the IPsec tunnel re-approval is carried out. Takes values in the range of [4..86400] seconds. Default value: disabled. |
39 | Create IPsec VPN policy and switch to its configuration mode. | esr(config)# security ipsec vpn <NAME> | <NAME> – VPN name, set by the string of up to 31 characters. |
40 | Define the matching mode of data required for VPN enabling. | esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# mode <MODE> | <MODE> – VPN operation mode, takes the following values: ike, manual. |
41 | Bind IPsec policy to VPN. | esr(config-ipsec-vpn)#ike ipsec-policy <NAME> | <NAME> – IPsec policy name, set by the string of up to 31 characters. |
42 | Set the DSCP value for the use in IP headers of IKE outgoing packets (optionally). | esr(config-ipsec-vpn)#ike dscp <DSCP> | <DSCP> – DSCP code value, takes values in the range of [0..63]. Default value: 63 |
43 | Set VPN activation mode. | esr(config-ipsec-vpn)#ike establish-tunnel <MODE> | <MODE> – VPN activation mode:
|
44 | Bind IKE gateway to VPN. | esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# ike gateway <NAME> | <NAME> – IKE gateway name, set by the string of up to 31 characters. |
45 | Set the time interval value in seconds after which the connection is closed, if no packet has been received or sent via SA (optionally). | esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# ike idle-time <TIME> | <TIME> – interval in seconds, takes values of [4..86400]. Default value: 0 |
46 | Disable key re-approval before the IKE connection is lost due to the timeout, the number of transmitted packets or bytes (optionally). | esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# ike rekey disable | Default value: disabled. |
47 | Configure the start of IKE connection keys re-approval before the expiration of the lifetime (optionally). | esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# ike rekey margin { seconds <SEC> | | <SEC> – time interval in seconds remaining before the connection release (set by the lifetimeseconds command). Takes values in the range of [4..86400]. <PACKETS> – number of packets remaining before the connection release (set by the lifetimepackets command). Takes values in the range of [4..86400]. <KB> – traffic volume in kilobytes remaining before the connection release (set by the lifetimekilobytes command). May take values [4..86400] |
48 | Set the level of margin seconds, margin packets, margin kilobytes values random spread (optionally). | esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# ike rekey randomization <VALUE> | <VALUE> – maximum ratio of values spread, takes values of [1..100]. Default value: 100 |
49 | Describe VPN (optionally). | esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# description <DESCRIPTION> | <DESCRIPTION> – profile description, set by the string of up to 255 characters. |
50 | Enable IPsec VPN. | esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# enable | |
51 | Enable XAUTH clients reconnection mode with one login/password (server only) (optional). | esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# security ike session uniqueids <MODE> | <MODE> – reconnect mode, may take the following values:
|
Remote Access IPsec VPN configuration example
Objective:
Configure Remote Access IPsec VPN between R1 and R2 using the second IPsec authentication factor, XAUTH. Configure router R1 as the IPsec VPN server, and router R2 as the IPsec VPN client.
R2 IP address: 120.11.5.1;
R1 IP address: 180.100.0.1;
For IPsec VPN clients:
- issue addresses from the subnet pool 192.0.2.0/24
- provide access to the LAN subnet 10.0.0.0/16
IKE:
- Diffie-Hellman group: 2;
- encryption algorithm: 3DES;
- authentication algorithm: SHA1.
IPSEC:
- encryption algorithm: 3DES;
- authentication algorithm: SHA1.
XAUTH:
- login: client1;
- password: password123.
Solution:
R1 configuration
Configure external network interface and identify its inherence to a security zone:esr# configure esr(config)# security zone untrusted esr(config-zone)# exit esr(config)# interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1 esr(config-if-gi)# security-zone untrusted esr(config-if-gi)# ip address 180.100.0.1/24 esr(config-if-gi)# exitCODETo configure security zones rules, you should create ISAKMP port profile:
esr(config)# object-group service ISAKMP esr(config-object-group-service)# port-range 500,4500 esr(config-object-group-service)# exitCODECreate IKE protocol profile. Select Diffie-Hellman group 2, 3DES encryption algorithm and SHA1 authentication algorithm in the profile. The given security parameters are used for IKE connection protection:
esr(config)# security ike proposal IKEPROP esr(config-ike-proposal)# dh-group 2 esr(config-ike-proposal)# authentication algorithm sha1 esr(config-ike-proposal)# encryption algorithm 3des esr(config-ike-proposal)# exitCODECreate IKE protocol policy. For the policy, specify the list of IKE protocol profiles that may be used for node, authentication key and XAUTH authentication method by key negotiation:
esr(config)# security ike policy IKEPOLICY esr(config-ike-policy)# pre-shared-key hexadecimal 123FFF esr(config-ike-policy)# authentication method xauth-psk-key esr(config-ike-policy)# proposal IKEPROP esr(config-ike-policy)# exitCODECreate an access profile and get in it a pair of username and password for the IPsec VPN client:
esr(config)# access profile XAUTH esr(config-access-profile)# user client1 esr(config-profile)# password ascii-text password123 esr(config-profile)# exit esr(config-access-profile)# exitCODECreate a pool of destination addresses from which IP clients will be issued IPsec VPN:
esr-1000(config)# address-assignment pool CLIENT_POOL esr-1000(config-pool)# ip prefix 192.0.2.0/24 esr-1000(config-pool)# exitCODECreate IKE protocol gateway. In this profile, you need to specify the IKE protocol policy, the local subnet, the destination address pool as the remote subnet, set the mode of traffic redirection to the tunnel according to the policy and use the second authentication factor XAUTH:
esr(config)# security ike gateway IKEGW esr(config-ike-gw)# ike-policy IKEPOLICY esr(config-ike-gw)# local address 180.100.0.1 esr(config-ike-gw)# local network 10.0.0.0/16 esr(config-ike-gw)# remote address any esr(config-ike-gw)# remote network dynamic pool CLIENT_POOL esr(config-ike-gw)# dead-peer-detection action clear esr(config-ike-gw)# mode policy-based esr(config-ike-gw)# xauth access-profile XAUTH esr(config-ike-gw)# exitCODECreate security parameters profile for IPsec tunnel. Specify 3DES encryption algorithm and SHA1 authentication algorithm in the profile. Use the following parameters to secure IPsec tunnel:
esr(config)# security ipsec proposal IPSECPROP esr(config-ipsec-proposal)# authentication algorithm sha1 esr(config-ipsec-proposal)# encryption algorithm 3des esr(config-ipsec-proposal)# exitCODECreate a policy for IPsec tunnel. For the policy, specify the list of IPsec tunnel profiles that may be used for node negotiation:
esr(config)# security ipsec policy IPSECPOLICY esr(config-ipsec-policy)# proposal IPSECPROP esr(config-ipsec-policy)# exitCODECreate IPsec VPN. For VPN, specify IKE protocol gateway, IPsec tunnel policy, key exchange mode and waiting mode for the incoming IPsec connection – by-request. When all parameters are entered, enable tunnel using the enable command.
esr(config)# security ipsec IPSECVPN esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# mode ike esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# ike establish-tunnel by-request esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# ike gateway IKEGW esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# ike ipsec-policy IPSECPOLICY esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# enable esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# exitCODEAllow esp protocol and udp ports 500, 4500 in the firewall configuration for establishing IPsec VPN:
esr(config)# security zone-pair untrusted self esr(config-zone-pair)# rule 1 esr(config-zone-pair-rule)# action permit esr(config-zone-pair-rule)# match protocol udp esr(config-zone-pair-rule)# match destination-port ISAKMP esr(config-zone-pair-rule)# enable esr(config-zone-pair-rule)# exit esr(config-zone-pair)# rule 2 esr(config-zone-pair-rule)# action permit esr(config-zone-pair-rule)# match protocol esp esr(config-zone-pair-rule)# enable esr(config-zone-pair-rule)# exit esr(config-zone-pair)# endCODER2 configuration
Configure external network interface and identify its inherence to a security zone:esr# configure esr(config)# interface gi 1/0/1 esr(config-if)# ip address 120.11.5.1/24 esr(config-if)# security-zone untrusted esr(config-if)# exitCODETo configure security zones rules, you should create ISAKMP port profile:
esr(config)# object-group service ISAKMP esr(config-addr-set)# port-range 500,4500 esr(config-addr-set)# exitCODECreate IKE protocol profile. Select Diffie-Hellman group 2, 3DES encryption algorithm and SHA1 authentication algorithm in the profile. The given security parameters are used for IKE connection protection:
esr(config)# security ike proposal IKEPROP esr(config-ike-proposal)# dh-group 2 esr(config-ike-proposal)# authentication algorithm sha1 esr(config-ike-proposal)# encryption algorithm 3des esr(config-ike-proposal)# exitCODECreate IKE protocol policy. For the policy, specify the list of IKE protocol profiles that may be used for node, authentication key, XAUTH authentication method by key and client authentication mode negotiation:
esr(config)# security ike policy IKEPOLICY esr(config-ike-policy)# pre-shared-key hexadecimal 123FFF esr(config-ike-policy)# authentication method xauth-psk-key esr(config-ike-policy)# authentication mode client esr(config-ike-policy)# proposal IKEPROP esr(config-ike-policy)# exitCODECreate an access profile and get in it a pair of username and password:
esr(config)# access profile XAUTH esr(config-access-profile)# user client1 esr(config-profile)# password ascii-text password123 esr(config-profile)# exit esr(config-access-profile)# exitCODECreate a loopback interface for terminating the IP address received from the IPsec VPN server:
esr(config)# interface loopback 8 esr(config-loopback)# exitCODECreate IKE protocol gateway. Specify the policy, the termination interface, the dynamic setting mode of the remote subnet, the access profile selection for XAUTH, and the mode of redirecting traffic to the tunnel by policy in this profile:
esr(config)# security ike gateway IKEGW esr(config-ike-gw)# ike-policy IKEPOLICY esr(config-ike-gw)# assign-interface loopback 8 esr(config-ike-gw)# local address 120.11.5.1 esr(config-ike-gw)# remote address 180.100.0.1 esr(config-ike-gw)# remote network dynamic client esr(config-ike-gw)# mode policy-based esr(config-ike-gw)# xauth access-profile xauth client client1 esr(config-ike-gw)# exitCODECreate security parameters profile for IPsec tunnel. Specify 3DES encryption algorithm and SHA1 authentication algorithm in the profile. Use the following parameters to secure IPsec tunnel:
esr(config)# security ipsec proposal IPSECPROP esr(config-ipsec-proposal)# authentication algorithm md5 esr(config-ipsec-proposal)# encryption algorithm aes128 esr(config-ipsec-proposal)# exitCODECreate a policy for IPsec tunnel. For the policy, specify the list of IPsec tunnel profiles that may be used for node negotiation:
esr(config)# security ipsec policy IPSECPOLICY esr(config-ipsec-policy)# proposal IPSECPROP esr(config-ipsec-policy)# exitCODECreate IPsec VPN. For VPN, specify IKE protocol gateway, IPsec tunnel policy, key exchange mode and connection establishment method. When all parameters are entered, enable tunnel using enable command.
esr(config)# security ipsec vpn IPSECVPN esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# mode ike esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# ike establish-tunnel immediate esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# ike gateway IKEGW esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# ike ipsec-policy IPSECPOLICY esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# enable esr(config-ipsec-vpn)# exitCODEAllow esp protocol and udp ports 500,4500 in the firewall configuration for establishing IPsec VPN:
esr(config)# security zone-pair untrusted self esr(config-zone-pair)# rule 1 esr(config-zone-pair-rule)# action permit esr(config-zone-pair-rule)# match protocol udp esr(config-zone-pair-rule)# match destination-port ISAKMP esr(config-zone-pair-rule)# enable esr(config-zone-pair-rule)# exit esr(config-zone-pair)# rule 2 esr(config-zone-pair-rule)# action permit esr(config-zone-pair-rule)# match protocol esp esr(config-zone-pair-rule)# enable esr(config-zone-pair-rule)# exit esr(config-zone-pair)# endCODETo view the tunnel status, use the following command:
esr# show security ipsec vpn status IPSECVPNCODETo view the tunnel configuration, use the following command:
esr# show security ipsec vpn configuration IPSECVPNCODE
In the firewall, you should enable ESP and ISAKMP protocol (UDP port 500, 4500).
LT tunnels configuration
LT (англ. Logical Tunnel) is a type of tunnels dedicated for transmission of routing information and traffic between different virtual routers (VRF Lite) configured on a router. LT tunnel might be used for organization of interaction between two or more VRF using firewall restrictions.
Configuration algorithm
Step | Description | Command | Keys |
|---|---|---|---|
1 | Create LT tunnels for each of existing VRF. | esr(config)# tunnel lt <ID> | <ID> – tunnel identifier, set in the range of [1..128]. |
2 | Specify the description of the configured tunnels (optionally). | esr(config-lt)# description <DESCRIPTION> | <DESCRIPTION> – tunnel description, set by the string of up to 255 characters. |
3 | Include each LT tunnel in the corresponding VFR. | esr(config-lt)# ip vrf forwarding <VRF> | <VRF> – VRF name, set by the string of up to 31 characters. |
4 | Include each LT tunnel in a security zone and configure interaction rules between zones or disable firewall for LT tunnel. | esr(config-lt)# security-zone<NAME> | <NAME> – security zone name, set by the string of up to 12 characters. |
esr(config-lt)# ip firewall disable | |||
5 | For each LT tunnel, set the opposite LT tunnel number (in another VRF). | esr(config-lt)# peer lt <ID> | <ID> – tunnel identifier, set in the range of [1..128]. |
6 | For each LT tunnel, specify IP address for packets routing. For interacting LT tunnels, IP addresses should locate in one IP subnet. | esr(config-lt)# ip address <ADDR/LEN> | <ADDR/LEN> – IP address and prefix of a subnet, defined as AAA.BBB.CCC.DDD/EE where each part AAA-DDD takes values of [0..255] and EE takes values of [1..32]. |
7 | Enable the tunnels. | esr(config-lt)# enable | |
8 | For each VRF configure required routing protocols via LT tunnel. | ||
9 | Specify the time interval during which the statistics on the tunnel load is averaged (optionally) | esr(config-lt)# load-average <TIME> | <TIME> – interval in seconds, takes values of [5..150]. Default value: 5 |
10 | Specify the size of MTU packets that can be passed by the bridge (optionally; possible if only VLAN is included in the bridge). | esr(config-lt)# mtu <MTU> | <MTU> – MTU value, takes values in the range of:
Default value: 1500. |
Configuration example
Objective:
Organize interaction between hosts terminated in two VRF vrf_1 and vrf_2.
Initial configuration:
hostname esr
ip vrf vrf_1
exit
ip vrf vrf_2
exit
interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
ip vrf forwarding vrf_1
ip firewall disable
ip address 10.0.0.1/24
exit
interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2
ip vrf forwarding vrf_2
ip firewall disable
ip address 10.0.1.1/24
exitSolution:
Create LT tunnels for each VRF, specifying IP address from one subnet:
esr(config)# tunnel lt 1
esr(config-lt)# ip vrf forwarding vrf_1
esr(config-lt)# ip firewall disable
esr(config-lt)# ip address 192.168.0.1/30
esr(config-lt)# exit
esr(config)# tunnel lt 2
esr(config-lt)# ip vrf forwarding vrf_2
esr(config-lt)# ip firewall disable
esr(config-lt)# ip address 192.168.0.2/30
esr(config-lt)# exitDesignate LT tunnel from VRF, which is necessary to establish link with, for each LT tunnel and activate them.
esr(config)# tunnel lt 1
esr(config-lt)# peer lt 2
esr(config-lt)# enable
esr(config-lt)# exit
esr(config)# tunnel lt 2
esr(config-lt)# peer lt 1
esr(config-lt)# enable
esr(config-lt)# exitIf none of dynamic routing protocols is configured in VRF, specify static routes for each VRF:
esr(config)# ip route vrf vrf_1 0.0.0.0/0 192.168.0.2
esr(config)# ip route vrf vrf_2 0.0.0.0/0 192.168.0.1